Abstract
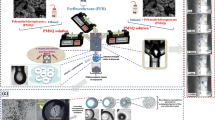
This paper reports an in situ photopolymerization method based on a microfluidic device to produce 5-fluorouracil loaded biocompatible poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA) microspheres with monodisperse size distribution for sustained drug release. Multiphase flow of 5-fluorouracil and PEGDA are dispersed to generate droplets in continuous hexadecane stream based on a T-junction microfluidic channel. The size of emulsion can be controlled from 16.7 to 85.7 µm in diameter by altering the flow rate ratio of the continuous phase and the dispersed phase. The droplets are polymerized in a serpentine channel region induced by UV irradiation. Optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy are performed to characterize the dispersity and morphology of the microbeads. A quantitative drug release study is conducted within the drug dosage range from 0.1 to 0.5 % w/w. It is shown that the PEGDA microbead-mediated release of 5-fluorouracil exhibits relatively fast elution in the first 12 h and sustained release over the next 156 h, under which the proliferation of Huh-7 tumor cells is effectively inhibited in vitro. These results demonstrate that monodisperse PEGDA microbeads could be utilized as promising carriers with long-term stability in a drug delivery and screening system for sustained release of 5-fluorouracil during chemotherapy.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen TM, Cullis PR (2004) Drug delivery systems: entering the mainstream. Science 303(5665):1818–1822. doi:10.1126/science.1095833
Barratt G (2003) Colloidal drug carriers: achievements and perspectives. Cell Mol Life Sci 60(1):21–37. doi:10.1007/s000180300002
Berkland C, Kim K, Pack DW (2003) PLG microsphere size controls drug release rate through several competing factors. Pharm Res 20(7):1055–1062. doi:10.1023/A:1024466407849
Berkland C, Kipper MJ, Narasimhan B, Kim KK, Pack DW (2004) Microsphere size, precipitation kinetics and drug distribution control drug release from biodegradable polyanhydride microspheres. J Control Release 94(1):129–141. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2003.09.011
Browning MB, Cosgriff-Hernandez E (2012) Development of a biostable replacement for PEGDA hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 13(3):779–786. doi:10.1021/bm201707z
Browning MB, Cereceres SN, Luong PT, Cosgriff-Hernandez EM (2014) Determination of the in vivo degradation mechanism of PEGDA hydrogels. J Biomed Mater Res A. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.35096
Chidambaram N, Burgess DJ (1999) A novel in vitro release method for submicron-sized dispersed systems. AAPS PharmSci 1(3)
Cho S, Park SJ, Ko SY, Park JO, Park S (2012) Development of bacteria-based microrobot using biocompatible poly(ethylene glycol). Biomed Microdevices 14(6):1019–1025. doi:10.1007/s10544-012-9704-1
Cristini V, Tan YC (2004) Theory and numerical simulation of droplet dynamics in complex flows—a review. Lab Chip 4(4):257–264. doi:10.1039/B403226h
Dashtimoghadam E, Mirzadeh H, Taromi FA, Nystrom B (2013) Microfluidic self-assembly of polymeric nanoparticles with tunable compactness for controlled drug delivery. Polymer 54(18):4972–4979. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2013.07.022
Duncanson WJ, Lin T, Abate AR, Seiffert S, Shah RK, Weitz DA (2012) Microfluidic synthesis of advanced microparticles for encapsulation and controlled release. Lab Chip 12(12):2135–2145. doi:10.1039/C2lc21164e
Durst CA, Cuchiara MP, Mansfield EG, West JL, Grande-Allen KJ (2011) Flexural characterization of cell encapsulated PEGDA hydrogels with applications for tissue engineered heart valves. Acta Biomater 7(6):2467–2476. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2011.02.018
Fang AP, Cathala B (2011) Smart swelling biopolymer microparticles by a microfluidic approach synthesis, in situ encapsulation and controlled release. Colloid Surf B 82(1):81–86. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.08.020
Garstecki P, Fuerstman MJ, Stone HA, Whitesides GM (2006) Formation of droplets and bubbles in a microfluidic T-junction—scaling and mechanism of break-up. Lab Chip 6(3):437–446. doi:10.1039/B510841a
Gupta A, Murshed SMS, Kumar R (2009) Droplet formation and stability of flows in a microfluidic T-junction. Appl Phys Lett 94(16). doi:10.1063/1.3116089
He TX, Liang QL, Zhang K, Mu X, Luo TT, Wang YM, Luo GA (2011) A modified microfluidic chip for fabrication of paclitaxel-loaded poly(l-lactic acid) microspheres. Microfluid Nanofluidics 10(6):1289–1298. doi:10.1007/s10404-010-0760-7
Huang KS, Lu K, Yeh CS, Chung SR, Lin CH, Yang CH, Dong YS (2009) Microfluidic controlling monodisperse microdroplet for 5-fluorouracil loaded genipin-gelatin microcapsules. J Control Release 137(1):15–19. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.02.019
Kantak C, Zhu QD, Beyer S, Bansal T, Trau D (2012) Utilizing microfluidics to synthesize polyethylene glycol microbeads for Forster resonance energy transfer based glucose sensing. Biomicrofluidics 6(2). doi:10.1063/1.3694869
Kohane DS (2007) Microparticles and nanoparticles for drug delivery. Biotechnol Bioeng 96(2):203–209. doi:10.1002/Bit.21301
Kong TT, Wu J, Yeung KWK, To MKT, Shum HC, Wang LQ (2013) Microfluidic fabrication of polymeric core-shell microspheres for controlled release applications. Biomicrofluidics 7(4). doi:10.1063/1.4819274
Lasic DD (1997) Recent developments in medical applications of liposomes: sterically stabilized liposomes in cancer therapy and gene delivery in vivo. J Control Release 48(2–3):203–222. doi:10.1016/S0168-3659(97)00045-X
Lassalle V, Ferreira ML (2007) PLA nano- and microparticles for drug delivery: an overview of the methods of preparation. Macromol Biosci 7(6):767–783. doi:10.1002/mabi.200700022
Lee HY, Mohammed KA, Peruvemba S, Goldberg EP, Nasreen N (2011) Targeted lung cancer therapy using ephrinA1-loaded albumin microspheres. J Pharm Pharmacol 63(11):1401–1410. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01306.x
Lee KJ, Yang SY, Ryu W (2012) Controlled release of bupivacaine HCl through microchannels of biodegradable drug delivery device. Biomed Microdevices 14(3):583–593. doi:10.1007/s10544-012-9637-8
Liang XL, Li XD, Yue XL, Dai ZF (2011) Conjugation of porphyrin to nanohybrid cerasomes for photodynamic diagnosis and therapy of cancer. Angew Chem Int Edit 50(49):11622–11627. doi:10.1002/anie.201103557
Majedi FS, Hasani-Sadrabadi MM, Emami SH, Shokrgozar MA, VanDersarl JJ, Dashtimoghadam E, Bertsch A, Renaud P (2013) Microfluidic assisted self-assembly of chitosan based nanoparticles as drug delivery agents. Lab Chip 13(2):204–207. doi:10.1039/C2lc41045a
Marre S, Jensen KF (2010) Synthesis of micro and nanostructures in microfluidic systems. Chem Soc Rev 39(3):1183–1202. doi:10.1039/B821324k
Mellott MB, Searcy K, Pishko MV (2001) Release of protein from highly cross-linked hydrogels of poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate fabricated by UV polymerization. Biomaterials 22(9):929–941. doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(00)00258-1
Nemir S, Hayenga HN, West JL (2010) PEGDA hydrogels with patterned elasticity: novel tools for the study of cell response to substrate rigidity. Biotechnol Bioeng 105(3):636–644. doi:10.1002/bit.22574
Nguyen KT, West JL (2002) Photopolymerizable hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 23(22):4307–4314. doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(02)00175-8
Ogonczyk D, Siek M, Garstecki P (2011) Microfluidic formulation of pectin microbeads for encapsulation and controlled release of nanoparticles. Biomicrofluidics 5(1). doi:10.1063/1.3569944
Oh JK, Drumright R, Siegwart DJ, Matyjaszewski K (2008) The development of microgels/nanogels for drug delivery applications. Prog Polym Sci 33(4):448–477. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2008.01.002
O’Hagan DT, Singh M, Ulmer JB (2006) Microparticle-based technologies for vaccines. Methods 40(1):10–19. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2006.05.0173
Ostrovidov S, Annabi N, Seidi A, Ramalingam M, Dehghani F, Kaji H, Khademhosseini A (2012) Controlled release of drugs from gradient hydrogels for high-throughput analysis of cell-drug interactions. Anal Chem 84(3):1302–1309. doi:10.1021/Ac202256c
Park JS, Lee JH, Shin HS, Lee TW, Kim MS, Khang G, Rhee JM, Lee HK, Lee HB (2007) Biodegradable polymer microspheres for controlled drug release. Tissue Eng Regen Med 4(3):347–359. doi:10.1007/3-540-45734-8_3
Siepmann J, Peppas NA (2011) Higuchi equation: derivation, applications, use and misuse. Int J Pharm 418(1):6–12. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.03.051
Soodak KF, Brennecka CR, Vernon BL (2013) In vitro characteristics of a gelling PEGDA-QT polymer system with model drug release for cerebral aneurysm embolization. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. doi:10.1002/jbmb.32969
Teh SY, Lin R, Hung LH, Lee AP (2008) Droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 8(2):198–220. doi:10.1039/B715524g
Varde NK, Pack DW (2004) Microspheres for controlled release drug delivery. Expert Opin Biol Ther 4(1):35–51. doi:10.1517/eobt.4.1.35.25256
Veronese FM, Mero A (2008) The impact of PEGylation on biological therapies. Biodrugs 22(5):315–329. doi:10.2165/00063030-200822050-00004
Wang LY, Ma GH, Su ZG (2005) Preparation of uniform sized chitosan microspheres by membrane emulsification technique and application as a carrier of protein drug. J Control Release 106(1–2):62–75. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.04.005
Wang JM, Xiao BL, Zheng JW, Chen HB, Zou SQ (2007) Effect of targeted magnetic nanoparticles containing 5-FU on expression of bcl-2, bax and caspase 3 in nude mice with transplanted human liver cancer. World J Gastroenterol 13(23):3171–3175
Wei Z, Hao JG, Yuan S, Li YJ, Juan W, Sha XY, Fang XL (2009) Paclitaxel-loaded Pluronic P123/F127 mixed polymeric micelles: formulation, optimization and in vitro characterization. Int J Pharm 376(1–2):176–185. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.04.030
Weiner AA, Shuck DM, Bush JR, Shastri VP (2007) In vitro degradation characteristics of photocrosslinked anhydride systems for bone augmentation applications. Biomaterials 28(35):5259–5270. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.08.022
Xin AX, Gaydos C, Mao JJ (2006) In vitro degradation behavior of photopolymerized PEG hydrogels as tissue engineering scaffold. 2006 28th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, vol 1–15:3773–3775. doi:10.1109/IEMBS.2006.260811
Yoshida S, Sato K, Takeuchi S (2013) Sequential micro-assembly of three dimensional biological microstructures from two dimensional cell-laden micro-plates. Proc Cirp 5:196–200. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2013.01.039
Zhou ZH, Cao DF, Liu LH, Liu QQ, Zhao YM, Zeng WN, Yi QF, Yang ZM, Zhou JA (2013) Fabrication and properties of gelatin/chitosan microspheres loaded with 5-fluorouracil. J Macromol Sci B 52(7):973–983. doi:10.1080/00222348.2012.746910
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a start-up grant from Nanyang Technological University College of Engineering, an Academic Research Fund Tier-1 (RG 26/11) and an Academic Research Fund Tier-2 (ARC 22/13) from the Ministry of Education of Singapore awarded to Y.K. The Ph.D. scholarship from Nanyang Technological University awarded to P.X. is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, P., Wu, Y., Menon, N.V. et al. Microfluidic synthesis of monodisperse PEGDA microbeads for sustained release of 5-fluorouracil. Microfluid Nanofluid 18, 333–342 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-014-1436-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-014-1436-5