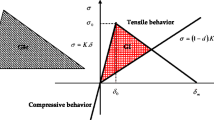
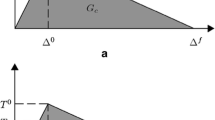
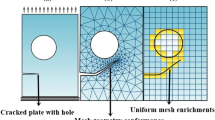
Abstract
Sub-laminate damage in the form of matrix cracking and delamination was simulated by using interface cohesive elements in the finite element (FE) software ABAQUS. Interface cohesive elements were inserted parallel to the fiber orientation in the transverse ply with equal spacing (matrix cracking) and between the interfaces (delamination). Matrix cracking initiation in the cohesive elements was based on stress traction separation laws and propagated under mixed-mode loading. We expanded the work of Shi et al. (Appl. Compos. Mater. 21, 57–70 2014) to include delamination and simulated additional [45/−45/0/90]s and [02/90n]s {n = 1,2,3} CFRP laminates and a [0/903]s GFRP laminate. Delamination damage was quantified numerically in terms of damage dissipative energy. We observed that transverse matrix cracks can propagate to the ply interface and initiate delamination. We also observed for [0/90n/0] laminates that as the number of 90° ply increases past n = 2, the crack density decreases. The predicted crack density evolution compared well with experimental results and the equivalent constraint model (ECM) theory. Empirical relationships were established between crack density and applied stress by linear curve fitting. The reduction of laminate elastic modulus due to cracking was also computed numerically and it is in accordance with reported experimental measurements.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones, R.M.: Mechanics of Composite Materials. Second Edition, Taylor and Francis Publication, Boca Rotan (2008)
Berthelot, J.M., Le Corre, J.-F.: A model for transverse cracking and delamination in cross-ply laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 60, 1055–1066 (2000)
Crossman, F.W., Wang, S.D.: The dependence of transverse cracking and delamination on ply thickness in Graphite/Epoxy laminates. Damage Composite Material op. ct. 118–39 (1984)
Wang, A.S.D., Kishore, N.N., Li, C.A.: Crack development in graphite-epoxy cross-ply laminates under uni-axial tension. Compos. Sci. Technol. 24, 1–31 (1985)
Wang, A.S.D.: Fracture mechanics of sub-laminate cracks in composite materials. Compos. Technol. Rev. 6, 45–62 (1984)
Highsmith, A.L., Reifsnider, K.L.: Stiffness reduction mechanism in composite laminates. Damage in Composite Materials. ASTM, STP 775, 103–117 (1982)
Berbinau, P., Soutis, C., Guz, I.A.: Compressive failure of 00 unidirectional carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics (CFRP) laminates by fiber micro buckling. Compos. Sci. Technol. 59, 1451–1455 (1999)
Anderson, T.L.: Fracture Mechanics- Fundamentals and Applications. CRC Press, New York (1995)
Kashtalyan, M., Soutis, C.: The effect of delamination induced by transverse cracks and splits on stiffness properties of composite laminates. Compos. A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 31, 107–119 (2000)
Kashtalyan, M., Soutis, C.: Stiffness degradation in cross-ply laminates damaged by transverse cracking and splitting. Compos. A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 31, 335–351 (2000)
Kashtalyan, M., Soutis, C.: Analysis of local delamination in composite laminates with angle-ply matrix cracks. Int. J. Solids Struct. 39, 1515–1537 (2002)
Kashtalyan, M., Soutis, C.: Mechanisms of internal damage and their effect on the behavior and properties of cross-ply composite laminates. Int. Appl. Mech. 38(6), 641–657 (2002)
Zhang, J., Soutis, C., Fan, J.: Strain energy release rate associated with local delamination in cracked composite laminates. Composites 25(9), 851–862 (1994)
Hashin, Z., Rotem, A.: A fatigue failure criterion for fiber reinforced materials. J. Compos. Mater. 7, 448–464 (1973)
Hashin, Z.: Failure criteria for uni-directional fiber composites. J. Appl. Mech. 47(1), 329–334 (1980)
Nairn, J.A.: The strain energy release rate of composite micro-cracking: a variational approach. J. Compos. Mater. 23(11), 1106–1129 (1989)
Varna, J., Berglund, L.A.: Multiple transverse cracking and stiffness reduction in cross-ply laminates. J. Compos. Technol. Res. 13(2), 97–106 (1991)
Varna, J., Berglund, L.A.: A model for prediction of the transverse cracking strain in cross-ply laminates. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 11(7), 708–728 (1992)
Berglund, L.A., Varna, J.: Thermo-elastic properties of composite laminates with transverse cracks. J. Compos. Technol. Res. 16(1), 77–87 (1994)
Zhang, J., Fan, J., Soutis, C.: Analysis of multiple matrix cracking in [±θm/90n]s composite laminates. Part1: In-plane stiffness properties. Composites 23(5), 291–298 (1992)
Zhang, J., Fan, J., Soutis, C.: Analysis of multiple matrix cracking in [±θm/90n]s composite laminates. Part 2: Development of transverse ply cracks. Composites 23(5), 299–304 (1992)
Smith, P.A., Boniface, L., Glass, N.F.C.: A comparison of transverse cracking phenomena in [0/90]s and [90/0]s CFRP laminates. Appl. Compos. Mater. 5, 11–23 (1998)
Berthelot, J.-M.: Transverse cracking and delamination in cross-ply glass-fiber and carbon fiber reinforced plastics laminates: static and fatigue loading. Appl. Mech. Rev. 56(1), 111–148 (2003)
Kachanov, L.M.: On the creep rupture time. Izv AN SSSR Otd Tekhn Nauk 8, 26–31 (1958)
Rabotnov, Y.N.: On the Equations of State for Creep. Progress in Appl. Mech. Prager Anniversary Volume. Macmillan, New York (1963)
Donadon, M.V., Iannucci, L., Falzon, B.G., Hodgkinson, J.M., Almeida, S.F.M.: A progressive failure model for composite laminates subjected to low-velocity impact damage. Comput. Struct. 86, 1232–1252 (2008)
Faggiani, A., Falzon, B.G.: Predicting low-velocity impact damage on a stiffened composite panel. Compos. A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 41, 737–749 (2010)
Iannucci, L., Ankersen, J.: An energy based damage model for thin laminated composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 66, 934–951 (2006)
Yokoyama, N.O., Donadon, M.V., Almeida, S.F.M.: A numerical study on the impact resistance of composite shells using an energy based failure model. Compos. Struct. 93, 142–152 (2010)
Barbero, E.J., Cortes, D.H.: A Mechanistic model for transverse damage initiation, evolution, and stiffness reduction in laminated composites. Compos. Part B. Eng. 41(2), 124–132 (2010)
Bouhala, L., Makradi, A., Belouettar, S., Kiefer-Kamal, H., Freres, P.: Modeling of failure in long fibers reinforced composites by X-FEM and cohesive zone model. Compos. Part B. Eng. 55, 352–361 (2013)
Shi, Y., Swait, T., Soutis, C.: Modeling damage evolution in composite laminates subjected to low-velocity impact. Compos. Struct. 94, 2902–2913 (2012)
Shi, Y., Pinna, C., Soutis, C.: Interface cohesive element to model matrix crack evolution in composite laminates. Appl. Compos. Mater. 21, 57–70 (2014)
Caputo, F., De Luca, A., Lamanna, G., Lopresto, V., Riccio, A.: Numerical investigation of onset and evolution of LVI damages in Carbon–Epoxy plates. Compos. Part B. Eng. 68, 385–391 (2015)
Riccio, A., De Luca, A., Di Felice, G., Caputo, F.: Modeling the simulation of impact induced damage onset and evolution in composites. Compos. Part B. Eng. 66, 340–347 (2014)
Carraro, P.A., Quaresimin, M.: A stiffness degradation model for cracked multidirectional laminates with cracks in multiple layers. Int. J. Solids Struct. 58, 34–51 (2015)
Sills, R.B., Thouless, M.D.: Cohesive-length scales for damage and toughening mechanisms. Int. J. Solids Struct. 55, 32–43 (2015)
Van der Meer, F.P., Davila, C.G.: Cohesive modeling of transverse cracking in laminates under in-plane loading with a single layer of elements per ply. Int. J. Solids Struct. 50, 3308–3318 (2013)
Reedy Jr., E.D.: Cohesive zone finite element analysis of crack initiation from a butt joint’s interface corner. Int. J. Solids Struct. 51, 4336–4344 (2014)
Han, Y., Hahn, H.T., Croman, R.B.: A simplified analysis of the transverse ply cracking in cross-ply laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 31, 165–177 (1988)
Hahn, H.T., Han, Y.M., Kim, R.Y.: Resistance curves for ply cracking in composite laminates. Proc 33rd. Int. SAMPE. Symp., 1101–8 (1998)
Fan, J., Zhang, J.: In-situ damage evolution and micro/macro transition for laminated composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 47(2), 107–118 (1993)
Camanho, P.P., Dávila, C.G.: Mixed-mode decohesion finite elements for the simulation of delamination in composite materials., Tech. Rep. NASA/TM-2002-211737 (2002)
Camanho, P.P., Dávila, C.G., de Moura, M.F.: Numerical simulation of the mixed-mode progressive delamination in composite materials. J. Compos. Mater. 37(16), 1415–1438 (2003)
ABAQUS.: ABAQUS Version 6.10, Dassault systems. Providence (2010)
Barbero, E.J.: Finite Element Analysis of Composite Materials Using Abaqus. CRC Press (2010)
Turon, A.: Simulation of Delamination in Composites Under Quasi-Static and Fatigue Loading Using Cohesive Zone Models. PhD Dissertation Universitat de Girona (2006)
Ankersen, J., Davies, G.A.O.: Interface elements–advantages and limitations in CPRP delamination modeling. In: 17th International Conference on Composite Materials. Edinburgh, UK (2009)
Pinho, S.T., Iannucci, L., Robinson, P.: Fracture toughness of the tensile and compressive fiber failure modes in laminated composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 66(13), 2069–2079 (2006)
Turon, A., Dávila, C.G., Camanho, P.P., Costa, J.: An engineering solution for mesh size effects in the simulation of delamination using cohesive zone models. Eng. Fract. Mech. 74, 1665–1682 (2007)
Daudeville, L., Allix, O., Ladevèze, P.: Delamination analysis by damage mechanics: Some applications. Compos. Eng. 5(1), 17–24 (1995)
Gonçalves, J.P.M., de Moura, M.F.S.F., de Castro, P.M.S.T., Marques, A.T.: Interface element including point-to-surface constraints for three-dimensional problems with damage propagation. Eng. Comput. 17(1), 28–47 (2000)
Mi, Y., Crisfield, M.A.: Analytical Derivation of Load/Displacement Relationships for Mixed-Mode Delamination and Comparison with Finite Element Results. Imperial College, Department of Aeronautics, London (1996)
Schelleckens, J.C.J., de Borst, R.: On the numerical integration of interface elements. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 36, 43–66 (1993)
Zou, Z., Reid, S.R., Li, S., Soden, P.D.: Modeling inter-laminar and intra-laminar damage in filament wound pipes under quasi-static indentation. J. Compos. Mater. 36, 477–499 (2002)
Hashin, Z.: Analysis of orthogonally cracked laminates under tension. Trans. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 54, 272–279 (1987)
Henaff-Gardin, C., Lafarie-Frenot, M.C., Gamby, D.: Doubly period matrix cracking in composite laminates Part 1: general in-plane loading. Compos. Struct. 36, 113–130 (1996)
Turon, A., Camanho, P.P., Costa, J., Renart, J.: Accurate simulation of delamination growth under mixed-mode loading using cohesive elements: definition of interlaminar strengths and elastic stiffness. Compos. Struct. 92, 1857–1864 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Human Resources Development Program (No. 20114010203070) of the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) Grant funded by the Korea government Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy. The research was supported by ‘Software Convergence Technology Development Program’, through the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (S1002-13-1004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, D., Roy, R., Kweon, JH. et al. Numerical Modeling of Combined Matrix Cracking and Delamination in Composite Laminates Using Cohesive Elements. Appl Compos Mater 23, 397–419 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-015-9465-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-015-9465-0