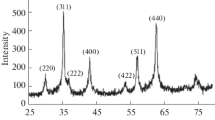
Abstract
This paper reports the removal of two widely used pharmaceuticals, namely dipyrone and diclofenac, by magnetic nickel ferrite nanoparticles. A method combining nickel ferrite nanoparticles and high-performance liquid chromatography was applied for the simultaneous monitoring of these polar compounds. The adsorption process of the target compounds on nickel ferrite nanoparticles was performed by using only 800 mg L−1 of the adsorbent at pH 5.8. From the experimental adsorption isotherms, maximum adsorption resulted 31.2 mg g−1 for dipyrone and 16.8 mg g−1 for diclofenac, with dipyrone having a slightly higher affinity for the surface than diclofenac. The presence of dissolved salts in water samples affected the adsorption with removal efficiency remaining between 30–42% for diclofenac and 40–60% for dipyrone. On the other hand, desorption of the drugs was achieved using methanol for diclofenac and ascorbic acid for dipyrone. This research provides the understanding of the adsorption behavior of polar pharmaceuticals on bare nickel ferrite nanoparticles, which promotes the large-scale application of these magnetic nanoparticles to the removal of pharmaceuticals from water samples and their further selective recovery.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agatonovic-Kustrin, S., Zivanovic, L., Zeevi, M., Radulovic, D.: Spectrophotometric study of diclofenac-Fe (III) complex. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 16, 147–153 (1997)
Agunbiade, F.O., Moodley, B.: Occurrence and distribution pattern of acidic pharmaceuticals in surface water, wastewater, and sediment of the msunduzi river,kwazulu-natal, south africa. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 35, 36–46 (2016)
Ahmad, S.M., Almeida, C., Neng, N.R., Nogueira, J.M.F.: Bar adsorptive microextraction (BAE) coated with mixed sorbent phases—enhanced selectivity for the determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in real matrices in combination with capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. B 1008, 115–124 (2016)
Ali, I.: New generation adsorbents for water treatment. Chem. Rev. 112, 5073–5091 (2012)
ASTM Standards D1141-Standard Practice for the Preparation of Substitute Ocean Water, ASTM International. http://www.astm.org/Standards/D1141.htm. Accessed 2 Feb 2017
Boatright, W.L.: Oxygen dependency of one-electron reactions generating ascorbate radicals and hydrogen peroxide from ascorbic acid. Food Chem. 196, 1361–1367 (2016)
Cashman, J.N.: The mechanisms of action of NSAIDs in analgesia. Drugs 52, 13–23 (1996)
Chunming, S.: Environmental implications and applications of engineered nanoscale magnetite and its hybrid nanocomposites: a review of recent literature. J. Hazard. Mater. 322, 48–84 (2017)
Dai, G., Wang, B., Huang, J., Dong, R., Deng, S., Yu, G.: Occurrence and source apportionment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the Beiyun River of Beijing, China. Chemosphere 119, 1033–1039 (2015)
Davis, M.B.: Reactions of L-ascorbic acid with transition metal complexes. Polyhedron 11, 285–321 (1992)
Decision (E.U.): 2015/495 of 20 March 2015 establishing a watch list of substances for Union-wide monitoring in the field of water policy pursuant to Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Off. J. Eur. Union L78, 40–42
De Franco, M.A.E., de Carvalho, C.B., Boneto, M.M., Soares, R.P., Féris, L.A.: Diclofenac removal from water by adsorption using activated carbon in batch mode and fixed-bed column: isotherms, thermodynamic study and breakthrough curves modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 181, 145–154 (2018)
De Oliveira, T., Guégan, R., Thiebault, T., Milbeau, C.L., Muller, F., Teixeira, V., Giovanela, M., Boussafir, M.: Adsorption of diclofenac onto organoclays: effects of surfactant and environmental (pH and temperature) conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 323, 558–566 (2017)
Feldmann, D.F., Zuehlke, S., Hebere, T.: Occurrence, fate and assessment of polar metamizole (dipyrone) residues in hospital and municipal wastewater. Chemosphere 71, 1754–1764 (2008)
Fernández, C., González-Doncel, M., Pro, J., Carbonell, G., Tarazona, J.V.: Occurrence of pharmaceutically active compounds in surface waters of the Henares-Jarama-Tajo river system (Madrid, Spain) and a potential risk characterization. Sci. Total Environ. 408, 543–551 (2010)
Gil, A., Santamaría, L., Korili, S.A.: Removal of caffeine and diclofenac from aqueous solution by adsorption on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 22, 25–28 (2018)
Goldman, A.: Modern Ferrites Technology, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2006)
Gomez, M.J., Malato, O., Ferrer, I., Aguera, A., Fernández-Alba, A.R.: Solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography–time-of-flight–mass spectrometry to evaluate pharmaceuticals in effluents. A pilot monitoring study. J. Environ. Monit. 9, 718–729 (2007)
Gorman, J.E., Clydesdale, F.M.: The behavior and stability of iron-ascorbate complexes in solution. J. Food Sci. 48, 1217–1225 (1983)
Gyenge-Szabó, Z., Szoboszlai, N., Frigyes, D., Záray, G., Mihucz, V.G.: Monitoring of four dipyrone metabolites in communal wastewater by solid phase extraction liquid chromatography electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 90, 58–63 (2014)
Harel, S.: Oxidation of ascorbic acid and metal ions as affected by NaCl. J. Agric. Food Chem. 42, 2402–2406 (1994)
He, L., Zhao, Z., Zhang, Y.: Synthesis of nickel ferrite precursors from low-grade nickel matte. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23, 2422–2430 (2013)
Hedenmalm, K., Spigset, O.: Agranulocytosis and other blood dyscrasias associated with dipyrone (metamizole). Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 58, 265–274 (2002)
Hu, X., Cheng, Z.: Removal of diclofenac from aqueous solution with multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified by nitric acid. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 23, 1551–1556 (2015)
Joshi, S., Kumar, M., Chhoker, S., Srivastava, G., Jewariya, M., Singh, V.N.: Structural, magnetic, dielectric and optical properties of nickel ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Mol. Struct. 1076, 55–62 (2014)
Klug, H.P., Alexander, L.E.: X-ray Diffraction Procedures for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (1974)
Kostopoulou, M., Nikolaou, A.: Analytical problems and the need for sample preparation in the determination of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in aqueous environmental matrices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 27, 1023–1035 (2008)
Kozlowska, M., Rodziewicz, P., Utesch, T., Mroginski, M.A., Kaczmarek-Kedziera, A.: Solvation of diclofenac in water from atomistic molecular dynamics simulations—interplay between solute–solute and solute–solvent interactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP08468D
Larsson, E., al-Hamimi, S., Jönsson, J.: Behaviour of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and eight of their metabolites during wastewater treatment studied by hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 485–486, 300–308 (2014)
Leroy, P., Tournassat, C., Bizi, M.: Influence of surface conductivity on the apparent zeta potential of TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 356, 442–453 (2011)
Levina, E.O., Penkov, N.V., Rodionova, N.N., Tarasov, S.A., Barykina, D.V., Vener, M.V.: Hydration of the carboxylate group in anti-inflammatory drugs: ATR-IR and computational studies of aqueous solution of sodium diclofenac. ACS Omega 3, 302–313 (2018)
Loginova, L.P., Konovalova, O.Y.: Test films for test-determinations on the base of reagents, immobilized in gelatinous gel. Talanta 77, 915–923 (2008)
Maaz, K., Karim, S., Mumtaz, A., Hasanain, S.K., Liu, J., Duan, J.L.: Synthesis and magnetic characterization of nickel ferrite nanoparticles prepared by coprecipitation route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 1838–1842 (2009)
Miller, J.N., Miller, J.C.: Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, 6th edn. Pearson Education Limited, New York (2010)
Ncibi, M.C., Sillanpää, M.: Optimized removal of antibiotic drugs from aqueous solutions using single, double and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. 298, 102–110 (2015)
Paíga, P., Lolić, A., Hellebuyck, F., Santos, L.H.M.L.M., Correia, M., Delerue-Matos, C.: Development of a SPE–UHPLC–MS/MS methodology for the determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and analgesic pharmaceuticals in seawater. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 106, 61–70 (2015)
Parolini, M., Binelli, A., Provini, A.: Chronic effects induced by ibuprofen on the freshwater bivalve Dreissenapolymorpha. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 74, 1586–1594 (2011)
Pierre, S.C., Schmidt, T., Brenneis, C., Michaelis, M., Geisslinger, G., Scholich, K.: Inhibition of cyclooxygenases by dipyrone. Br. J. Pharmacol. 151, 494–503 (2007)
Plaza, R.C., de Vicente, J., Gómez-Lopera, S., Delgado, A.V.: Stability of dispersions of colloidal nickel ferrite spheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 242, 306–313 (2001)
Shanmugavel, T., Gokul Raj, G., Ramesh Kumar, G., Rajarajan, G., Saravanan, D.: Cost effective preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline nickel ferrites (NiFe2O4) in low temperature regime. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 27, 176–181 (2015)
Sonmez, M., Verisan, C., Voicu, G., Ficai, D., Ficai, A., Oprea, A.E., Vlad, M., Andronescu, E.: Extended release of vitamins from magnetite loaded polyanionic polymeric beads. Int. J. Pharm. 510, 457–464 (2016)
Sreeja, V., Jayaprabha, K.N., Joy, P.A.: Water-dispersible ascorbic-acid-coated magnetite nanoparticles for contrast enhancement in MRI. Appl. Nanosci. 5, 435–441 (2015)
Suarez, W.T., Pessoa-Neto, O.D., Vicentini, F.C., Janegitz, B.C., Faria, R.C., Fatibello-Filho, O.: Flow injection spectrophotometric determination of dipyrone in pharmaceutical formulations using Fe(III) as reagent. Anal. Lett. 44, 340–348 (2011)
Szabó, Z., Szoboszlai, N., Jámbor, É, Gulyás, G., Lóránd, T., Ohmacht, R., Záray, G., Mihucz, V.G.: Determination of four dipyrone metabolites in Hungarian municipal wastewater by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 107, 152–157 (2013)
Teixeira, M.F.S., Dadamos, T.R.L.: An electrochemical sensor for dipyrone determination based on nickel-salen film modified electrode. Procedia Chem. 1, 297–300 (2009)
Tiwari, D., Lalhriatpuia, C., Lee, S.-M.: Hybrid materials in the removal of diclofenac sodium from aqueous solutions: batch and column studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 30, 167–173 (2015)
Wang, L., Li, J., Wang, Y., Zhao, L., Jiang, Q.: Adsorption capability for Congo red on nanocrystalline MFe2O4 (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) spinel ferrites. Chem. Eng. J. 181–182, 72–79 (2012)
Wang, Y., Ma, J., Zhu, J., Ye, N., Zhang, X., Huang, H.: Multi-walled carbon nanotubes with selected properties for dynamic filtration of pharmaceuticals and personal care products. Water Res. 92, 104–112 (2016)
Wei, H., Deng, S., Huang, Q., Nie, Y., Wang, B., Huang, J., Yu, G.: Regenerable granular carbon nanotubes/alumina hybrid adsorbents for diclofenac sodium and carbamazepine removal from aqueous solution. Water Res. 47, 4139–4147 (2013)
World Health Organization Press: Pharmaceuticals in drinking-water, WHO/HSE/WSH/11.05, Switzerland (2011)
Xiao, J., Xie, Y., Cao, H.: Organic pollutants removal in wastewater by heterogeneous photocatalytic ozonation. Chemosphere 121, 1–17 (2015)
Zhang, L., Liu, X., Guo, X., Su, M., Xu, T., Song, X.: Investigation on the degradation of brilliant green induced oxidation by NiFe2O4 under microwave irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 173, 737–742 (2011)
Zhang, C., Li, Y., Jiang, Y., Wang, T.J.: Size-dependent fluoride removal performance of a magnetic Fe3O4@Fe–Ti adsorbent and its defluoridation in a fluidized bed. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 56, 2425–2432 (2017)
Acknowledgements
V. Springer acknowledges the National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET, Argentina) and Universidad Nacional del Sur (Argentina) for the financial support from a research fellowship program. Funds from CONICET, FONCyT and SGCyT-UNS are acknowledged. This work received financial support from the European Union (FEDER funds POCI/01/0145/FEDER/007265) and National Funds (FCT/MEC, Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia and Ministério da Educação e Ciência) under the Partnership Agreement PT2020 UID/QUI/50006/2013. L. Barreiros thanks FCT and POPH (Programa Operacional Potencial Humano) for her Post-Doc grant FCT SFRH/BPD/89668/2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Springer, V., Barreiros, L., Avena, M. et al. Nickel ferrite nanoparticles for removal of polar pharmaceuticals from water samples with multi-purpose features. Adsorption 24, 431–441 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-018-9953-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-018-9953-2