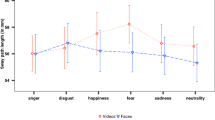
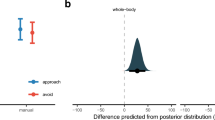
Abstract
Embodiment theories emphasize the role played by sensory and motor processes in psychological states, such as social information processing. Motivated by this idea, we examined how whole-body postural behaviors couple to social affective cues, viz., pictures of smiling and angry faces. We adopted a Simon-like paradigm, whereby healthy female volunteers were asked to select and initiate a forward or backward step on a force plate in response to the gender of the poser (male/female), regardless of emotion. Detailed analysis of the spatiotemporal unfolding of the body center of pressure during the steps revealed that task-irrelevant emotion had no effect on the initiation times of the steps, i.e., there was no evidence of an affective Simon effect. An unexpected finding was that steps were initiated relatively slow in response to female angry faces. This Stroop-like effect suggests that postural behavior is influenced by whether certain stimulus features match or mismatch.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Note that in contrast to the previous analysis, step direction has now become the between-subject factor due to the way we regrouped the data.
References
Adams J (2010) Embodied cognition. Phenomenol Cogn Sci 9:619–628
Adams RB, Ambady N, Macrae CN, Kleck RE (2006) Emotional expressions forecast approach-avoidance behavior. Motiv Emot 30:179–188
Alexopoulos T, Ric F (2007) The evaluation-behavior link: direct and beyond valence. J Exp Soc Psychol 43:1010–1016
Barratt D, Bundesen C (2012) Attentional capture by emotional faces is contingent on attentional control settings. Cognit Emot 26:1223–1237
Barsalou LW, Niedenthal PM, Barbey A, Ruppert J (2003) Social embodiment. In: Ross B (ed) The psychology of learning and motivation (Vol 43). Academic Press, San Diego, pp 43–92
Becker DV, Kenrick DT, Neuberg SL, Blackwell KC, Smith DM (2007) The confounded nature of angry men and happy women. J Exp Soc Psychol 92:179–190
Carlson RA, Avraamides MN, Cary M, Strasberg S (2007) What do hands externalize in simple arithmetic? J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn 33:747–756
Carver CS, Harmon-Jones E (2009) Anger is an approach-related affect: evidence and implications. Psychol Bull 135:183–204
Chen M, Bargh JA (1999) Consequences of automatic evaluation: immediate behavioral predispositions to approach or avoid the stimulus. Pers Soc Psychol Bull 25:215–224
Dru V, Cretenet J (2008) Influence of unilateral behaviors on the judgment of valenced stimuli. Cortex 44:717–727
Duscherer K, Holender D, Molenaar E (2008) Revisiting the affective Simon effect. Cogn Emot 22:193–217
Eder AB, Klauer KC (2009) A common-coding account of the bidirectional evaluation-behavior link. J Exp Psychol Gen 138:218–235
Gangopadhyay N (2011) The extended mind: born to be wild? A lesson from action-understanding. Phenomenol Cogn Sci 10:377–397
Gélat T, Coudrat L, Le Pellec A (2011) Gait initiation is affected during emotional conflict. Neurosci Lett 497:64–67
Glenberg A, Kaschak M (2002) Grounding language in action. Psychon Bull Rev 9:558–565
Gold JM, Barker JD, Barr S, Bittner JL, Bromfield WD, Chu N, Ra Goode, Lee D, Simmons M, Srinath A (2013) The efficiency of dynamic and static facial expression recognition. J Vis 13:1–12
Harmon-Jones E, Gable PA, Price TF (2011) Leaning embodies desire: evidence that leaning forward increases relative left frontal cortical activation to appetitive stimuli. Biol Psychol 87:311–313
Heuer K, Rinck M, Becker ES (2007) Avoidance of emotional facial expressions in social anxiety: the Approach-Avoidance Task. Behav Res Ther 45:2990–3001
Hillman CH, Rosengren KS, Smith DP (2004) Emotion and motivated behavior: postural adjustments to affective picture viewing. Biol Psychol 66:51–62
Koch S, Holland RW, Hengstler M, Van Knippenberg A (2009) Body locomotion as regulatory process. Psychol Sci 20:549–550
Markman AB, Brendl CM (2005) Constraining theories of embodied cognition. Psychol Sci 16:6–10
Marsh AA, Ambady N, Kleck RE (2005) The effects of fear and anger facial expressions on approach- and avoidance-related behaviors. Emotion 5:119–124
Naugle KM, Hass CJ, Joyner J, Coombes SA, Janelle CM (2011) Emotional state affects the initiation of forward gait. Emotion 11:267–277
Naugle KM, Hass CJ, Bowers D, Janelle CM (2012) Emotional state affects gait initiation in individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 12:207–219
Niedenthal PM (2007) Embodying emotion. Science 316:1002–1005
Niedenthal PM, Barsalou LW, Winkielman P, Krauth-Gruber S, Ric F (2005) Embodiment in attitudes, social perception, and emotion. Pers Soc Psychol Rev 9:184–211
Price TF, Peterson CK, Harmon-Jones E (2012) The emotive neuroscience of embodiment. Motiv Emot 36:27–37
Roelofs K, Minelli A, Mars RB, van Peer J, Toni I (2009a) On the neural control of social emotional behavior. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci 4:50–58
Roelofs K, van Peer J, Berretty E, de Jong P, Spinhoven P, Elzinga BM (2009b) Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis responsiveness is associated with increased avoidance behavior in social phobia. Biol Psychiat 65:336–343
Roelofs K, Hagenaars M, Stins JF (2010a) Facing freeze: social threat induces bodily freeze in humans. Psychol Sci 21:1575–1581
Roelofs K, Putman P, Schouten S, Lange W-G, Volman I, Rinck M (2010b) Gaze direction differentially affects avoidance tendencies to happy and angry faces in socially anxious individuals. Behav Res Ther 48:290–294
Seidel E-M, Habel U, Kirschner M, Gur RC, Derntl B (2010) The impact of facial emotional expressions on behavioral tendencies in women and men. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 36:500–507
Stins JF, Beek PJ (2011) Organization of voluntary stepping in response to emotion inducing pictures. Gait Posture 34:164–168
Stins JF, Roelofs K, Villan J, Kooijman K, Hagenaars MA, Beek PJ (2011) Walk to me when I smile, step back when I’m angry: emotional faces modulate whole-body approach-avoidance behaviors. Exp Brain Res 212:603–611
Van Peer JM, Rotteveel M, Spinhoven P, Tollenaar MS, Roelofs K (2010) Affect-congruent approach and withdrawal movements of happy and angry faces facilitate affective categorisation. Cogn Emot 24:863–875
Volman I, Roelofs K, Koch S, Verhagen L, Toni I (2011) Anterior prefrontal cortex inhibition impairs control over social emotional actions. Curr Biol 21:1766–1770
Von Borries AKL, Volman I, De Bruijn ERA, Bulten BH, Verkes RJ, Roelofs K (2012) Psychopaths lack the automatic avoidance of social threat: relation to instrumental aggression. Psychiat Res 200:716–766
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by VIDI Grant (#452-07-008) from the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO) awarded to K.R.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Special Section on “Embodied Social Cognition,” guest-edited by Fernando Marmolejo Ramos and Amedeo Dangiulli.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stins, J.F., Lobel, A., Roelofs, K. et al. Social embodiment in directional stepping behavior. Cogn Process 15, 245–252 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10339-013-0593-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10339-013-0593-x