Abstract
Background
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are the most common cause of severe long-term pain and physical disability. High prevalence of musculoskeletal pain among medical and other health science students has been reported globally. However, little is known about the magnitude of the problem in Ethiopia among medical and health science students. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the prevalence and identify the associated risk factors of MSDs among medical and health science students in Ethiopia.
Methods
Institution based cross-sectional study was conducted from March to May 2018. A stratified random sampling technique was applied to select 422 study participants, and the data was collected by a standardized Nordic questionnaire for the analysis of musculoskeletal symptoms. Bivariate and multivariable binary logistic regression analyses were performed using SPSS version 20.
Results
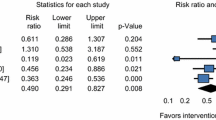
The prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders in any part of the body region among medicine and nursing students was 69.4% (95% CI, 64.9, 73.9). Lower back pain was the most commonly reported body site and its prevalence increased as the year of study increases, ranging from 38% among 2nd year to 74.4% among 5th-year students. As the year of study/academic year increased, the odds of developing musculoskeletal disorders were higher. Furthermore, this study showed that a poorly designed sitting chair was a risk factor for musculoskeletal pain.
Conclusion
Ergonomic interventions focusing on modification of workstations, and promoting and delivering ongoing ergonomic education are very important to reduce the problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article. The data that support the findings of this study are also available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AOR:
-
Adjusted odds ratio
- BMI:
-
Body mass Index
- CI:
-
Confidence Interval
- COR:
-
Crude odds ratio
- LBP:
-
Low back pain
- MSDs:
-
Musculoskeletal disorders
- SPSS:
-
Statistical Package for Social Science
- UK:
-
United Kingdom
References
Abledu JK, Offei EB (2015) Musculoskeletal disorders among first-year Ghanaian students in a nursing college. Afr Health Sci 15(2):444–449
Alhariri S, Ahmed A, Kalas A, Chaudhry H, Tukur K, Sendhil V, Muttappallymyalil J (2016) Self-reported musculoskeletal disorders and their associated factors among university students in Ajman, UAE. Gulf Med J 5(s2):S61–S70
Alshagga MA, Nimer AR, Yan LP, Ibrahim IAA, Al-ghamdi SS, Al-dubai SAR (2013) Prevalence and factors associated with neck, shoulder and low back pains among medical students in a Malaysian medical college. BMC Res Notes 6:244. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-6-244
Alshayhan FA, Saadeddin M (2018) Prevalence of low back pain among health sciences students. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 28(3):165–170
Anderson SP, Oakman J (2016) Allied health professionals and work-related musculoskeletal disorders: a systematic review. Saf Health Work 7(4):259–267
Bid DD, Alagappan TR, Dhanani HP, Goyani PS, Narielwala ZS (2017) Musculoskeletal health, quality of life, and related risk factors among physiotherapy students. Physiotherapy J Indian Assoc Physiotherapists 11(2):53–57
Bot SD, Terwee CB, Van Der Windt DA, Van Der Beek AJ, Bouter LM, Dekker J (2007) Work-related physical and psychosocial risk factors for sick leave in patients with neck or upper extremity complaints. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 80(8):733–741
Brink Y, Louw Q, Grimmer K, Jordaan E (2015) The relationship between sitting posture and seated-related upper quadrant musculoskeletal pain in computing south African adolescents: a prospective study. Man Ther 20(6):820–826
Buckle PW, Devereux JJ (2002) The nature of work-related neck and upper limb musculoskeletal disorders. Appl Ergon 33(3):207–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-6870(02)00014-5
Chang CH, Amick BC III, Menendez CC, Katz JN, Johnson PW, Robertson M, Dennerlein JT (2007) Daily computer usage correlated with undergraduate students' musculoskeletal symptoms. Am J Ind Med 50(6):481–488
Dianat I, Karimi MA, Hashemi AA, Bahrampour S (2013) Classroom furniture and anthropometric characteristics of Iranian high school students: proposed dimensions based on anthropometric data. Appl Ergon 44(1):101–108
Ekpenyong CE, Daniel NE, Aribo E (2013) Associations between academic stressors, reaction to stress, coping strategies and musculoskeletal disorders among college students. Ethiop J Health Sci 23(2):98–112
Goon D (2017) Musculoskeletal problems associated with university students computer users: a cross-sectional study. Online J Health Allied Scs 16(2):7 Available at URL: http://www.ojhas.org/issue62/2017-2-7.html
Hänninen O, Vuorikari K, Koskelo R (2007) Sitting and standing postures are corrected by adjustable furniture with lowered muscle tension in high-school students. Ergonomics 50(10):1643–1656
Haroon H, Mehmood S, Imtiaz F, Ali SA, Sarfraz M (2018) Musculoskeletal pain and its associated risk factors among medical students of a public sector university in Karachi, Pakistan. J Pakistan Med Assoc 68(4):682–688
Hayes M, Smith D, Cockrell D (2009) Prevalence and correlates of musculoskeletal disorders among Australian dental hygiene students. Int J Dent Hyg 7(3):176–181
Hayes MJ, Smith DR, Taylor JA (2014) Musculoskeletal disorders in a 3 year longitudinal cohort of dental hygiene students. Am Dental Hygienists Assoc 88(1):36–41
Iqbal M, Ahmad A, Khattak S, Hammad SM, Zeb GS, Daud M (2017) Frequency of low back pain in under graduate students of Khyber Medical University. J Riphah College Rehabilitaion Sci 5(1):25–28
Kuorinka I, Jonsson B, Kilbom A, Vinterberg H, Biering-Sørensen F, Andersson G, Jørgensen K (1987) Standardised Nordic questionnaires for the analysis of musculoskeletal symptoms. Appl Ergon 18(3):233–237
Leggat PA, Smith DR, Clark MJ (2008) Prevalence and correlates of low back pain among occupational therapy students in northern Queensland. Can J Occup Ther 75(1):35–41. https://doi.org/10.2182/cjot.07.014
Modarresi M, Tafti AMF, Touri MK, Aghakoochak A (2017) Prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders and their relationship with some work-related factors among of faculty members of Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences of Yazd in 2015. J Clin Basic Res 1(3):29–35
Nkhata LA, Esterhuizen TM, Siziya S, Phiri PD, Munalula-Nkandu E, Shula H (2015) The prevalence and perceived contributing factors for work-related musculoskeletal disorders among nurses at the university teaching hospital in Lusaka, Zambia. Sci J Pub Health 3(4):508–513. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sjph.20150304.18
Nordin NAM, Singh DKA, Kanglun L (2014) Low back pain and associated risk factors among health science undergraduates. Sains Malaysiana 43(3):423–428
Nyland LJ, Grimmer KA (2003) Is undergraduate physiotherapy study a risk factor for low back pain? A prevalence study of LBP in physiotherapy students. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 4:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-4-22
Penkala S, El-Debal H, Coxon K (2018) Work-related musculoskeletal problems related to laboratory training in university medical science students: a cross sectional survey. BMC Public Health 18:1208. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-6125-y
Podniece Z, Heuvel S, Blatter B (2008) Work-related musculoskeletal disorders: prevention report. European Agency for Safety and Health at Work, Luxembourg
Rafie F, Zamani Jam A, Shahravan A, Raoof M, Eskandarizadeh A (2015) Prevalence of upper extremity musculoskeletal disorders in dentists: symptoms and risk factors. J Environ Pub Health 2015:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/517346
Rimpilainen S (2016) Cost of low back pain. Digital Health and Care Institute, Glasgow. https://doi.org/10.17868/65329
Sardar KP, Khan RF, Kumar K, Zaidi AB (2014) Work-related musculoskeletal pain among dental students at Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi. J Pakistan Dental Assoc 23(3):117–121
Sirajudeen MS, Alaidarous M, Waly M, Alqahtani M (2018) Work-related musculoskeletal disorders among faculty members of College of Applied Medical Sciences, Majmaah University, Saudi Arabia: a cross-sectional study. Int J Health Sci 12(4):18–25
Smith DR (2002) Hand dermatitis and musculoskeletal disorders among female nursing students in Japan. Yamanashi Med J 17(3):63–67
Smith DR, Leggat PA (2004) Musculoskeletal disorders among rural Australian nursing students. Aust J Rural Health 12(6):241–245
Smith DR, Leggat PA (2007) Back pain in the young: a review of studies conducted among school children and university students. Curr Pediatr Rev 3(1):69–77. https://doi.org/10.2174/157339607779941624
Smith DR, Sato M, Miyajima T, Mizutani T, Yamagata Z (2003) Musculoskeletal disorders self-reported by female nursing students in Central Japan: a complete cross-sectional survey. Int J Nurs Stud 40(7):725–729
Smith DR, Choe M-A, Chae YR, Jeong J-S, Jeon MY, An GJ (2005a) Musculoskeletal symptoms among Korean nursing students. Contemp Nurse 19(1–2):151–160
Smith DR, Wei N, Ishitake T, Wang R-S (2005b) Musculoskeletal disorders among Chinese medical students. Kurume Med J 52(4):139–146
Tantawy SA, Abdul Rahman A, Abdul Ameer M (2017) The relationship between the development of musculoskeletal disorders, body mass index, and academic stress in Bahraini University students. Korean J Pain 30(2):126–133. https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2017.30.2.126
Tirgar A, Aghalari Z, Salari F (2014) Musculoskeletal disorders & ergonomic considerations in computer use among medical sciences students. J Ergon 1(3):55–64
Van Niekerk S-M, Louw QA, Hillier S (2012) The effectiveness of a chair intervention in the workplace to reduce musculoskeletal symptoms. A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 13:145. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-13-145
Vujcic I, Stojilovic N, Dubljanin E, Ladjevic N, Ladjevic I, Sipetic-Grujicic S (2018) Low back pain among medical students in Belgrade (Serbia): a cross-sectional study. Pain Res Manag 2018:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8317906
Wami SD, Demssie AF, Wassie MM, Ahmed AN (2016) Patient safety culture and associated factors: a quantitative and qualitative study of healthcare workers’ view in Jimma zone hospitals, Southwest Ethiopia. BMC Health Serv Res 16:495. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-016-1757-z
Warren N (2010) Causes of musculoskeletal disorders in dental hygienists and dental hygiene students: a study of combined biomechanical and psychosocial risk factors. Work 35(4):441–454. https://doi.org/10.3233/WOR-2010-0981
Woolf AD, Åkesson K (2001) Understanding the burden of musculoskeletal conditions: the burden is huge and not reflected in national health priorities. BMJ 322(7294):1079–1080. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.322.7294.1079
Woolf AD, Pfleger B (2003) Burden of major musculoskeletal conditions. Bull World Health Organ 81(9):646–656
Yasobant S, Rajkumar P (2014) Work-related musculoskeletal disorders among health care professionals: a cross-sectional assessment of risk factors in a tertiary hospital, India. Indian J Occup Enviro Med 18(2):75–81
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SDW: contributed to the study design, data collection, data analysis, interpretations of the results, and manuscript write-up. TH: to the study design, data collection, data analysis, interpretations of the results, and manuscript write-up. GY: to the study design, data collection, data analysis, interpretations of the results, and manuscript write-up. GA: contributed to data analysis, interpretations of the results, and manuscript write-up and review. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical clearance was obtained from the Ethical Review Committee of Institute of Public Health, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Gondar. Those medicine and nursing students in University of Gondar who were selected to participate were informed about the purpose of the study, the importance of their participation, and their ability to withdraw at any time. Written consent was obtained prior to data collection.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wami, S.D., Mekonnen, T.H., Yirdaw, G. et al. Musculoskeletal problems and associated risk factors among health science students in Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. J Public Health (Berl.) 29, 943–949 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-020-01201-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-020-01201-6