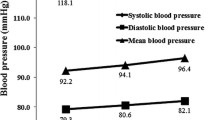
Abstract
Aim
The lifestyle habits of young people are often associated with that of middle-aged and older adults, and intervention from a young age is important for the prevention of lifestyle-related diseases. Hypertension is a lifestyle-related disease, and an increasing number of patients are suffering from it. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the factors that cause fluctuations in blood pressure in university students.
Subject and methods
The survey was conducted from 2011 to 2019 and included 14,720 male and 6,039 female university students. The questionnaire included items such as age, sex, weight control orientation, and lifestyle habits. Height, weight, and systolic and diastolic blood pressures were measured. Body mass indices (BMI) were calculated, and the participants were classified as underweight, normal body type, or obese. In addition, abnormal blood pressure (ABP) was defined as systolic/diastolic blood pressure above 120 and/or 80 mmHg.
Results
A multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that ABP was significantly associated with snacking (odds ratio, 95% confidence interval 0.68, 0.52–0.90) in males with underweight; sleep duration ≥ 6 h (1.10, 1.02–1.19), snacking (0.84, 0.75–0.96), and weight decreasing orientation (1.22, 1.12–1.32) in males with normal body types; exercise habits (0.75, 0.56–1.00) in females with normal body types.
Conclusion
The present study revealed different risk factors by body type associated with ABP in Japanese university students. In particular, weight loss orientation in a standard-bodied male may be a risk factor for ABP. Our study suggests that interventions by body type may prevent lifestyle-related diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets created during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Arai H, Kiuchi A, Ishii T, Urai R, Nakamura T (2006) The effects of an intervention program aimed at lifestyle modification on sedentary behavior in male students of a Japanese university. School Health 2:9–16. https://doi.org/10.20812/jash.SH-2006_012
Blumenthal JA, Sherwood A, Gullette ECD, Babyak M, Waugh R, Georgiades A, Craighead LW, Tweedy D, Feinglos M, Appelbaum M, Hayano J, Hinderliter A (2000) Exercise and weight loss reduce blood pressure in men and women with mild hypertension: effects on cardiovascular, metabolic, and hemodynamic functioning. Arch Intern Med 160:1947–1958. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.160.13.1947
Chen X, Wang Y (2008) Tracking of blood pressure from childhood to adulthood: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Circulation 117:3171–3180. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.730366
Gangwisch JE, Heymsfield SB, Boden-Albala B, Buijs RM, Kreier F, Pickering TG, Rundle AG, Zammit GK, Malaspina D (2006) Short sleep duration as a risk factor for hypertension: analyses of the first National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Hypertension 47:833–839. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000217362.34748.e0
Gradisar M, Gardner G, Dohnt H (2011) Recent worldwide sleep patterns and problems during adolescence: a review and meta-analysis of age, region, and sleep. Sleep Med 12:110–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2010.11.008
Guo X, Zheng L, Wang J, Zhang X, Zhang X, Li J, Sun Y (2013) Epidemiological evidence for the link between sleep duration and high blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med 14:324–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2012.12.001
Hatanaka Y, Tamakoshi A, Tsushita K (2012) Impact of body mass index on men in their 20s and the effects of subsequent changes in body weight upon the rates of hypertension and diabetes and medical costs in their 40s. J Occup Health 54:141–149. https://doi.org/10.1539/sangyoeisei.B11018
Irazusta A, Hoyos I, Irazusta J, Ruiz F, Díaz E, Gil J (2007) Increased cardiovascular risk associated with poor nutritional habits in first-year university students. Nutr Res 27:387–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2007.05.007
Japan Society for the Study of Obesity (2016) Guidelines for the management of obesity disease. https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/naika/107/2/107_262/_pdf/-char/ja. Accessed 8 Feb 2021
Keller K, Rodríguez López S, Carmenate Moreno M (2017) Association between meal intake behavior and blood pressure in Spanish adults. Nutr Hosp 34: 654–660. https://doi.org/10.20960/nh.47
Liang Y, Mi J (2011) Pubertal hypertension is a strong predictor for the risk of adult hypertension. Biomed Environ Sci 24:459–466. https://doi.org/10.3967/0895-3988.2011.05.002
Mato M, Tsukasaki K (2020) Relationship between breakfast consumption and health-related habits among university students in Japan. Jpn J Public Health 67: 791–799. https://doi.org/10.11236/jph.67.11_791
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (2017a) Patient Survey. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/kanja/17/dl/kanja-01.pdf. Accessed 30 May 2019
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (2017b) National Health and Nutrition Survey. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/k-iryohi/17/dl/kekka.pdf. Accessed 10 Apr 2020
Miyawaki C, Ohara K, Mase T, Kouda K, Fujitani T, Momoi K, Kaneda H, Murayama R, Okita Y, Nakamura H (2019) The purpose and the motivation for future practice of physical activity and related factors in Japanese university students. J Hum Sport Exerc 14. https://doi.org/10.14198/jhse.2019.141.05
Monden S (2002) Consciousness, knowledge and behavior on lifestyle related diseases of students. Jpn J Public Health 49: 554–563. https://doi.org/10.11236/jph.49.6_554
Nishizawa Y, Kida K, Nishizawa K, Hashiba S, Saito K, Mita R (2003) Perception of self-physique and eating behavior of high school students in Japan. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 57:189–196. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1819.2003.01100.x
Ohara K, Kato Y, Mase T, Kouda K, Miyawaki C, Fujita Y, Okita Y, Nakamura H (2014) Eating behavior and perception of body shape in Japanese university students. Eat Weight Disord-Stud Anorex 19:461–468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-014-0130-7
Ponzo V, Ganzit GP, Soldati L, De Carli L, Fanzola I, Maiandi M, Durazzo M, Bo S (2015) Blood pressure and sodium intake from snacks in adolescents. Eur J Clin Nutr 69:681–686. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2015.9
Sakamaki R, Amamoto R, Mochida Y, Shinfuku N, Toyama K (2005) A comparative study of food habits and body shape perception of university students in Japan and Korea. Nutr J 4:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-4-31
Selem SS, Castro MA, Cesar CL, Marchioni DM, Fisberg RM (2014) Associations between dietary patterns and self-reported hypertension among Brazilian adults: a cross-sectional population-based study. J Acad Nutr Diet 114:1216–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2014.01.007
Stock AA, Lee S, Nahmod NG, Chang A-M (2020) Effects of sleep extension on sleep duration, sleepiness, and blood pressure in college students. Sleep Health 6:32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2019.10.003
Tsutatani H, Funamoto M, Sugiyama D, Kuwabara K, Miyamatsu N, Watanabe K, Okamura T (2017) Association between lifestyle factors assessed by standard question items of specific health checkup and the incidence of metabolic syndrome and hypertension in community dwellers: a five-year cohort study of National Health Insurance beneficiaries in Habikino City. Jpn J Public Health 64: 258–269. https://doi.org/10.11236/jph.64.5_258
Umemura S, Arima H, Arima S, Asayama K, Dohi Y, Hirooka Y, Horio T, Hoshide S, Ikeda S, Ishimitsu T, Ito M, Ito S, Iwashima Y, Kai H, Kamide K, Kanno Y, Kashihara N, Kawano Y, Kikuchi T, Kitamura K, Kitazono T, Kohara K, Kudo M, Kumagai H, Matsumura K, Matsuura H, Miura K, Mukoyama M, Nakamura S, Ohkubo T, Ohya Y, Okura T, Rakugi H, Saitoh S, Shibata H, Shimosawa T, Suzuki H, Takahashi S, Tamura K, Tomiyama H, Tsuchihashi T, Ueda S, Uehara Y, Urata H, Hirawa N (2019) The Japanese Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertens Res 42:1235–1481. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-019-0284-9
van Strien T, Frijters JER, Bergers GPA, Defares PB (1986) The Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire (DEBQ) for assessment of restrained, emotional, and external eating behavior. Int J Eat Disord 5:295–315. https://doi.org/10.1002/1098-108X(198602)5:2<295::AID-EAT2260050209>3.0.CO;2-T
Whelton SP, Chin A, Xin X, He J (2002) Effect of aerobic exercise on blood pressure. Ann Intern Med 136:493–503. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-136-7-200204020-00006
Yamashiro K, Tanei S, Burapadaja S, Ogata F, Kawasaki N (2019) Survey on physical or mental health status of university students in Japan and Thailand. J Allied Health Sci 10: 69–78. https://doi.org/10.15563/jalliedhealthsci.10.69
Yasunaga A, Kawano Y, Kamahori Y, Noguchi K (2014) Individual and environmental factors related to stage of change in exercise behavior: a cross-sectional study of female Japanese undergraduate students. J Phys Act Health 11:62–67. https://doi.org/10.1123/jpah.2011-0210
Acknowledgements
Part of this study was conducted with the support of the Antiaging center, Kindai university.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.Y., Y.U., and N.K. contributed to the concept and designed the study. K.Y. and Y.U. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. S.T., F.O., and T.N interpreted the data and helped to write the manuscript. F.O., T.N., S.T., and N.K. supervised the findings of the study and reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Pharmacy, Kindai University (Approval No. 08–001, 12–033, and 15–072).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashiro, K., Utaka, Y., Tanei, S. et al. A survey on the relationship between blood pressure and self-reported lifestyle habits and ideal body image in Japanese university students: a cross-sectional study. J Public Health (Berl.) 32, 9–16 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-022-01783-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-022-01783-3