Abstract
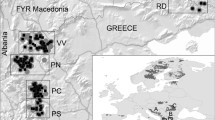
Understanding natal dispersal patterns is fundamental in the ecology and conservation biology of large wild carnivores. In this study, we used two approaches to determine genetic variation and dispersal patterns of brown bears in the Shiretoko Peninsula, eastern Hokkaido, Japan. The first approach was a large-scale genetic analysis. We analyzed haplotypes from the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) control region of 760 individual samples collected throughout the peninsula during 1998–2016. We detected seven haplotypes, including two that were confirmed for the first time. In females, the distribution of haplotypes was geographically structured, whereas haplotypes in males were distributed widely throughout the peninsula. Only some males in the lower peninsula had haplotypes that were not detected within the peninsula. The second approach was a local-scale genetic analysis, including intensive focal sampling in the Rusha area, a special wildlife protection area on the peninsula. Proportions of mtDNA haplotypes in adult bears were investigated and compared between the sexes. Although more than half of the females had the same haplotype, males had more diverse haplotypes, suggesting that they came to the Rusha area from other regions. Thus, our study revealed that mtDNA haplotype distribution has been maintained by female philopatry, and that bears exhibit male-biased dispersal. Furthermore, the lower peninsula appears to act as a contact zone between the peninsula and mainland Hokkaido, which is important for maintaining genetic diversity.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Bellemain E, Swenson JE, Taberlet P (2006) Mating strategies in relation to sexually selected infanticide in a non-social carnivore: the Brown bear. Ethology 112:238–246. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0310.2006.01152.x
Bergl RA, Vigilant L (2007) Genetic analysis reveals population structure and recent migration within the highly fragmented range of the Cross River gorilla (Gorilla gorilla diehli). Mol Ecol 16:501–516. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.03159.x
Blanchard BM, Knight RR (1991) Movements of yellowstone grizzly bears. Biol Conserv 58:41–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3207(91)90044-A
Calenge C (2006) The package “adehabitat” for the R software: a tool for the analysis of space and habitat use by animals. Ecol Model 197:516–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOLMODEL.2006.03.017
Clobert J, Le Galliard J-F, Cote J et al (2009) Informed dispersal, heterogeneity in animal dispersal syndromes and the dynamics of spatially structured populations. Ecol Lett 12:197–209. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2008.01267.x
Cummings MP (2014) PAUP* (phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (and other methods)). Dict Bioinforma Comput Biol
Dahle B, Swenson JE (2003) Seasonal range size in relation to reproductive strategies in brown bears Ursus arctos. J Anim Ecol 72:660–667
Delibes M, Gaona P, Ferreras P (2001) Effects of an attractive sink leading into maladaptive habitat selection. Am Nat 158:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1086/321319
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02553.x
Glenn LP, Miller LH (1980) Seasonal movements of an Alaska peninsula brown bear population. Bears Their Biol Manag 4:307–312. https://doi.org/10.2307/3872885
Greenwood PJ (1980) Mating systems, philopatry and dispersal in birds and mammals. Anim Behav 28:1140–1162. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-3472(80)80103-5
Hirata D, Mano T, Abramov AV, Baryshnikov GF, Kosintsev PA, Vorobiev AA, Raichev EG, Tsunoda H, Kaneko Y, Murata K, Fukui D, Masuda R (2013) Molecular phylogeography of the brown bear (Ursus arctos) in northeastern Asia based on analyses of complete mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol Biol Evol 30:1644–1652. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst077
Hokkaido Government (2017) Brown bear management plan in Hokkaido. http://www.pref.hokkaido.lg.jp/ks/skn/higuma/hokkaido_bear_management_plan05.pdf
Howard WE (1960) Innate and environmental dispersal of individual vertebrates. Am Midl Nat 63:152–161. https://doi.org/10.2307/2422936
Itoh T, Sato Y, Mano T, Iwata R (2009) Estimating a suitable microsatellite marker set for individual identification and parentage tests of brown bear (Ursus arctos) in the Akan–Shiranuka region, eastern Hokkaido, Japan. Jpn For Soc Springer 14:117–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10310-009-0110-3
Itoh T, Sato Y, Kobayashi K, Mano T, Iwata R (2012) Effective dispersal of brown bears (Ursus arctos) in eastern Hokkaido, inferred from analyses of mitochondrial DNA and microsatellites. Mammal Study 37:29–41. https://doi.org/10.3106/041.037.0104
Itoh T, Sato Y, Tsuruga H, Mano T, Kohira M, Yamanaka M, Kasai S, Kobayashi K, Iwata R (2013) Estimating the population structure of brown bears in eastern Hokkaido based on microsatellite analysis. Acta Theriol (Warsz) 58:127–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13364-012-0095-8
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kohira M, Okada H, Nakanishi M, Yamanaka M (2009) Modeling the effects of human-caused mortality on the brown bear population on the Shiretoko peninsula, Hokkaido, Japan. Ursus 20:12–21
Kojola I, Danilov PI, Laitala H-M et al (2003) Brown bear population structure in core and periphery: analysis of hunting statistics from Russian Karelia and Finland. Ursus 14:17–20
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Leigh JW, Bryant D (2015) POPART: full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol Evol 6:1110–1116. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12410
Lewis TM, Pyare S, Hundertmark KJ (2015) Contemporary genetic structure of brown bears (Ursus arctos) in a recently deglaciated landscape. J Biogeogr 42:1701–1713. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12524
Lunt DH, Whipple LE, Hyman BC (1998) Mitochondrial DNA variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs): utility and problems in molecular ecology. Mol Ecol 7:1441–1455. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294x.1998.00495.x
Mace RD, Waller JS (1997) Spatial and temporal interaction of male and female grizzly bears in northwestern Montana. J Wildl Manag 61:39–52. https://doi.org/10.2307/3802412
Masuda R, Tamura T, Takahashi O (2006) Ancient DNA analysis of brown bear skulls from a ritual rock shelter site of the Ainu culture at Bihue, central Hokkaido, Japan. Anthropol Sci 114:211–215. https://doi.org/10.1537/ase.051219
Matsuhashi T, Masuda R, Mano T, Yoshida MC (1999) Microevolution of the mitochondrial DNA control region in the Japanese brown bear (Ursus arctos) population. Mol Biol Evol 16:676–684
Matsuhashi T, Masuda R, Mano T, Murata K, Aiurzaniin A (2001) Phylogenetic relationships among worldwide populations of the brown bear Ursus arctos. Zool Sci 18:1137–1143. https://doi.org/10.2108/zsj.18.1137
McLellan BN, Hovey FW (2001) Natal dispersal of grizzly bears. Can J Zool 79:838–844. https://doi.org/10.1139/z01-051
Meredith EP, Rodzen JA, Banks JD, Jones KC (2009) Characterization of 29 tetranucleotide microsatellite loci in black bear (Ursus americanus) for use in forensic and population applications. Conserv Genet 10:693–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-008-9617-y
Moore JA, Draheim HM, Etter D, Winterstein S, Scribner KT (2014) Application of large-scale parentage analysis for investigating natal dispersal in highly vagile vertebrates: a case study of American black bears (Ursus americanus). PLoS One 9:e91168. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0091168
Nylander J (2004) MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author. Uppsala University
Ostrander EA, Sprague GF, Rine J (1993) Identification and characterization of dinucleotide repeat (CA)n markers for genetic mapping in dog. Genomics 16:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1006/GENO.1993.1160
Paetkau D, Calvert W, Stirling I, Strobeck C (1995) Microsatellite analysis of population structure in Canadian polar bears. Mol Ecol 4:347–354. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.1995.tb00227.x
Paetkau D, Shields GF, Strobeck C (1998) Gene flow between insular, coastal and interior populations of brown bears in Alaska. Mol Ecol 7:1283–1292. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294x.1998.00440.x
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Pritchard JK, Wen X, Falush D (2010) Documentation for structure software: Version 2.3. http://pritch.bsd.uchicago.edu/structure.html. Accessed 19 Sep 2018
Proctor MF, McLellan BN, Strobeck C, Barclay RM (2004) Gender-specific dispersal distances of grizzly bears estimated by genetic analysis. Can J Zool 82:1108–1118. https://doi.org/10.1139/z04-077
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, van der Mark P et al (2012) MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 61:539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
Sæther B-E, Engen S, Swenson JE, Bakke Ø, Sandegren F, Saether BE, Bakke O (1998) Assessing the viability of Scandinavian Brown bear, Ursus arctos, populations: the effects of uncertain parameter estimates. Oikos 83:403–416. https://doi.org/10.2307/3546856
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sato Y, Itoh T, Mori Y, Satoh Y, Mano T (2011) Dispersal of male bears into peripheral habitats inferred from mtDNA haplotypes. Ursus 22:120–132. https://doi.org/10.2192/URSUS-D-10-00037.1
Schregel J, Kopatz A, Hagen SB et al (2012) Limited gene flow among brown bear populations in far northern Europe? Genetic analysis of the east-west border population in the Pasvik Valley. Mol Ecol 21:3474–3488. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05631.x
Schwartz CC, Keating KA, Reynolds HVI et al (2003) Reproductive maturation and senescence in the female brown bear. Ursus 14:109–119
Shafer ABA, Côté SD, Coltman DW (2011) Hot spots of genetic diversity descended from multiple Pleistocene Refugia in an alpine ungulate. Evolution (N Y) 65:125–138. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.2010.01109.x
Shimozuru M, Yamanaka M, Nakanishi M, Moriwaki J, Mori F, Tsujino M, Shirane Y, Ishinazaka T, Kasai S, Nose T, Masuda Y, Tsubota T (2017) Reproductive parameters and cub survival of brown bears in the Rusha area of the Shiretoko peninsula, Hokkaido, Japan. PLoS One 12:e0176251. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176251
Støen O-G, Zedrosser A, Sæbø S, Swenson JE (2006) Inversely density-dependent natal dispersal in brown bears Ursus arctos. Oecologia 148:356–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-006-0384-5
Taberlet P, Bouvet J (1994) Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism, phylogeography, and conservation genetics of the brown bear Ursus arctos in Europe. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 255:195–200. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.1994.0028
Taberlet P, Swenson JE, Sandegren F, Bjarvall A (1995) Localization of a contact zone between two highly divergent mitochondrial DNA lineages of the brown bear Ursus arctos in Scandinavia. Conserv Biol 9:1255–1261
Taberlet P, Camarra J-J, Griffin S, Uhres E, Hanotte O, Waits LP, Dubois-Paganon C, Burke T, Bouvet J (1997) Noninvasive genetic tracking of the endangered Pyrenean brown bear population. Mol Ecol 6:869–876. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294X.1997.00251.x
Waits L, Paetkau D, Strobeck C et al (1999) Genetics of the bears of the world. In: Herrero S, Peyton B, Servheen C (eds) Bears: status survey and conservation action plan. The International Union for Conservation of Nature, Gland, pp 25–32
Worton BJ (1989) Kernel methods for estimating the utilization distribution in home-range studies. Ecology 70:164–168. https://doi.org/10.2307/1938423
Yamamoto K, Tsubota T, Komatsu T et al (2002) Sex identification of Japanese black bear, Ursus thibetanus japonicus, by PCR based on Amelogenin gene. J Vet Med Sci 64:505–508. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.64.505
Zedrosser A, Støen O-G, Sæbø S, Swenson JE (2007) Should I stay or should I go? Natal dispersal in the brown bear. Anim Behav 74:369–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ANBEHAV.2006.09.015
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Hatsusaburo Ose, the president of Shiretoko Fishery Cooperative, and all members of the cooperative for their kind support. We thank all members of Shiretoko Nature Foundation and South Shiretoko Brown bear Information Center for generous support. We also thank all people involved in the field research.
The English in this document has been checked by at least two professional editors, both native speakers of English. For a certificate, please see: http://www.textcheck.com/certificate/4GZ0WW
Funding
This study was conducted as part of the Kim-un Kamuy Project which was financially supported by AIR DO Co., Ltd. This study was financially supported also by Daikin Industries, Ltd. and The Mitsui & Co. Environment Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics statement
All procedures were conducted in accordance with the Guidelines for Animal Care and Use of Hokkaido University, and were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Graduate School of Veterinary Medicine, Hokkaido University (Permit Number: JU1106, JU1151, JU1152 and 15009).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirane, Y., Shimozuru, M., Yamanaka, M. et al. Sex-biased natal dispersal in Hokkaido brown bears revealed through mitochondrial DNA analysis. Eur J Wildl Res 64, 65 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-018-1222-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-018-1222-x