Abstract
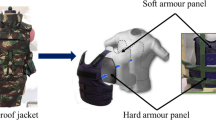
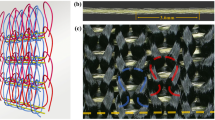
Textile materials can be used as a soft solution to protect the human body of the soldier and as a hard solution to provide more efficient armour for various types of vehicles. Their advantages are numerous in terms of performance versus weight, forming ability and availability of different types of high-performance yarns. Special attention has been given to the 3D warp interlock fabrics structure in the above applications. For the soft protection application, a body armour adapted to the female breast was designed based on different layers of 3D warp interlock fabric made of para-aramid yarns. A compromise was found between the formability criterion, which facilitates the adaptation of the body armour to the body, and the kinetic energy absorption in ballistic impact, which tends to minimize the blunt trauma criterion. For hard protection, a new vehicle up-armour was found to protect the interior from the high-velocity impact of projectiles. A compromise was also found to optimize the kinetic energy absorption in this high-velocity impact and the capacity of dynamic deformation of the protection solution to avoid structural damage and keep the integrity of the armour solution safe.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statements
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abtew, M.A., Boussu, F., Bruniaux, P., Loghin, C., Cristian, I.: Ballistic impact mechanisms – A review on textiles and fibre-reinforced composites impact responses. Compos. Struct. 223, 110966 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPSTRUCT.2019.110966
Crouch, I.G.: Body armour – New materials, new systems. Def. Technol. 15, 241–253 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2019.02.002
Cherif, C.: Textile Materials for Lightweight Constructions. (2016)
Abtew, M.A., Boussu, F., Bruniaux, P., Loghin, C., Cristian, I., Chen, Y., Wang, L.: Influences of fabric density on mechanical and moulding behaviours of 3D warp interlock para-aramid fabrics for soft body armour application. Compos. Struct. 204, 402–418 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.07.101
Mayo, J.B., Wetzel, E.D., Hosur, M.V., Jeelani, S.: Stab and puncture characterization of thermoplastic-impregnated aramid fabrics. Int. J. Impact Eng. 36, 1095–1105 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2009.03.006
Gürgen, S., Kuşhan, M.C.: The ballistic performance of aramid based fabrics impregnated with multi-phase shear thickening fluids, (2017)
Laun, H.M., Bung, R., Schmidt, F.: Rheology of extremely shear thickening polymer dispersions a) (passively viscosity switching fluids) . J. Rheol. (N. Y. N. Y). 35, 999–1034 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1122/1.550257
Reddy, P.R.S., Savio, S.G., Madhu, V.: Ceramic Composite Armour for Ballistic Protection. In: Handbook of Advanced Ceramics and Composites (2019)
Boussu, F., Provost, B., Lefebvre, M., Coutellier, D.: New Textile Composite Solutions for Armouring of Vehicles. (2019)
Madhu, V., Bhat, T.B.: Armour protection and affordable protection for futuristic combat vehicles. Def. Sci. J. (2011). https://doi.org/10.14429/dsj.61.365
Boussu, F., Picard, S., Soulat, D.: Interesting mechanical properties of 3D warp interlock fabrics. In: Al, Y.K. et (ed.) Narrow and Smart Textiles. pp. 21–31. Springer International Publishing (2018)
Boussu, F.: Different interesting applications of 3D warp interlock fabrics. In: ITechstyle Summit. , Cruise Terminal, Port of Leixoes, Porto , Portugal (2018)
Kececi, A., Boussu, F., Soulat, D.: Interesting properties of 3D warp interlock fabrics as fibrous reinforcement for composite materials. In: 33rd Technical Conference of the American Society for Composites 2018 (2018)
L. Tong A.P. Mouritz M. Bannister: 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites. Elsevier Science (2002)
A Miravete: 3-D Textile Reinforcements in Composite Materials. Woodhead Publishing (1999)
Mouritz, A.P., Bannister, M.K., Falzon, P.J., Leong, K.H.: Review of applications for advanced three-dimensional fibre textile composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 30, 1445–1461 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-835X(99)00034-2
Sheng, S.Z., Hoa, S.V.: Modeling of 3D Angle Interlock Woven Fabric Composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 16, 45–58 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1106/089270503023206
Ansar, M., Xinwei, W., Chouwei, Z.: Modeling strategies of 3D woven composites: A review. Compos. Struct. 93, 1947–1963 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.03.010
Department of Trade and Industry, U.: HYBRIDMAT 4 : advances in the manufacture of 3-D preform reinforcement for advanced structural composites in aerospace - a mission to the USA. , London (2006)
Hu, J.: 3-D Fibrous Assemblies 1st Edition Properties. Woodhead Publishing, Applications and Modelling of Three-Dimensional Textile Structures (2008)
Zhang, C.: Characterization and Modeling of 3D Woven Composites, (2003)
Behera, B.K.(, Mishra, R.: 3-Dimensional Weaving. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 33, 274–287 (2008)
Naik, N.K., Azad, S.N.M., Prasad, P.D.: Stress and Failure Analysis of 3D Angle Interlock Woven Composites. J. Compos. Mater. 36, 93–123 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998302036001303
Hufenbach, W., Böhm, R., Thieme, M., Winkler, A., Mäder, E., Rausch, J., Schade, M.: Polypropylene/glass fibre 3D-textile reinforced composites for automotive applications. Mater. Des. 32, 1468–1476 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2010.08.049
Yi, H.L., Ding, X.: Conventional Approach on Manufacturing 3D Woven Preforms Used for Composites. J. Ind. Text. 34, 39–50 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1177/1528083704045847
Brandt, J., Drechsler, K., Arendts, F.J.: Mechanical performance of composites based on various three-dimensional woven-fibre preforms. Compos. Sci. Technol. 56, 381–386 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0266-3538(95)00135-2
Lomov, S. V, Bogdanovich, A.E., Ivanov, D.S., Mungalov, D., Karahan, M., Verpoest, I.: A comparative study of tensile properties of non-crimp 3D orthogonal weave and multi-layer plain weave E-glass composites. Part 1: Materials, methods and principal results. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 40, 1134–1143 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2009.03.012
Kuo, W.-S., Fang, J., Lin, H.-W.: Failure behavior of 3D woven composites under transverse shear. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 34, 561–575 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-835X(03)00123-4
Kuo, W.-S., Ko, T.-H., Chen, C.-P.: Effect of weaving processes on compressive behavior of 3D woven composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 38, 555–565 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2006.02.025
Cox, B.N., Dadkhah, M.S.: The Macroscopic Elasticity of 3D Woven Composites. J. Compos. Mater. 29, 785–819 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1177/002199839502900606
C. Dufour, F. Boussu, P. Wang, D. Soulat, X.L.: Analyse du comportement de renforts tissés interlock lors du procédé de préformage. In: 21ème Congrès Français de Mécanique. , Bordeaux, France (2013)
Nawab, N.: Etude de moulabilité des tissus 3D multi-couches interlocks, (2009)
Ding, X., Yi, H.L.: Parametric Representation of 3D Woven Structure. In: 6th Asian Textile Conference. , Hong Kong, China (2001)
LEFEBVRE, M.: Résistance à l’impact balistique de matériaux composites à renforts Interlocks tissés. Application au blindage de véhicules
Chen, X., Yang, D.: Use of 3D Angle-Interlock Woven Fabric for Seamless Female Body Armor: Part 1: Ballistic Evaluation. Text. Res. J. 80, 1581–1588 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517510363187
Othman, A.R., Hassan, M.H.: Effect of different construction designs of aramid fabric on the ballistic performances. Mater. Des. 44, 407–417 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.07.061
S. B. Brantner: Police History: The evolution of women in American law enforcement
Chen, X., Yang, D.: Use of Three-dimensional Angle-interlock Woven Fabric for Seamless Female Body Armor : Part II : Mathematical Modeling. Text. Res. J. 80, 1589–1601 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517510363188
Mulat, A.A., Bruniaux, P., Boussu, F., Loghin, C., Cristian, I., Chen, Y., Wang, L.: Female seamless soft body armor pattern design system with innovative reverse engineering approaches. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 98, 2271–2285 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2386-y
Yang, D., Chen, X.: Multi-layer pattern creation for seamless front female body armor panel using angle-interlock woven fabrics. Text. Res. J. 87, 1–6 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517516631315
Mahbub, R., Wang, L., Arnold, L.: Design of knitted three-dimensional seamless female body armour vests. Int. J. Fash. Des. Technol. Educ. 7, 198–207 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/17543266.2014.956152
Abtew, M.A., Bruniaux, P., Boussu, F., Loghin, C., Cristian, I., Chen, Y., Wang, L.: Female seamless soft body armor pattern design system with innovative reverse engineering approaches. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2386-y
Abtew, M.A., Bruniaux, P., Boussu, F., Loghin, C., Cristian, I., Chen, Y., Wang, L.: A systematic pattern generation system for manufacturing customized seamless multi-layer female soft body armour through dome-formation (moulding) techniques using 3D warp interlock fabrics. J. Manuf. Syst. 49, 61–74 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2018.09.001
Abtew, M.A., Bruniaux, P., Boussu, F., Loghin, C., Cristian, I., Chen, Y.: Development of comfortable and well-fitted bra pattern for customized female soft body armor through 3D design process of adaptive bust on virtual mannequin. Comput. Ind. 100, 7–20 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2018.04.004
Mulat, A.A., Boussu, F., Bruniaux, P., Hong, Y.: Dynamic impact surface damage analysis of 3d woven para-aramid armour panels using ndi technique. Polymers (Basel). (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060877
Mawkhlieng, U., Majumdar, A., Laha, A.: A review of fibrous materials for soft body armour applications. RSC Adv. 10, 1066–1086 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra06447h
Abtew, M.A., Boussu, F., Bruniaux, P., Loghin, C., Cristian, I., Chen, Y., Wang, L.: Ballistic impact performance and surface failure mechanisms of two-dimensional and three-dimensional woven p-aramid multi-layer fabrics for lightweight women ballistic vest applications. J. Ind. Text. 50, 1351–1383 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/1528083719862883
M. B. Mukasey, J. L. Sedgwick, D.W.H.: Ballistic Resistance of Body Armor NIJ Standard-0101.06. , Washington, DC 20531 (2008)
Mulat, A.A., Boussu, F., Bruniaux, P., Loghin, C., Cristian, I.: Engineering of 3D warp interlock p-aramid fabric structure and its energy absorption capabilities against ballistic impact for body armour applications. Compos. Struct. 225, 111179 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111179
Abtew, M.A., Boussu, F., Bruniaux, P., Loghin, C., Cristian, I.: Enhancing the Ballistic Performances of 3D Warp Interlock Fabric Through Internal Structure as New Material for Seamless Female Soft Body Armor Development. Appl. Sci. 10, 1–19 (2020)
Z. (Gama) Haque, B., M. Kearney, M., W. Gillespie, J.: Advances in Protective Personnel and Vehicle Armors. Recent Patents Mater. Sci. (2012). https://doi.org/10.2174/1874465611205020105
S. Nauman, I. Cristian, F. Boussu, V.K.: Intelligent textiles for armoured vehicles. In: Chapman, R. (ed.) Smart Textiles for protection,. Woodhead Publishing (2010)
Padaki, N.V., Alagirusamy, R., Deopura, B.L., Fangueiro, R.: Influence of preform interlacement on the low velocity impact behavior of multilayer textile composites. J. Ind. Text. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1177/1528083710366723
Lefebvre, M., Boussu, F., Coutellier, D., Vallee, D.: Influence of the vacuum resin process, on the ballistic behaviour of lightweight armouring solutions. In: EPJ Web of Conferences (2012)
Appleby-Thomas, G.J., Hazell, P.J.: The impact of structural composite materials. Part 2: Hypervelocity impact and shock. J. Strain Anal. Eng. Des. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1177/0309324712448299
F. Boussu, V.B.: Method of manufacturing a composite, especially a bulletproof composite, and composite obtained
Savage, G.M.: Fabric- and fibre-reinforced laminate armours, (1989)
Dorey, G.: Fracture of composite and damages tolerance. Agards Lect. (1987)
Laboratory, U.A. research: MIL-PRF-46103E, Performace specification armor: lightweight composite, Type III 12.7 mm (0.50 caliber), Class 2B - Hard steel core armor piercing (AP) projectile at 500 meters range (2000 ft (610 m) per second).
F. Boussu, X. Legrand, V.K.: Energy absorption inside a 3D Textile Composite Structure. In: The Fiber Society Spring 2008 Conference. , Mulhouse, France
Boussu, F., Legrand, X.: Delamination behaviour of 3D Warp Interlock Structures. In: First world conference on 3D fabrics and their applications. , Manchester, UK
Boussu, F., Veyet, F., Lefebvre, M.: Recent advances in textile composite for impact protection. In: World Journal of Engineering. pp. 53–66 (2010)
NATO: STANAG 4569 Land (Edition 1) - Niveaux de protection à assurer aux occupants des véhicules logistiques et des véhicules blindés légers. , Brussels, Belgium
Lefebvre, M., Boussu, F., Coutellier, D.: Study of impact behaviour of three warp interlock structures. Comparison with existing protections. In: LWAG Light-Weight Armour for Defence & Security. , Haifa, Israël (2011)
Lefebvre, M., Boussu, F., Coutellier, D.: Influence des paramètres de tissage sur des structures interlock soumises à l’impact balistique. In: JNC 17, Journées Nationales Composites. , Poitiers, France (2011)
Lee, B.L., Song, J.W., Ward, J.E.: Failure of Spectra®* Polyethylene Fiber-Reinforced Composites under Ballistic Impact Loading. J. Compos. Mater. (1994). https://doi.org/10.1177/002199839402801302
B. Provost, F. Boussu, D. Coutellier, D. Vallee, F.R.: New 3D warp interlock composite for armouring of vehicles. In: 4th RMUTP International Conference: Textiles & Fashion. , Bangkok, Thailand (2012)
M. Lefebvre, F. Boussu, D. Coutellier, D.V.: Influence of the geometrical structures and resin rate inside composites structures on the ballistic behaviour under high velocity impact. In: Mechanics of Nano, Micro and Macro Composite Structures. , Torino, Italy (2012)
Provost, B., Boussu, F., Coutellier, D., Vallee, D., Rondot, F.: High velocity impact on different hybrid architectures of 2D laminated and 3D warp interlock fabric composite. EPJ Web Conf. 26, (2012). https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/20122601052
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank DGA, ARQUUS, SMDTex and CREL for helping us by funding or doing the impact tests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boussu, F., Abtew, M.A. & Bruniaux, P. 3D Warp Interlock Fabric Structure and their Applications in Soft and Hard Armour Protections. Appl Compos Mater 29, 65–82 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-021-09955-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-021-09955-2