Abstract
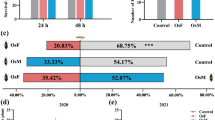
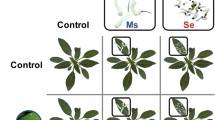
The invasive stink bug Halyomorpha halys is established in many European and American agro-ecosystems, where it causes severe crop losses. Potential control measures might include enhancement of plant defences. When attacked by herbivorous insects that oviposit on it, the plant may respond by priming direct defences, which might affect the development of future brood. Halyomorpha halys attacks numerous plant species in the invaded areas. Here, we investigated whether Vicia faba plants challenged by H. halys females can impair the development of its offspring through the activation of induced direct defences. We measured the weight and dimension of nymphs that developed on oviposition-experienced plants after 7 and 17 days from hatching. Nymphs that developed on oviposition-experienced plants weighed less compared to those that developed either on control plants or on plants solely subjected to H. halys feeding, and third instars showed shorter dimensions (tibia length). In addition, when oviposition-experienced plants were attacked by nymphs, higher and more rapid expression of two jasmonic acid-dependent genes (cysteine proteinase inhibitor gene and NAI1) was detected, possibly due to a mechanism of priming. Increased expression of the salicylic acid-responsive PR1 gene was also detected in egg-experienced plants, although the response was delayed compared to JA-dependent genes. Our results suggest that V. faba plants recognize H. halys oviposition as a warning signal and pre-activate defences against future nymphal herbivory.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali M, Sugimoto K, Ramadan A, Arimura G (2013) Memory of plant communications for priming anti-herbivore responses. Sci Rep 3:1872
Austel N, Eilers EJ, Meiners T, Hilker M (2016) Elm leaves ‘warned’ by insect egg deposition reduce survival of hatching larvae by a shift in their quantitative leaf metabolite pattern. Plant Cell Environ 39:366–376
Bandoly M, Hilker M, Steppuhn A (2015) Oviposition by Spodoptera exigua on Nicotiana attenuata primes induced plant defence against larval herbivory. Plant J 83:661–672
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B 57:289–300
Beyaert I, Köpke D, Stiller J, Hammerbacher A, Yoneya K, Schmidt A, Gershenzon J, Hilker M (2012) Can insect egg deposition ‘warn’a plant of future feeding damage by herbivorous larvae? Proc R Soc Lond B 279:101–108
Büchel K, McDowell E, Nelson W, Descour A, Gershenzon J, Hilker M, Soderlund C, Gang DR, Fenning T, Meiners T (2012) An elm EST database for identifying leaf beetle egg-induced defense genes. BMC Genom 13:242
Chen MS (2008) Inducible direct plant defense against insect herbivores: a review. Insect Sci 15:101–114
Cheng Y, Zhang H, Yao J, Wang X, Xu J, Han Q, Wei G, Huang L, Kang Z (2012) Characterization of non-host resistance in broad bean to the wheat stripe rust pathogen. BMC Plant Biol 12:96
Chiappini E, Salerno G, Berzolla A, Iacovone A, Reguzzi MC, Conti E (2012) Role of volatile semiochemicals in host location by the egg parasitoid Anagrus breviphragma. Entomol Exp Appl 144:311–316
Colazza S, Fucarino A, Peri E, Salerno G, Conti E, Bin F (2004) Insect oviposition induces volatile emission in herbaceous plants that attracts egg parasitoids. J Exp Biol 207:47–53
Conrath U (2011) Molecular aspects of defence priming. Trends Plant Sci 16:524–531
Conrath U, Beckers GJ, Langenbach CJ, Jaskiewicz MR (2015) Priming for enhanced defense. Annu Rev Phytopathol 53:97–119
Conti E, Colazza S (2012) Chemical ecology of egg parasitoids associated with true bugs. Psyche (Camb Mass) 2012:651015
Conti E, Jones WA, Bin F, Vinson SB (1996) Physical and chemical factors involved in host recognition behavior of Anaphes iole Girault, an egg parasitoid of Lygus hesperus Knight (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae; Heteroptera: Miridae). Biol Control 7:10–16
Conti E, Jones WA, Bin F, Vinson SB (1997) Oviposition behavior of Anaphes iole, an egg parasitoid of Lygus hesperus (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae; Heteroptera: Miridae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 90:91–101
Conti E, Zadra C, Salerno G, Leombruni B, Volpe D, Frati F, Marucchini C, Bin F (2008) Changes in the volatile profile of Brassica oleracea due to feeding and oviposition by Murgantia histrionica (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Eur J Entomol 105:839–847
Conti E, Salerno G, Leombruni B, Frati F, Bin F (2010) Short-range allelochemicals from a plant-herbivore association: a singular case of oviposition-induced synomone for an egg parasitoid. J Exp Biol 213:3911–3919
Desurmont GA, Donoghue MJ, Clement WL, Agrawal AA (2011) Evolutionary history predicts plant defense against an invasive pest. P Natl Acad Sci 108:7070–7074
Desurmont GA, Harvey J, van Dam NM, Cristescu SM, Schiestl FP, Cozzolino S, Anderson P, Larsson MC, Kindlmann P, Danner H (2014) Alien interference: disruption of infochemical networks by invasive insect herbivores. Plant Cell Environ 37:1854–1865
Dicke M, van Poecke RM (2002) Signalling in plant–insect interactions: signal transduction in direct and indirect plant defence. In: Scheel D, Wasternack C (eds) Plant signal transduction, vol 38. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 289–316
Digilio MC, Corrado G, Sasso R, Coppola V, Iodice L, Pasquariello M, Bossi S, Maffei ME, Coppola M, Pennacchio F, Rao R, Guerrieri E (2010) Molecular and chemical mechanisms involved in aphid resistance in cultivated tomato. New Phytol 187:1089–1101
Erb M, Meldau S, Howe GA (2012) Role of phytohormones in insect-specific plant reactions. Trends Plant Sci 17:250–259
Farmer E, Ryan C (1990) Interplant communication: airborne methyl jasmonate induces synthesis of proteinase inhibitors in plant leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:7713–7716
Geiselhardt S, Yoneya K, Blenn B, Drechsler N, Gershenzon J, Kunze R, Hilker M (2013) Egg laying of cabbage white butterfly (Pieris brassicae) on Arabidopsis thaliana affects subsequent performance of the larvae. PLoS ONE 8:e59661
Giacometti R, Zavala JA (2016) Soybean response to pest attack. In: Fletcher B (ed) Soybeans: cultivation, nutritional properties and effects on health. Nova Science Publishers, New York, pp 35–62
Giacometti R, Barneto J, Barriga LG, Sardoy PM, Balestrasse K, Andrade AM, Pagano EA, Alemano SG, Zavala JA (2016) Early perception of stink bug damage in developing seeds of field-grown soybean induces chemical defences and reduces bug attack. Pest Manag Sci 72:1585–1594
Goni R, García P, Foissac S (2009) The qPCR data statistical analysis. Integromics White Paper 1–9
Gutierrez N, Giménez MJ, Palomino C, Avila CM (2011) Assessment of candidate reference genes for expression studies in Vicia faba L. by real-time quantitative PCR. Mol Breed 28:13–24
Heil M (2014) Herbivore-induced plant volatiles: targets, perception and unanswered questions. New Phytol 204:297–306
Hellemans J, Vandesompele J (2011) Quantitative PCR data analysis–unlocking the secret to successful results. In: Kennedy S, Oswald N (eds) PCR troubleshooting and optimization. The essential guide. Caister Academic Press, Norfolk, UK, pp 1–13
Hilker M, Fatouros NE (2015) Plant responses to insect egg deposition. Annu Rev Entomol 60:493–515
Hilker M, Fatouros NE (2016) Resisting the onset of herbivore attack: plants perceive and respond to insect eggs. Curr Opin Plant Biol 32:9–16
Hilker M, Meiners T (2008) Chemoecology of insect eggs and egg deposition. Blackwell, Berlin
Humann J, Jung S, Zheng P, Cheng C-H, Lee T, Frank M, McGaughey D, Scott K, Yu J, Ficklin S, Sanad M, Hough H, Coyne C, McGee R, Main D (2016) Cool Season Food Legume Genome Database: An up-to-date resource enabling genetics, genomics and breeding research in pea, lentil, faba bean and chickpea. In: Proceedings of the international plant and animal genome conference, January 2016, San Diego, CA, USA
Kim J, Tooker JF, Luthe DS, De Moraes CM, Felton GW (2012) Insect eggs can enhance wound response in plants: a study system of tomato Solanum lycopersicum L. and Helicoverpa zea Boddie. PLoS ONE 7:e37420
Kroes A, van Loon JJ, Dicke M (2014) Density-dependent interference of aphids with caterpillar-induced defenses in Arabidopsis: involvement of phytohormones and transcription factors. Plant Cell Physiol 56:98–106
Leon-Reyes A, Spoel SH, De Lange ES, Abe H, Kobayashi M, Tsuda S, Millenaar FF, Welschen RA, Ritsema T, Pieterse CM (2009) Ethylene modulates the role of NONEXPRESSOR OF PATHOGENESIS-RELATED GENES1 in cross talk between salicylate and jasmonate signaling. Plant Physiol 149:1797–1809
Leskey TC, Short BD, Butler BR, Wright SE (2012) Impact of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål), in mid-Atlantic tree fruit orchards in the United States: case studies of commercial management. Psyche (Camb Mass) 2012:535062
Martorana L, Foti MC, Rondoni G, Conti E, Colazza S, Peri E (2017) An invasive insect herbivore disrupts plant volatile-mediated tritrophic signalling. J Pest Sci 90:1079–1085
Matsushima R, Fukao Y, Nishimura M, Hara-Nishimura I (2004) NAI1 gene encodes a basic-helix-loop-helix-type putative transcription factor that regulates the formation of an endoplasmic reticulum–derived structure, the ER body. Plant Cell 16:1536–1549
Moraes MCB, Laumann R, Sujii ER, Pires C, Borges M (2005) Induced volatiles in soybean and pigeon pea plants artificially infested with the neotropical brown stink bug, Euschistus heros, and their effect on the egg parasitoid, Telenomus podisi. Entomol Exp Appl 115:227–237
Moraes MC, Pareja M, Laumann RA, Hoffmann-Campo CB, Borges M (2008) Response of the parasitoid Telenomus podisi to induced volatiles from soybean damaged by stink bug herbivory and oviposition. J Plant Interact 3:111–118
Ocaña S, Seoane P, Bautista R, Palomino C, Claros GM, Torres AM, Madrid E (2015) Large-scale transcriptome analysis in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) under Ascochyta fabae infection. PLoS ONE 10:e0135143
Pashalidou FG, Lucas-Barbosa D, van Loon JJ, Dicke M, Fatouros NE (2013) Phenotypic plasticity of plant response to herbivore eggs: effects on resistance to caterpillars and plant development. Ecology 94:702–713
Peiffer M, Felton GW (2014) Insights into the saliva of the brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). PLoS ONE 9:e88483
Peterson JA, Ode PJ, Oliveira-Hofman C, Harwood JD (2016) Integration of plant defense traits with biological control of arthropod pests: challenges and opportunities. Front Plant Sci 7:1794
Pinheiro J, Bates D, DebRoy S, Sarkar D, the R Development Core Team (2012) nlme: linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R package version 3.1-104
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Rasband W (1997) ImageJ. US National Institutes of Health, Bethesda
Reymond P (2013) Perception, signaling and molecular basis of oviposition-mediated plant responses. Planta 238:247–258
Reymond P, Farmer EE (1998) Jasmonate and salicylate as global signals for defense gene expression. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:404–411
Rondoni G, Onofri A, Ricci C (2012) Differential susceptibility in a specialised aphidophagous ladybird, Platynaspis luteorubra (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), facing intraguild predation by exotic and native generalist predators. Biocontrol Sci Technol 22:1334–1350
Rondoni G, Bertoldi V, Malek R, Foti MC, Peri E, Maistrello L, Haye T, Conti E (2017a) Native egg parasitoids recorded from the invasive Halyomorpha halys successfully exploit volatiles emitted by the plant–herbivore complex. J Pest Sci 80:1087–1095
Rondoni G, Ielo F, Ricci C, Conti E (2017b) Behavioural and physiological responses to prey-related cues reflect higher competitiveness of invasive vs. native ladybirds. Sci Rep 7:3716
Salerno G, De Santis F, Iacovone A, Bin F, Conti E (2013) Short-range cues mediate parasitoid searching behavior on maize: the role of oviposition-induced plant synomones. Biol Control 64:247–254
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Smith JR, Hesler SP, Loeb GM (2014) Potential impact of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) on grape production in the Finger Lakes Region of New York. J Entomol Sci 49:290–303
Staines K, Batra A, Mwangi W, Maier HJ, Van Borm S, Young JR, Fife M, Butter C (2016) A versatile panel of reference gene assays for the measurement of chicken mRNA by quantitative PCR. PLoS ONE 11:e0160173
Terra WR, Ferreira C (1994) Insect digestive enzymes: properties, compartmentalization and function. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B Comp Biochem 109:1–62
Timbó RV, Hermes-Lima M, Silva LP, Mehta A, Moraes MCB, Paula DP (2014) Biochemical aspects of the soybean response to herbivory injury by the brown stink bug Euschistus heros (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). PLoS ONE 9:e109735
Vet LEM, Dicke M (1992) Ecology of infochemical use by natural enemies in a tritrophic context. Annu Rev Entomol 37:141–172
War AR, Paulraj MG, Ahmad T, Buhroo AA, Hussain B, Ignacimuthu S, Sharma HC (2012) Mechanisms of plant defense against insect herbivores. Plant Signal Behav 7:1306–1320
Willems E, Leyns L, Vandesompele J (2008) Standardization of real-time PCR gene expression data from independent biological replicates. Anal Biochem 379:127–129
Woodard AM, Ervin GN, Marsico TD (2012) Host plant defense signaling in response to a coevolved herbivore combats introduced herbivore attack. Ecol Evol 2:1056–1064
Zheng S-J, Dicke M (2008) Ecological genomics of plant-insect interactions: from gene to community. Plant Physiol 146:812–817
Zhu-Salzman K, Zeng R (2015) Insect response to plant defensive protease inhibitors. Annu Rev Entomol 60:233–252
Zuur AF, Ieno EN, Walker NJ, Saveliev AA, Smith GM (2009) Mixed effects models and extensions in ecology with R. Springer, New York
Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Research and Innovation Staff Exchange (RISE) H2020-MSCA-RISE-2015 of the European Union with the project Impact of invasive alien true bug species in native trophic webs—INVASIoN (GA 690952) and by Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Perugia Project 2015.0349.021. GR wishes to thank Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Perugia for personal funding. The authors are grateful to Lara Maistrello, Elena Costi (University of Modena and Reggio Emilia) and Giacomo Vaccari (Consorzio Fitosanitario Provinciale di Modena) for providing field-collected stink bugs, to Andrea Luchetti, Luciana Bartoli, Daniela Fortini and Cesare Dentini for maintaining the stink bug and egg parasitoid cultures and for helping in field collection, and to Luca Bonciarelli for technical assistance in the laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals (vertebrates) performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by T. Haye.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rondoni, G., Bertoldi, V., Malek, R. et al. Vicia faba plants respond to oviposition by invasive Halyomorpha halys activating direct defences against offspring. J Pest Sci 91, 671–679 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-018-0955-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-018-0955-3