Abstract
Ultrasound elastography is a relatively new diagnostic technique for measuring tissue elasticity (hardness). This review describes the types and evaluation methods of elastographies used in diagnosing pancreatic tumors. It also evaluates the diagnostic ability of transabdominal (US) or endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) elastography for pancreatic tumors, based on findings from a search of published articles. Twenty articles (2096 cases) were selected from the databases. The types of elastography used for the diagnosis of pancreatic tumors were strain elastography and shear wave elastography. The evaluation methods of elastography and their diagnostic abilities (sensitivity and specificity) were 0.78 (95% confidence interval 0.65–0.87) and 0.82 (0.63–0.94) for color pattern diagnosis (US), 0.82 (0.77–0.86) and 0.70 (0.64–0.76) for color pattern diagnosis (EUS), 0.94 (0.90–0.97) and 0.87 (0.81–0.92) for strain ratio (EUS), 0.92 (0.90–0.94) and 0.79 (0.75–0.82) for histogram analysis (EUS), and 0.90 (0.82–0.95) and 0.82 (0.57–0.72) for shear wave elastography. In conclusion, there are many types of elastographies and evaluation methods, and the diagnostic ability for pancreatic tumors is high for each evaluation method.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu DM, Gong TT, Zhu Q. Endoscopic ultrasound elastography for differential diagnosis of pancreatic masses: a meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58:1125–31.
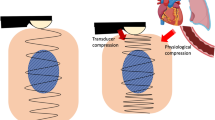
Shiina T. JSUM ultrasound elastography practice guidelines: basics and terminology. J Med Ultrason. 2013;40:309–23.
Nakashima K, Shiina T, Sakurai M, et al. JSUM ultrasound elastography practice guidelines: breast. J Med Ultrason. 2013;40:359–91.
Lyshchik A, Higashi T, Asato R, et al. Thyroid gland tumor diagnosis at US elastography. Radiology. 2005;237:202–11.
Tsutsumi M, Miyagawa T, Matsumura T, et al. The impact of real-time tissue elasticity imaging (elastography) on the detection of prostate cancer: clinicopathological analysis. Int J Clin Oncol. 2007;12:250–5.
Kudo M, Shiina T, Moriyasu F, et al. JSUM ultrasound elastography practice guidelines: liver. J Med Ultrasonics. 2013;40:325–57.
Hirooka Y, Kuwahara T, Irisawa A, et al. JSUM ultrasound elastography practice guidelines: pancreas. J Med Ultrason. 2015;42:151–74.
Kuwahara T, Hirooka Y, Kawashima H, et al. Quantitative diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis using EUS-elastography. J Gastroenterol. 2017;52:868–74.
Kuwahara T, Hirooka Y, Kawashima H, et al. Usefulness of shear wave elastography as a quantitative diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;33:756–61.
Kuwahara T, Hirooka Y, Kawashima H, et al. Quantitative evaluation of pancreatic tumor fibrosis using shear wave elastography. Pancreatology. 2016;16:1063–8.
Hashizume K, Hirooka Y, Kawashima H, et al. The propagation display method improves the reproducibility of pancreatic shear wave elastography. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019;45:2242–7.
Ohno E, Hirooka Y, Kawashima H, et al. Feasibility and usefulness of endoscopic ultrasonography-guided shear-wave measurement for assessment of autoimmune pancreatitis activity: a prospective exploratory study. J Med Ultrason. 2001;2019(46):425–33.
Giovannini M, Hookey LC, Bories E, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound elastography: the first step towards virtual biopsy? Preliminary results in 49 patients. Endoscopy. 2006;38:344–8.
Itokawa F, Itoi T, Sofuni A, et al. EUS elastography combined with the strain ratio of tissue elasticity for diagnosis of solid pancreatic masses. J Gastroenterol. 2011;46:843–53.
Itoh Y, Itoh A, Kawashima H, et al. Quantitative analysis of diagnosing pancreatic fibrosis using EUS-elastography (comparison with surgical specimens). J Gastroenterol. 2014;49:1183–92.
Uchida H, Hirooka Y, Itoh A, et al. Feasibility of tissue elastography using transcutaneous ultrasonography for the diagnosis of pancreatic diseases. Pancreas. 2009;38:17–22.
Kawada N, Tanaka S, Uehara H, et al. Feasibility of second-generation transabdominal ultrasound-elastography to evaluate solid pancreatic tumors: preliminary report of 36 cases. Pancreas. 2012;41:978–80.
Janssen J, Schlörer E, Greiner L. EUS elastography of the pancreas: feasibility and pattern description of the normal pancreas, chronic pancreatitis, and focal pancreatic lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;65:971–8.
Hirche TO, Ignee A, Barreiros AP, et al. Indications and limitations of endoscopic ultrasound elastography for evaluation of focal pancreatic lesions. Endoscopy. 2008;40:910–7.
Lee TH, Cho YD, Cha SW, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound elastography for the pancreas in Korea: a preliminary single center study. Clin Endosc. 2013;46:172–7.
Chantarojanasiri T, Hirooka Y, Kawshima H, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound in diagnosis of solid pancreatic lesions: elastography or contrast-enhanced harmonic alone versus the combination. Endosc Int Open. 2017;5:E1136–E1143143.
Ignee A, Jenssen C, Arcidiacono PG, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound elastography of small solid pancreatic lesions: a multicenter study. Endoscopy. 2018;50:1071–9.
Kongkam P, Lakananurak N, Navicharern P, et al. Combination of EUS-FNA and elastography (strain ratio) to exclude malignant solid pancreatic lesions: a prospective single-blinded study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;30:1683–9.
Rustemović N, Kalauz M, Grubelić Ravić K, et al. Differentiation of pancreatic masses via endoscopic ultrasound strain ratio elastography using adjacent pancreatic tissue as the reference. Pancreas. 2017;46:347–51.
Okasha H, Elkholy S, El-Sayed RW, et al. Real time endoscopic ultrasound elastography and strain ratio in the diagnosis of solid pancreatic lesions. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:5962–8.
Kim SY, Cho JH, Kim YJ, et al. Diagnostic efficacy of quantitative endoscopic ultrasound elastography for differentiating pancreatic disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;32:1115–22.
Săftoiu A, Vilmann P, Gorunescu F, et al. Neural network analysis of dynamic sequences of EUS elastography used for the differential diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;68:1086–94.
Săftoiu A, Vilmann P, Gorunescu F, et al. Efficacy of an artificial neural network-based approach to endoscopic ultrasound elastography in diagnosis of focal pancreatic masses. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10(84–90):e1.
Opačić D, Rustemović N, Kalauz M, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound elastography strain histograms in the evaluation of patients with pancreatic masses. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:4014–9.
Iglesias-Garcia J, Larino-Noia J, Abdulkader I, et al. Quantitative endoscopic ultrasound elastography: an accurate method for the differentiation of solid pancreatic masses. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:1172–80.
Carrara S, Di Leo M, Grizzi F, et al. EUS elastography (strain ratio) and fractal-based quantitative analysis for the diagnosis of solid pancreatic lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;87:1464–73.
Goertz RS, Schuderer J, Strobel D, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse shear wave elastography (ARFI) of acute and chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic tumor. Eur J Radiol. 2016;85:2211–6.
Onoyama T, Koda M, Fujise Y, et al. Utility of virtual touch quantification in the diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Imaging. 2017;42:64–7.
Kitano M, Kudo M, Yamao K, et al. Characterization of small solid tumors in the pancreas: the value of contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107:303–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Takamichi Kuwahara, Kazuo Hara, Nobumasa Mizuno, Shin Haba, and Nozomi Okuno declare no conflicts of interest related to this study.
Ethical statements
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Kuwahara, T., Hara, K., Mizuno, N. et al. Present status of ultrasound elastography for the diagnosis of pancreatic tumors: review of the literature. J Med Ultrasonics 47, 413–420 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-020-01026-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-020-01026-6