Abstract
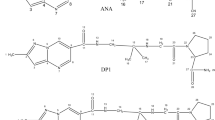
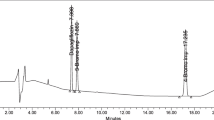
A novel ultra-performance liquid chromatography with UV detector technique was established for simultaneous determination of two antidiabetic drugs, dapagliflozin (DAPA) and metformin (MET), followed by a stress degradation study. Main degradation product was chromatographically separated and precisely characterized via LC-MS/MS. Chromatographic separation done on a Symmetry® Acclaim™ RSLC 120 C18 column (100 mm, 2.1 mm, 2.2 µm), column temperature was maintained at 60 °C. Mobile phase was a mixture of potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer, pH (3.5)—acetonitrile (50:50, v/v) at flow rate of 0.4 mL/min. The method has displayed an adequate detection at concentration ranges of 1–50 µg/mL for dapagliflozin propanediol monohydrate and 0.5–100 µg/mL for metformin hydrochloride. DAPA was then exposed to different stress conditions include alkaline, acidic, oxidative and ultraviolet light. A study of the degradation kinetics in alkaline medium for DAPA has proved that the degradation follows a pseudo-first-order reaction. The proposed method was effectively applied for the analysis of laboratory prepared mixtures as well as a combined pharmaceutical formulation with 1:200 ratio of DAPA: MET. No significant difference was found regarding accuracy and precision upon statistical comparison between the obtained results and those of the reported method. Validation was conducted in compliance with the ICH guidelines proving that method is selective, linear, precise and accurate. The simplicity and sensitivity of this method allows its use in the quality control tests of the two cited drugs.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rojas L, Gomes M (2013) Diabetol Metab Syndr 5:1–15
Ahmed M (2010) Int J Diabetes Mellitus 2:125–126
Jani B, Shah K, Kapupara P (2015) Int J Res Dev Pharm L Sci 4:1569–1576
Jani B, Shah V, Kapupara P (2015) J Bioequivalence Stud 1:1–7
Yunoos M, Sankar G (2015) Asian J Pharm Clin Res 8:320–326
Shyamala B, Nidhi M, Kavitha, Pooja, Sharma J (2015) Am J Biol Pharm Res 2:109–113
Deepan T (2017) Eur J Appl Sci 9:189–199
Chitra K, Eswaraiah C, Rao M (2015) J Chem Pharm Res 7:45–49
Sanagapati M, Dhanalakshmi K, Reddy G, Sreenivasa S (2014) J Adv Pharm Educ Res 4:350–353
Manasa S, Dhanalakshmi K, Reddy G, Kavitha B (2014) Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 27:270–272
Manasa S, Dhanalakshmi K, Nagarjunareddy G, Sreenivasa S (2014) IJPSR 5:5394–5397
Sanagapati M, Dhanalakshmi K, Reddy G, Sreenivasa S (2014) Int J Pharm Sci Drug Res 6:250–252
Aubry H, Gu R, Magnier L, Morgan X, Xu M, Tirmenstein B, Wang Y, Deng J, Cai P, Couerbe, Arnold M (2010) Bioanalysis 2:2001–2009
Bhushan R, Gupta D, Jain A (2006) J Planar Chromatogr Mod TLC 19:288–296
Sengupta P, Bhaumik U, Ghosh A, Sarkar A, Chromatographia, 2009, 69, 1243–1250
Elbagary R, Elkady E, Ayoub B (2011) Int J Biomed Sci 7:201–208
Wang M, Miksa I (2007) J Chromatogr B: Biomed Sci Appl 856:318–327
Georgita C, Albu F, David V, Medvedovici A (2007) J Chromatogr B 854:211–218
Ali M, Rafiuddin S, Ghori M, Khatri A, Chromatographia, 2008, 67, 517–525
Lai E, Feng S (2006) J Chromatogr B 843:94–99
Elbagary R, Elkady E, Ayoub B, Talanta, 2011, 85, 673–680
Zhang L, Tian Y, Zhang Z, Chen Y (2007) J Chromatogr B 854:91–98
Ali H, Duraidi I, Saket M, Abu-Nameh E (2009) J AOAC Int 92:119–124
Elbagary R, Elkady E, Ayoub B (2013) Eur J Chem 4:360–365
Ghassempour M, Ahmadi S, Ebrahimi, Aboul-Enein H, Chromatographia, 2006, 64, 101–104
Elbagary R, Elkady E, Ayoub B (2011) Int J Biomed Sci 7:62–69
Tahara K, Yonemoto A, Yoshiyama Y, Nakamura T, Aizawa M, Fujita Y, Nishikawa T (2006) Biomed Chromatogr 20:1200–1205
Pawar S, Meshram G, Phadke M, Chromatographia, 2008, 68, 1063–1066
Elbagary R, Elkady E, Ayoub B (2013) Eur J Chem 4:444–449
Mowaka S,., Ayoub B, Pharmazie, 2017, 72, 67–72
Mowaka S, Elkady E, Elmazar M, Ayoub B, Microchem J, 2017, 130, 360–365
Ayoub B, Abdel-Aziz O, Pharmazie, 2016, 71, 683–690
Ayoub B (2015) RSC Adv 5:95703–95709
Mowaka S, Mohamed D (2015) RSC Adv 5:60467–60481
Miller JN, Miller JC, Statistics and chemometrics for analytical chemistry, 5th edn, Pearson Education Limited, Harlow, 2005
ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guideline, Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology, Q2 (R1), Current step 4 version, Parent guidelines on Methodology, 1996, incorporated in November 2005
ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guidelines, Q1A (R2) Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products, 2003
Funding
This study was self-funded, no fund is received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest of any kind.
Research involving human or animal participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaghary, W.A., Mowaka, S. & Hendy, M.S. Kinetic Degradation Study of Dapagliflozin Coupled with UHPLC Separation in the Presence of Major Degradation Product and Metformin. Chromatographia 82, 777–789 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-019-03702-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-019-03702-3