Abstract
Objective
To clarify the relationship between myelin water fraction (MWF) and R1⋅R2* and to develop a method to calculate MWF directly from parameters derived from QPM, i.e., MWF converted from QPM (MWFQPM).
Materials and methods
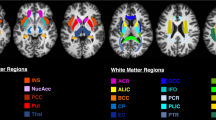
Subjects were 12 healthy volunteers. On a 3 T MR scanner, dataset was acquired using spoiled gradient-echo sequence for QPM. MWF and R1⋅R2* maps were derived from the multi-gradient-echo (mGRE) dataset. Volume-of-interest (VOI) analysis using the JHU-white matter (WM) atlas was performed. All the data in the 48 WM regions measured VOI were plotted, and quadratic polynomial approximations of each region were derived from the relationship between R1·R2* and the two-pool model-MWF. The R1·R2* map was converted to MWFQPM map. MWF atlas template was generated using converted to MWF from R1·R2* per WM region.
Results
The mean MWF and R1·R2* values for the 48 WM regions were 11.96 ± 6.63%, and 19.94 ± 4.59 s−2, respectively. A non-linear relationship in 48 regions of the WM between MWF and R1·R2* values was observed by quadratic polynomial approximation (R2 ≥ 0.963, P < 0.0001).
Discussion
MWFQPM map improved image quality compared to the mGRE-MWF map. Myelin water atlas template derived from MWFQPM may be generated with combined multiple WM regions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Laule C, Vavasour IM, Moore GR, Oger J, Li DK, Paty DW, MacKay AL (2004) Water content and myelin water fraction in multiple sclerosis. A T2 relaxation study. J Neurol 251 (3):284–293.
MacKay A, Whittall K, Adler J, Li D, Paty D, Graeb D (1994) In vivo visualization of myelin water in brain by magnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med 31(6):673–677
Whittall KP, MacKay AL, Graeb DA, Nugent RA, Li DK, Paty DW (1997) In vivo measurement of T2 distributions and water contents in normal human brain. Magn Reson Med 37(1):34–43
Kolind SH, Madler B, Fischer S, Li DK, MacKay AL (2009) Myelin water imaging: Implementation and development at 3.0T and comparison to 1.5T measurements. Magn Reson Med 62 (1):106–115.
Oh J, Han ET, Pelletier D, Nelson SJ (2006) Measurement of in vivo multi-component T2 relaxation times for brain tissue using multi-slice T2 prep at 1.5 and 3 T. Magn Reson Imaging 24 (1):33–43.
Du YP, Chu R, Hwang D, Brown MS, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Singel D, Simon JH (2007) Fast multi-slice mapping of the myelin water fraction using multicompartment analysis of T2* decay at 3T: a preliminary postmortem study. Magn Reson Med 58(5):865–870
Lee J, Hyun JW, Lee J, Choi EJ, Shin HG, Min K, Nam Y, Kim HJ, Oh SH (2021) So You Want to Image Myelin Using MRI: An Overview and Practical Guide for Myelin Water Imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 53(2):360–373
Prasloski T, Rauscher A, MacKay AL, Hodgson M, Vavasour IM, Laule C, Madler B (2012) Rapid whole cerebrum myelin water imaging using a 3D-GRASE sequence. Neuroimage 63(1):533–539
Piredda GF, Hilbert T, Canales-Rodriguez EJ, Pizzolato M, von Deuster C, Meuli R, Pfeuffer J, Daducci A, Thiran JP, Kober T (2021) Fast and high-resolution myelin water imaging: Accelerating multi-echo GRASE with CAIPIRINHA. Magn Reson Med 85(1):209–222
Deoni SC, Rutt BK, Arun T, Pierpaoli C, Jones DK (2008) Gleaning multi-component T1 and T2 information from steady-state imaging data. Magn Reson Med 60(6):1372–1387
Girard OM, Prevost VH, Varma G, Cozzone PJ, Alsop DC, Duhamel G (2015) Magnetization transfer from inhomogeneously broadened lines (ihMT): Experimental optimization of saturation parameters for human brain imaging at 1.5 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 73 (6):2111–2121.
Hwang D, Kim DH, Du YP (2010) In vivo multi-slice mapping of myelin water content using T2* decay. Neuroimage 52(1):198–204
Lee H, Nam Y, Lee HJ, Hsu JJ, Henry RG, Kim DH (2018) Improved three-dimensional multi-echo gradient-echo based myelin water fraction mapping with phase related artifact correction. Neuroimage 169:1–10
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000) Voxel-based morphometry–the methods. Neuroimage 11(6 Pt 1):805–821
Lee H, Nam Y, Kim DH (2019) Echo time-range effects on gradient-echo based myelin water fraction mapping at 3T. Magn Reson Med 81(4):2799–2807
Alonso-Ortiz E, Levesque IR, Paquin R, Pike GB (2017) Field inhomogeneity correction for gradient-echo myelin water fraction imaging. Magn Reson Med 78(1):49–57
Warntjes JB, Leinhard OD, West J, Lundberg P (2008) Rapid magnetic resonance quantification on the brain: Optimization for clinical usage. Magn Reson Med 60(2):320–329
Taniguchi Y, Yokosawa S, Shirai T, Sato R, Amemiya T, Soutome Y, Bito Y, Ochi H (2022) Three-dimensional Multi-parameter Mapping of Relaxation Times and Susceptibility Using Partially RF-spoiled Gradient Echo. Magn Reson Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.2463/mrms.mp.2021-0045
Matsumoto Y, Harada M, Kanazawa Y, Taniguchi Y, Ono M, Bito Y (2022) Quantitative parameter mapping of contrast agent concentration and relaxivity and brain tumor extracellular pH. Sci Rep 12(1):2171
Amemiya T, Yokosawa S, Taniguchi Y, Sato R, Soutome Y, Ochi H, Shirai T (2022) Simultaneous Arterial and Venous Imaging Using 3D Quantitative Parameter Mapping. Magn Reson Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.2463/mrms.mp.2021-0170
Kanazawa Y, Harada M, Taniguchi Y, Hayashi H, Abe T, Otomo M, Matsumoto Y, Ono M, Ito K, Bito Y, Haga A (2022) Myelin-weighted imaging derived from quantitative parameter mapping. Eur J Radiol 156:110525
Brett M, Johnsrude IS, Owen AM (2002) The problem of functional localization in the human brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 3(3):243–249
Grabner G, Janke AL, Budge MM, Smith D, Pruessner J, Collins DL (2006) Symmetric atlasing and model based segmentation: an application to the hippocampus in older adults. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 9(Pt 2):58–66
Jenkinson M, Smith S (2001) A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Med Image Anal 5(2):143–156
Jenkinson M, Bannister P, Brady M, Smith S (2002) Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. Neuroimage 17(2):825–841
Whittall KP (1969) MacKay AL (1989) Quantitative interpretation of NMR relaxation data. J Magn Reson 84(1):134–152
Glasser MF, Van Essen DC (2011) Mapping human cortical areas in vivo based on myelin content as revealed by T1- and T2-weighted MRI. J Neurosci 31(32):11597–11616
Ganzetti M, Wenderoth N, Mantini D (2014) Whole brain myelin mapping using T1- and T2-weighted MR imaging data. Front Hum Neurosci 8:671
Wakana S, Caprihan A, Panzenboeck MM, Fallon JH, Perry M, Gollub RL, Hua K, Zhang J, Jiang H, Dubey P, Blitz A, van Zijl P, Mori S (2007) Reproducibility of quantitative tractography methods applied to cerebral white matter. Neuroimage 36(3):630–644
Akaike H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Autom Control 19(6):716–723
Uddin MN, Figley TD, Solar KG, Shatil AS, Figley CR (2019) Comparisons between multi-component myelin water fraction, T1w/T2w ratio, and diffusion tensor imaging measures in healthy human brain structures. Sci Rep 9(1):2500
Webb S, Munro CA, Midha R, Stanisz GJ (2003) Is multi-component T2 a good measure of myelin content in peripheral nerve? Magn Reson Med 49(4):638–645
Nam Y, Lee J, Hwang D, Kim DH (2015) Improved estimation of myelin water fraction using complex model fitting. Neuroimage 116:214–221
Funding
This study was partly supported by JSPS KAKENHI [Grant no. 20K07997].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: YK, HM, and YT; methodology: YK and YT; formal analysis and investigation: SK, YK, and YM; writing—original draft preparation: SK and YK; writing—review and editing: YK, YT, and HH; funding acquisition: YK and HM; resources: YT, KI, and YB; supervision: AH.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
MH received a research grant from FUJIFILM Healthcare Corporation; YT, KI, and YB are employees of FUJIFILM Healthcare Corporation; the other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Tokushima University Hospital.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the study participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kitano, S., Kanazawa, Y., Harada, M. et al. Conversion map from quantitative parameter mapping to myelin water fraction: comparison with R1·R2* and myelin water fraction in white matter. Magn Reson Mater Phy (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-024-01155-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-024-01155-w