Abstract
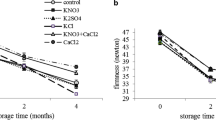
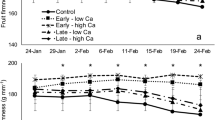
Improper management of nutrition and environmental stresses leads to a reduction in yield and an increase in some disorders, especially sunburn in apple. The present research was conducted with the aim of reducing or eliminating the disorder of sunburn using calcium and boron in apple (Malus × domestica Borkh. cv. ‘Golden Delicious’). The effect of different treatments of calcium and boron applied twice for reducing sunburn and the quantitative and qualitative characteristics of ‘Golden Delicious’ apples were investigated. The results showed that the first treatment (mid-May) had significant effects on the fruit characteristics compared with the control. The results also showed that foliar application of 1% calcium and 2 g/L boron in mid-May has a better effect on reducing sunburn and increasing the quality of ‘Golden Delicious’ apple, and it is suggested to use this in the orchards. Preventive foliar application of calcium and boron not only significantly reduces pre-harvest sunburn damage, but can also have a positive effect on the characteristics of the fruit after harvest.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Bakeer SM (2016) Effect of ammonium nitrate fertilizer and calcium chloride foliar sprayon fruit cracking and sunburn of Manfalouty pomegranate trees. Sci Hort 209:300–308
Cakmak I, Romheld V (1997) Boron deficiency-induced impairments of cellular functions in plants. Plant Soil 193:71–83
Cakmak I, Kurz H, Marschner H (1995) Short-term effects of boron, germanium and high light intensity on membrane permeability in boron deficient leaves of sunflower. Physiol Plant 95:11–18
Demmig-Adams B, Adams WW, Logan BA, Verhoven AS (1995) Xanthophyll cycledependent energy dissipation and flexible photosystem II efficiency in plants acclimated to light sress. Aust J Plant Physiol 22:249–260
Dugger WM (1983) Boron in plant metabolism. In: Lauchli A, Bieleski RL (eds) Encyclopedia of plant physiology. New Series, vol 15. Springer, Berlin, pp 626–650
Fageria MS, Dhaka RS, Chaudhary NL (1995) Determination of maturity standards of dates. Acta Hortic 23:426–432
Glenn DM, Prado E, Erez A, McFerson J, Puterka GJ (2002) A reflective processed-kaolin particle film affects fruit temperature, radiation reflection and sunburn in apple. J Am Soc Hort Sci 127:188–193
Hepaksoy S, Aksoy U, Can HZ (1998) Determination of relationship between fruit cracking and somephysiological responses, leaf characteristic and nutritional status of some pomegranate varieties. CIHEAM Opt Med 42:87–92
Khalifa RKM, Omania M, Hafez S, Abd-El H (2009) Influence of foliar spraying with boron and calcium on productivity, fruit quality, nutritional status and controlling of blossom end rot disease of Anna apple trees. World J Agr Sci 5:237–349
Loomis WD, Durst RW (1991) Boron and cell walls. Cur Top Plant Biochem Physiol 10:149–178
Loomis WD, Durst RW (1992) Chemistry and biology of boron. Biofactors 4:229–239
Lotze E, Hoffman EW (2014) Foliar application of calcium plus boron reduces the incidence of sunburn in ‘Golden Delicious’ apple. J Hort Sci Biotech 89:607–612
Lukaszewski KM, Blevins DG (1996) Root growth inhibition in boron-deficient or aluminium-stressed squash may be a result of impaired ascorbate metabolism. Plant Physiol 112:1135–1140
Ma F, Cheng L (2003) The sun-exposed peel of apple fruit has higher xanthophyllscycledependent thermal dissipation and antioxidants of the ascorbate-glutathione pathway than the shaded peel. Plant Sci 165:819–827
Marschner H (1995) Mineral Nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, San Diego, p 889
Merzlyak MN, Solovchenko AE (2002) Patterns of pigment changes in apple fruits during adaptation to high sunlight and sunscaled development. Plant Biochem Physiol 40:679–684
Muller P, Li XP, Niyogi K (2001) Nonphotochemical quenching. A response to excess light energy. Plant Physiol 125:1558–1566
Ritenour MA, Kochhar S, Schrader L, Hsu T, Ku M (2001) Characterization of heat shock protein expression in apple peel under field and laboratory conditions. J Am Soc Hort Sci 126:564–570
Schrader L, Zhang J, Sun J (2003) Envirnomental stresses that cause sunburn of apple. Acta Hort 618:397–405
Schrader LE, Kahn C, Elfving DC (2009) Sunburn browning decreases at-harvest internal fruit quality of apples (Malus domestica Borkh.). Int J Fruit Sci 9:425–437
Shelp BJ (1993) Physiology and biochemistry of boron in plants. In: Gupta UC (ed) Boron and its role in crop protection. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 53–85
Stanley D (1998) Particle films: a new kind of plant protectant. Agr Res 46:16–19
Watkins R, Smith RA (1982) IBPGR descriptor list for apple (Malus). Committee on disease resistance breeding and use of genebanks. C.E.C. Secretariat, Brussels, p 35
Westwood MN (1978) Temperate-zone pomology. WH Freeman, San Francisco, p 435 (Williams IH, Martin AP and White RP)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. Khadivi and A. Hosseini conducted the experiments and collected the data; A. Khadivi analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. Both authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A. Khadivi and A.-S. Hosseini declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
For this study, we acquired permission to study the fruit species issued by the Agricultural and Natural Resources Ministry of Iran. The either cultivated or wild-growing plants sampled comply with relevant institutional, national, and international guidelines and domestic legislation of Iran.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khadivi, A., Hosseini, AS. Effect of Calcium and Boron in Reducing the Incidence of Sunburn in Apple (Malus × domestica Borkh. cv. ‘Golden Delicious’). Applied Fruit Science 66, 781–786 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10341-024-01067-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10341-024-01067-y