Abstract
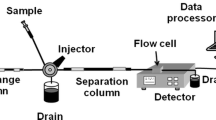
This method demonstrated an ion chromatography (IC) technique with suppressed conductance for the determination of residual trimethylamine hydrochloride (TMAC) in the synthesis of 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (CHPTAC). The key point is the silicon-based C18 reversed-phase liquid chromatography column coupled with ion suppression chromatography for analysis. Due to the matrix of CHPTAC having a significant effect on the accuracy of ion chromatography (IC) determination, a standard addition method was used to calculate the influence of the matrix in CHPTAC samples on the accuracy of detection substances. The detection limit of this method was 0.1 μg mL−1 (signal to noise, S/N = 3), and the recovery of standard addition of TMAC was in the range 98.0–102.0%. The relative standard deviation (RSD) ranged from 0.8 to 1.26%, which showed that this optimized method has a good measurement precision and demonstrates satisfactory reliabilities. The experimental results showed that using a C18 reversed-phase chromatographic column can significantly reduce the problem of IC being susceptible to matrix effects and significantly improve the detection sensitivity of IC on the detection of TMAC in CHPTAC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang C, Wei YU (2005) Study on synthesis of cationic etherifying agent CHPTAC. Shandong Chem Ind 34:3–10. https://doi.org/10.19319/j.cnki.issn.1008-021x
Pal S, Mal D, Singh RP (2005) Cationic starch: an effective flocculating agent. Carbohyd Polym 59(4):417–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2004.06.047
Yang YQ, Li ZZ (2006) Syntheses and properties of cationic lignin surfactant. J Nanjing For Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 30(6):47–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-2076-2
Butrim SM, Bil’Dyukevich TD, Butrim NS, Yurkshtovich TL (2020) Hydrogels based on cross-linked cationic cellulose derivatives. Chem Nat Compd 56(6):1106–1110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-020-03237-2
Marestin C, Mercier R (2010) Microwave-assisted synthesis of polymers in aqueous media. RSC Green Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/9781849730990-00145
Cheng H, Xu HJ, Fan L, Chen XY (2018) Improved synthesis and properties of N-(3-octadecyl amine-2-hydroxyl) propyl trimethyl ammonium chloride. Tenside Surfact Det 55(3):238–245. https://doi.org/10.3139/113.110564
Yang JZ, Guo NN (2007) Study on synthesis of 3-chloro-2- hydroxyl-propyl triethylammonium chloride. J Hunan Uni of Arts and Sci (Nat Sci Edi) 19(04):14–16. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-6164.2007.04.019
Yang JZ, Lin L, Tang Q (2003) The study on synthesis of cationic etherification agent “CHPTAC” under aqueous process. Fine Chem Intermed 33(006):20–22. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1009-9212.2003.06.006
Tao ZY, Chai XS, Wu SB (2011) Determination of epichlorohydrin and 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol in synthesis of cationic etherifying reagent by headspace gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1218(37):6518–6521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.07.015
Liu FF, Sun J, Sun HL (2002) Gas chromatographic determination of micro-organic impurities in 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride. Chin J Chromatogr A 20(4):362–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-002-0022-7
Liu SH, Zhong ZH, Han K, Chen C, Zhang L, Gao QS, Liu W, Hu QZ. A method for detecting biquaternary ammonium salt in cationic etherifying agent and its application. CN Patent Application, 112147259 A
He LP, He JL (2012) Study on crystallization process of cationic etherifying agent (CHPTA). Fine Chem Intermed 42(002):49–59. https://doi.org/10.19342/j.cnki.issn.1009-9212.2012.02.013
Ol T, Tsukamoto T, Arai H, Kakihana H (1988) Boron isotope separation by ion-exchange chromatography using an anion-exchange resin in halide forms. J Chromatogr A 450(3):343–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(01)83589-5
Fritz JS (1987) Ion chromatography. Am Chem Soc 59(4):335A-344A. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00131a737
Jackson PE (2001) Determination of inorganic ions in drinking water by ion chromatography. Trac Trend in Anal Chem 20(6):320–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-9936(01)00070-X
Conboy JJ, Henion JD, Martin MW, Zweigenbaum JA (1990) Ion chromatography/mass spectrometry for the determination of organic ammonium and sulfate compounds. Analy Chem 62(8):800–807. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00207a006
Yamamoto S, Miyagawa E (1999) Retention behavior of very large biomolecules in ion-exchange chromatography. J Chromatogr A 852(1):25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(99)00594-4
Bhandari D, Bowman BA, Patel AB, Chambers DM, De Jesus VR, Blount BC (2018) UPLC-ESI-MS/MS method for the quantitative measurement of aliphatic diamines, trimethylamine N-oxide, and β-methylamino-l-alanine in human urine. J Chromatogr B 1083:86–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.02.043
Yu H, Mou SF (2006) Effect of temperature on the retention of amino acids and carbohydrates in high-performance anion-exchange chromatography. J Chromatogra A 1118(1):118–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2005.12.051
Hong Y, Li R (2008) Effect of column temperature on the retention of inorganic anions and organic acids in non-suppressed anion-exchange IC. Chromatographia 68(s7–8):611–616. https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-008-0774-4
Yarita T, Aoyagi Y, Otake T (2015) Evaluation of the impact of matrix effect on quantification of pesticides in foods by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry using isotope-labeled internal standards. J Chromatogra A 1396:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.03.075
Ito S, Tsukada K (2002) Matrix effect and correction by standard addition in quantitative liquid chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins. J Chromatogra A 943(1):39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(01)01429-7
Wilson NS, Gilroy J, Dolan JW, Snyder LR (2004) Column selectivity in reversed-phase liquid chromatography: VI. Columns with embedded or end-capping polar groups. J Chromatogra A 1026(1–2):91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2003.11.041
Gregor HP, Belle J, Marcus RA (1955) Studies on ion-exchange resins. XIII. Selectivity coefficients of quaternary base anion exchange resins toward univalent anions. J Am Chem Soc 77(10):2713–2719. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01615a011
Funding
The authors thank the Shandong Natural Science Foundation (ZR2013BQ024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Investigation, writing—original draft: KH; software, validation: ZZ; methodology, supervision: LZ, QH, WJ; review and editing, project administration: SL.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, K., Zhong, Z., Zhang, L. et al. C18 Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography Column Coupled with Ion Chromatography: a Method for the Determination of Trimethylamine Hydrochloride Residues in Cationic Etherifying Agent. Chromatographia 85, 83–89 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-021-04117-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-021-04117-9