Abstract
Objective
We introduce a non-invasive MR-Acoustic Radiation Force Imaging (ARFI)-based elastography method that provides both the local shear modulus and temperature maps for the monitoring of High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) therapy.
Materials and methods
To take tissue anisotropy into account, the local shear modulus μ is determined in selected radial directions around the focal spot by fitting the phase profiles to a linear viscoelastic model, including tissue-specific mechanical relaxation time τ. MR-ARFI was evaluated on a calibrated phantom, then applied to the monitoring of HIFU in a gel phantom, ex vivo and in vivo porcine muscle tissue, in parallel with MR-thermometry.
Results
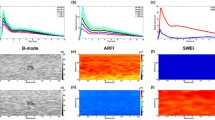
As expected, the shear modulus polar maps reflected the isotropy of phantoms and the anisotropy of muscle. In the HIFU monitoring experiments, both the shear modulus polar map and the thermometry map were updated with every pair of MR-ARFI phase images acquired with opposite MR-ARFI-encoding. The shear modulus was found to decrease (phantom and ex vivo) or increase (in vivo) during heating, before remaining steady during the cooling phase. The mechanical relaxation time, estimated pre- and post-HIFU, was found to vary in muscle tissue.
Discussion
MR-ARFI allowed for monitoring of viscoelasticity changes around the HIFU focal spot even in anisotropic muscle tissue.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jolesz FA (2009) MRI-guided focused ultrasound surgery. Annu Rev Med 60:417–430
Kim Y (2015) Advances in MR image-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound therapy. Int J Hyperthermia 31:225–232
Kuroda K (2018) MR techniques for guiding high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) treatments. J Magn Reson Imaging 47:316–331
Ebbini ES, Ter Haar G (2015) Ultrasound-guided therapeutic focused ultrasound: current status and future directions. Int J Hyperthermia 31:77–89
Ebbini ES, Simon C, Liu D (2018) Real-time ultrasound thermography and thermometry. IEEE Signal Process Mag 35:166–174
Geoghegan R, ter Haar G, Nightingale K, Marks L, Natarajan S (2021) Methods of monitoring thermal ablation of soft tissue tumors – a comprehensive review. Med Phys 49:769–791
Lewis MA, Staruch RM, Chopra R (2015) Thermometry and ablation monitoring with ultrasound. Int J Hyperthermia 31:163–181
Odéen H, Parker DL (2019) Magnetic resonance thermometry and its biological applications - Physical principles and practical considerations. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 110:34–61
Rieke V, Pauly KB (2008) MR Thermometry. J Magn Reson Imaging 27:376–390
De Poorter J (1995) Noninvasive MRI thermometry with the proton resonance frequency method: study of susceptibility effects. Magn Reson Med 34:359–367
Ishihara Y, Calderon A, Watanabe H, Okamoto K, Suzuki Y, Kuroda K, Suzuki Y (1995) A precise and fast temperature mapping using water proton chemical shift. Magn Reson Med 34:814–823
Kokuryo D, Kumamoto E, Kuroda K (2020) Recent technological advancements in thermometry. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 163–164:19–39
Arnal B, Pernot M, Tanter M (2011) Monitoring of thermal therapy based on shear modulus changes: II. Shear wave imaging of thermal lesions. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 58:1603–1611
Chen J, Woodrum DA, Glaser KJ, Murphy MC, Gorny K, Ehman R (2014) Assessment of in vivo laser ablation using MR elastography with an inertial driver. Magn Reson Med 72:59–67
Corbin N, Vappou J, Breton E, Boehler Q, Barbé L, Renaud P, de Mathelin M (2016) Interventional MR elastography for MRI-guided percutaneous procedures: interventional MR elastography. Magn Reson Med 75:1110–1118
Mariani A, Kwiecinski W, Pernot M, Balvay D, Tanter M, Clement O, Cuenod CA, Zinzindohoue F (2014) Real time shear waves elastography monitoring of thermal ablation: in vivo evaluation in pig livers. J Surg Res 188:37–43
Sapin-de Brosses E, Pernot M, Tanter M (2011) The link between tissue elasticity and thermal dose in vivo. Phys Med Biol 56:7755–7765
Muthupillai R, Lomas DJ, Rossman PJ, Greenleaf JF, Manduca A, Ehman RL (1995) Magnetic resonance elastography by direct visualization of propagating acoustic strain waves. Science 269:1854–1857
Wu T, Felmlee JP, Greenleaf JF, Riederer SJ, Ehman RL (2001) Assessment of thermal tissue ablation with MR elastography. Magn Reson Med 45:80–87
Kim K, Breton E, Gangi A, Vappou J (2020) Simultaneous fat-referenced proton resonance frequency shift thermometry and MR elastography for the monitoring of thermal ablations. Magn Reson Med 84:339–347
Le Y, Glaser K, Rouviere O, Ehman R, Felmlee JP (2006) Feasibility of simultaneous temperature and tissue stiffness detection by MRE. Magn Reson Med 55:700–705
Chu B, Apfel RE (1982) Acoustic radiation pressure produced by a beam of sound. J Acoust Soc Am 72:1673–1687
Torr GR (1984) The acoustic radiation force. Am J Phys 52:402–408
Nightingale K, McAleavey S, Trahey G (2003) Shear-wave generation using acoustic radiation force: in vivo and ex vivo results. Ultrasound Med Biol 29:1715–1723
Larrat B, Pernot M, Aubry J-F, Sinkus R, Tanter M, Fink M (2008) Radiation force localization of HIFU therapeutic beams coupled with magnetic resonance-elastography treatment monitoring in vivo application to the rat brain. In: 2008 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium. pp 451–454
McDannold N, Maier SE (2008) Magnetic resonance acoustic radiation force imaging. Med Phys 35:3748–3758
Holbrook AB, Ghanouni P, Santos JM, Medan Y, Butts Pauly K (2011) In vivo MR acoustic radiation force imaging in the porcine liver. Med Phys 38:5081–5089
Kaye EA, Chen J, Pauly KB (2011) Rapid MR-ARFI method for focal spot localization during focused ultrasound therapy. Magn Reson Med 65:738–743
Larrat B, Pernot M, Aubry J-F, Dervishi E, Sinkus R, Seilhean D, Marie Y, Boch A-L, Fink M, Tanter M (2010) MR-guided transcranial brain HIFU in small animal models. Phys Med Biol 55:365–388
Souchon R, Salomir R, Beuf O, Milot L, Grenier D, Lyonnet D, Chapelon J, Rouvière O (2008) Transient MR elastography (t-MRE) using ultrasound radiation force: theory, safety, and initial experiments in vitro. Magn Reson Med 60:871–881
Auboiroux V, Viallon M, Roland J, Hyacinthe J-N, Petrusca L, Morel DR, Goget T, Terraz S, Gross P, Becker CD, Salomir R (2012) ARFI-prepared MRgHIFU in liver: simultaneous mapping of ARFI-displacement and temperature elevation, using a fast GRE-EPI sequence. Magn Reson Med 68:932–946
de Bever JT, Odéen H, Hofstetter LW, Parker DL (2018) Simultaneous MR thermometry and acoustic radiation force imaging using interleaved acquisition. Magn Reson Med 79:1515–1524
Bitton RR, Kaye E, Dirbas FM, Daniel BL, Pauly KB (2012) Toward MR-guided high intensity focused ultrasound for presurgical localization: Focused ultrasound lesions in cadaveric breast tissue. J Magn Reson Imaging 35:1089–1097
Bour P, Marquet F, Ozenne V, Toupin S, Dumont E, Aubry J-F, Lepetit-Coiffe M, Quesson B (2017) Real-time monitoring of tissue displacement and temperature changes during MR-guided high intensity focused ultrasound. Magn Reson Med 78:1911–1921
Ilovitsh A, Fite BZ, Ilovitsh T, Ferrara KW (2019) Acoustic radiation force imaging using a single-shot spiral readout. Phys Med Biol 64:125004
Qiao Y, Zou C, Chuanli C, Tie C, Wan Q, Peng H, Liang D, Liu X, Zheng H (2020) Simultaneous acoustic radiation force imaging and MR thermometry based on a coherent echo-shifted sequence. Quant Imaging Med Surg 10:1823–1836
Vappou J, Bour P, Marquet F, Ozenne V, Quesson B (2018) MR-ARFI-based method for the quantitative measurement of tissue elasticity: application for monitoring HIFU therapy. Phys Med Biol 63:095018
Schmidt JL, Tweten DJ, Benegal AN, Walker CH, Portnoi TE, Okamoto RJ, Garbow JR, Bayly PV (2016) Magnetic resonance elastography of slow and fast shear waves illuminates differences in shear and tensile moduli in anisotropic tissue. J Biomech 49:1042–1049
Kaye EA, Pauly KB (2013) Adapting MRI acoustic radiation force imaging for in vivo human brain focused ultrasound applications. Magn Reson Med 69:724–733
Dadakova T, Krafft AJ, Özen AC, Bock M (2018) Optimization of acoustic radiation force imaging: influence of timing parameters on sensitivity. Magn Reson Med 79:981–986
D’Errico J (2012) Matlab functions: fminsearchbnd, fminsearchcon (https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/8277-fminsearchbnd-fminsearchcon) MATLAB Central File Exchange
Farrer AI, Odéen H, de Bever J, Coats B, Parker DL, Payne A, Christensen DA (2015) Characterization and evaluation of tissue-mimicking gelatin phantoms for use with MRgFUS. J Ther Ultrasound 3:9
Cabras P, Auloge P, Bing F, Rao PP, Hoarau S, Dumont E, Durand A, Maurin B, Wach B, Cuvillon L, Breton E, Gangi A, Vappou J (2022) A new versatile MR-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) device for the treatment of musculoskeletal tumors. Sci Rep 12:9095
Lefebvre P, Tse Ve Koon K, Brusseau E, Nicolle S, Palierne J-F, Lambert S, Grenier D (2016) Comparison of Viscoelastic Property Characterization of Plastisol Phantoms with Magnetic Resonance Elastography and High-Frequency Rheometry. In: Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. pp 1216–1219
Vappou J, Breton E, Choquet P, Goetz C, Willinger R, Constantinesco A (2007) Magnetic resonance elastography compared with rotational rheometry for in vitro brain tissue viscoelasticity measurement. Magn Reson Mater Phy 20:273
Kruse SA, Smith JA, Lawrence AJ, Dresner MA, Manduca A, Greenleaf JF, Ehman RL, Kruse SA, Smith JA, Lawrence AJ, Dresner MA, Manduca A, Greenleaf JF (2000) Tissue characterization using magnetic resonance elastography: preliminary results\ast. Phys Med Biol 45:1579–1590
Sapin-de Brosses E, Gennisson J-L, Pernot M, Fink M, Tanter M (2010) Temperature dependence of the shear modulus of soft tissues assessed by ultrasound. Phys Med Biol 55:1701–1718
Hofstetter LW, Odéen H, Bolster BD, Mueller A, Christensen D, Payne A, Parker DL (2019) Efficient shear wave elastography using transient acoustic radiation force excitations and MR displacement encoding. Magn Reson Med 81:3153–3167
Hofstetter LW, Odéen H, Bolster BD, Christensen DA, Payne A, Parker DL (2021) Magnetic resonance shear wave elastography using transient acoustic radiation force excitations and sinusoidal displacement encoding. Phys Med Biol 66:055027
Liu Y, Liu J, Fite BZ, Foiret J, Ilovitsh A, Leach JK, Dumont E, Caskey CF, Ferrara KW (2017) Supersonic transient magnetic resonance elastography for quantitative assessment of tissue elasticity. Phys Med Biol 62:4083–4106
Ishak O, Breton E, Choquet K, Josset A, Cabras P, Vappou J (2023) Monitoring MR-guided high intensity focused ultrasound therapy using transient supersonic shear wave MR-elastography. Phys Med Biol 68(3):035013. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/acac5e
Chatelin S, Charpentier I, Corbin N, Meylheuc L, Vappou J (2016) An automatic differentiation-based gradient method for inversion of the shear wave equation in magnetic resonance elastography: specific application in fibrous soft tissues. Phys Med Biol 61:5000–5019
Acknowledgements
This work has benefitted from funding of the FUI (Fonds Unique Interministériel, BPI France) for the UFOGUIDE project, and the ANR (Agence Nationale de la Recherche) French national program “Investissements d’Avenir” for the LABEX-CAMI (ANR-11-LABX-0004), the IHU Strasbourg (Institute of Image Guided Surgery, ANR-10-IAHU-0002) and the LabCom TechnoFUS lab (ANR-21-LCV3-0007-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The in vivo experiment was led following the 3R principle for more humane research, and in following local legal ethics regulation (registered project APAFIS #14092-2018031513247711v1). The animal was maintained under gaseous anaesthesia during imaging (1.8% isoflurane), with appropriate pain management (Propofol 1mg/kg) during HIFU. At the end of the experiment, the animal was euthanized through anaesthetics overdose (10 min, 5% isoflurane) coupled to IV injection of saturated KCl solution (0.5 mL/kg).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (MP4 1342 KB)
Supplementary file3 (MP4 1130 KB)
Supplementary file4 (MP4 1870 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Choquet, K., Vappou, J., Cabras, P. et al. Magnetic Resonance Acoustic Radiation Force Imaging (MR-ARFI) for the monitoring of High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) ablation in anisotropic tissue. Magn Reson Mater Phy 36, 737–747 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-023-01062-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-023-01062-6