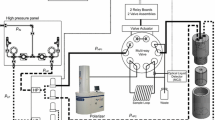
Abstract
Dissolution-DNP is a method to boost liquid-state NMR sensitivity by several orders of magnitude. The technique consists in hyperpolarizing samples by solid-state dynamic nuclear polarization at low temperature and moderate magnetic field, followed by an instantaneous melting and dilution of the sample happening inside the polarizer. Although the technique is well established and the outstanding signal enhancement paved the way towards many applications precluded to conventional NMR, the race to develop new methods allowing higher throughput, faster and higher polarization, and longer exploitation of the signal is still vivid. In this work, we review the most recent advances on dissolution-DNP methods trying to overcome the original technique’s shortcomings. The review describes some of the new approaches in the field, first, in terms of sample formulation and properties, and second, in terms of instrumentation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abragam A (1961) The principles of nuclear magnetism. University Press, Oxford
Hirsch ML, Kalechofsky N, Belzer A, Rosay M, Kempf JG (2015) Brute-force hyperpolarization for NMR and MRI. J Am Chem Soc 137:8428–8434
Walker TG, Happer W (1997) Spin-exchange optical pumping of noble-gas nuclei. Rev Mod Phys 69:629–642
Natterer J, Bargon J (1997) Parahydrogen induced polarization. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 31:293–315
Abragam A, Goldman M (1978) Principles of dynamic nuclear-polarization. Rep Prog Phys 41:395–467
Overhauser AW (1953) Polarization of nuclei in metals. Phys Rev 92:411
Carver TR, Slichter CP (1953) Polarization of nuclear spins in metals. Phys Rev 92:212
van den Brandt B, Hautle P, Konter JA, Kurdzesau F (2008) Dynamic nuclear polarization—from polarized targets to metabolic imaging. Appl Magn Reson 34:475–481
Becerra LR, Gerfen GJ, Temkin RJ, Singel DJ, Griffin RG (1993) Dynamic nuclear polarization with a cyclotron resonance maser at 5 T. Phys Rev Lett 71:3561–3564
Gerfen GJ, Becerra LR, Hall DA, Griffin RG, Temkin RJ, Singel DJ (1995) High frequency (140 GHz) dynamic nuclear polarization: polarization transfer to a solute in frozen aqueous solution. J Chem Phys 102:9494–9497
Griesinger C, Bennati M, Vieth HM, Luchinat C, Parigi G, Höfer P, Engelke F, Glaser SJ, Denysenkov V, Prisner TF (2012) Dynamic nuclear polarization at high magnetic fields in liquids. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 64:4–28
Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH, Fridlund B, Gram A, Hansson G, Hansson L, Lerche MH, Servin R, Thaning M, Golman K (2003) Increase in signal-to-noise ratio of > 10,000 times in liquid-state NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:10158–10163
Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH (2016) On the present and future of dissolution-DNP. J Magn Reson 264:3–12
Nelson SJ, Kurhanewicz J, Vigneron DB, Larson PEZ, Harzstark AL, Ferrone M, van Criekinge M, Chang JW, Bok R, Park I, Reed G, Carvajal L, Small EJ, Munster P, Weinberg VK, Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH, Chen AP, Hurd RE, Odegardstuen LI, Robb FJ, Tropp J, Murray JA (2018) Metabolic Imaging of Patients with Prostate Cancer Using Hyperpolarized [1-13$C]Pyruvate. Sci Transl Med 5:198ra108
van Heeswijk RB, Uffmann K, Comment A, Kurdzesau F, Perazzolo C, Cudalbu C, Jannin S, Konter JA, Hautle P, van den Brandt B, Navon G, van der Klink JJ, Gruetter R (2009) Hyperpolarized 6$Li as a sensor of nanomolar contrast agents. Magn Reson Med 61:1489–1493
Bowen S, Hilty C (2008) Time-resolved dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem 120:5313–5315
Lee Y, Heo GS, Zeng H, Wooley KL, Hilty C (2013) Detection of living anionic species in polymerization reactions using hyperpolarized NMR. J Am Chem Soc 135:4636–4639
Lerche MH, Jensen PR, Karlsson M, Meier S (2015) NMR insights into the inner workings of living cells. Anal Chem 87:119–132
Harris T, Eliyahu G, Frydman L, Degani H (2009) Kinetics of hyperpolarized C-13(1)-pyruvate transport and metabolism in living human breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:18131–18136
Pinon AC, Capozzi A, Ardenkjær-Larsen JH (2020) Hyperpolarized water through dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization with UV-generated radicals. Commun Chem 3:57
Olsen G, Markhasin E, Szekely O, Bretschneider C, Frydman L (2016) Optimizing water hyperpolarization and dissolution for sensitivity-enhanced 2D biomolecular NMR. J Magn Reson 264:49–58
Szekely O, Olsen GL, Felli IC, Frydman L (2018) High-resolution 2D NMR of disordered proteins enhanced by hyperpolarized water. Anal Chem 90:6169–6177
Harris T, Szekely O, Frydman L (2014) On the potential of hyperpolarized water in biomolecular NMR studies. J Phys Chem B 118:3281–3290
Chappuis Q, Milani J, Vuichoud B, Bornet A, Gossert AD, Bodenhausen G, Jannin S (2015) Hyperpolarized water to study protein-ligand interactions. J Phys Chem Lett 6:1674–1678
Wenckebah WTh (2016) Essentials of dynamic nuclear polarization. Ridderprint B.V, Ridderkerk
de Boer W (1976) Dynamic orientation of nuclei at low temperatures. J Low Temp Phys 22:185–212
de Boer W, Borghini M, Morimoto K, Niinikoski TO, Udo F (1974) Dynamic polarization of protons, deuterons, and carbon-13 nuclei: thermal contact between nuclear spins and an electron spin-spin interaction reservoir. J Low Temp Phys 15:249–267
Wind RA, Duijvestijn MJ, van der Lugt C, Manenschijn A, Vriend J (1985) Applications of dynamic nuclear polarization in 13$C NMR in solids. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 17:33–67
Borghini M (1971) Mechanism of nuclear dynamic polarization by electron-nucleus dipolar coupling in solids. European Organization for Nuclear Research, Geneva (Switzerland)
Borghini M (1968) Spin-temperature model of nuclear dynamic polarization using free radicals. Phys Rev Lett 20:419
Hwang CF, Hill DA (1967) Phenomenological model for the new effect in dynamic polarization. Phys Rev Lett 19:1011–1014
Guarin D, Marhabaie S, Rosso A, Abergel D, Bodenhausen G, Ivanov KL, Kurzbach D (2017) Characterizing thermal mixing dynamic nuclear polarization via cross-talk between spin reservoirs. J Phys Chem Lett 8:5531–5536
Hurd RE, Yen Y-F, Chen A, Ardenkjaer-Larsen J-H (2012) Hyperpolarized 13$C metabolic imaging using dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization. J Magn Reson Imaging 36:1314–1328
Heckmann J, Meyer W, Radtke E, Reicherz G (2006) Electron spin resonance and its implication on the maximum nuclear polarization of deuterated solid target materials. Phys Rev B 74:134418
Johanneson H, Macholl S, Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH (2009) Dynamic nuclear polarization of [1-13$C]pyruvic acid at 4.6 T. J Magn Reson 197:167–175
Cheng T, Capozzi A, Takado Y, Balzan R, Comment A (2013) Over 35% liquid-state 13$C polarization obtained via dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization at 7 T and 1 K using ubiquitous nitroxyl radicals. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:20819–20822
Jannin S, Bornet A, Melzi R, Bodenhausen G (2012) High field dynamic nuclear polarization at 6.7 T: 13$C polarization above 70% within 20 min. Chem Phys Lett 549:99–102
Ardenkjaer-Larsen J-H, Leach AM, Clarke N, Urbahn J, Anderson D, Skloss TW (2011) Dynamic nuclear polarization polarizer for sterile use intent. NMR Biomed 24:927–932
Comment A, Merritt ME (2014) Hyperpolarized magnetic resonance as a sensitive detector of metabolic function. Biochemistry 53:7333–7357
Capozzi A, Patel S, Wenckebach WT, Karlsson M, Lerche MH, Ardenkjær-Larsen JH (2019) Gadolinium effect at high-magnetic-field DNP: 70% 13 C polarization of [U- 13 C] glucose using trityl. J Phys Chem Lett 10:3420–3425
Friesen-Waldner L, Chen A, Mander W, Scholl TJ, McKenzie CA (2012) Optimisation of dynamic nuclear polarisation of [1-(13)C] pyruvate by addition of gadolinium-based contrast agents. J Magn Reson 223:85–89
Lumata L, Merritt ME, Malloy CR, Sherry AD, Kovacs Z (2012) Impact of Gd3 + on DNP of [1-13$C] pyruvate doped with trityl OX063, BDPA, or 4-oxo-TEMPO. J Phys Chem A 116:5129–5138
Bornet A, Milani J, Vuichoud B, Linde AJP, Bodenhausen G, Jannin S (2014) Microwave frequency modulation to enhance dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization. Chem Phys Lett 602:63–67
Kiselev YF, Niinikoski TO (1996) EPR and dynamic nuclear polarization with frequency modulation. The Netherlands, Amsterdam, pp 389–391
Adeva B, al. (1996) Large enhancement of deuteron polarization with frequency modulated microwaves. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect 372:339–343
Bornet A, Melzi R, Linde AJP, Hautle P, van den Brandt B, Jannin S, Bodenhausen G (2003) Boosting dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization by cross polarization. J Phys Chem Lett 4:111–114
Kurdzesau F, van den Brandt B, Comment A, Hautle P, Jannin S, van der Klink JJ, Konter JA (2008) Dynamic nuclear polarization of small labelled molecules in frozen water-alcohol solutions. J Phys Appl Phys. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/41/15/155506
Milani J, Vuichoud B, Bornet A, Miéville P, Mottier R, Jannin S, Bodenhausen G (2015) A magnetic tunnel to shelter hyperpolarized fluids. Rev Sci Instrum 86:024101
Ardenkjær-Larsen JH, Bowen S, Petersen JR, Rybalko O, Vinding MS, Ullisch M, Nielsen NC (2018) Cryogen-free dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization polarizer operating at 3.35 T, 6.70 T and 10.1 T. Magn Reson Med 81(3):2184–2194
Cheng T, Gaunt AP, Marco-Rius I, Gehrung M, Chen AP, Klink JJ, Comment A (2020) A multisample 7 T dynamic nuclear polarization polarizer for preclinical hyperpolarized MR. NMR Biomed. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.4264
Yoshihara HAI, Can E, Karlsson M, Lerche MH, Schwitter J, Comment A (2016) High-field dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization of [1-C-13]pyruvic acid. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18:12409–12413
Lama B, Collins JHP, Downes D, Smith AN, Long JR (2016) Expeditious dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization without glassing agents: expeditious dissolution DNP without glassing agents. NMR Biomed 29:226–231
Stephenson JL (1956) Ice crystal growth during the rapid freezing of tissues. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 2:45–52
Hall RS, Board SJ, Clare AJ, Duffey RB, Playle TS, Poole DH (1969) Inverse leidenfrost phenomenon. Nature 224:266–267
Cavagna A (2009) Supercooled liquids for pedestrians. Phys Rep 476:51–124
Haida O, Suga H, Seki S (1977) Calorimetric study of the glassy state XII. Plural glass-transition phenomena of ethanol. J Chem Thermodyn 9:1133–1148
Lumata L, Merritt ME, Kovacs Z (2013) Influence of deuteration in the glassing matrix on 13$C dynamic nuclear polarization. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:7032–7035
Lumata L, Kovacs Z, Sherry AD, Malloy C, Hill S, van Tol J, Yu L, Song L, Merritt ME (2013) Electron spin resonance studies of trityl OX063 at a concentration optimal for DNP. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:9800–9807
Miéville P, Ahuja P, Sarkar R, Jannin S, Vasos PR, Gerber-Lemaire S, Mishkovsky M, Comment A, Gruetter R, Ouari O et al (2010) Scavenging free radicals to preserve enhancement and extend relaxation times in NMR using dynamic nuclear polarization. Angew Chem 122:6318–6321
Cheng T, Mishkovsky M, Junk MJN, Münnemann K, Comment A (2016) Producing radical-free hyperpolarized perfusion agents for in vivo magnetic resonance using spin-labeled thermoresponsive hydrogel. Macromol Rapid Commun 37:1074–1078
Vuichoud B, Bornet A, de Nanteuil F, Milani J, Canet E, Ji X, Mieville P, Weber E, Kurzbach D, Flamm A, Konrat R, Gossert AD, Jannin S, Bodenhausen G (2016) Filterable agents for hyperpolarization of water, metabolites, and proteins. Chem Eur J 22:14696–14700
Gajan D, Bornet A, Vuichoud B, Milani J, Melzi R, van Kalkeren HA, Veyre L, Thieuleux C, Conley MP, Gruning WR, Schwarzwalder M, Lesage A, Coperet C, Bodenhausen G, Emsley L, Jannin S (2014) Hybrid polarizing solids for pure hyperpolarized liquids through dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:14693–14697
Ji X, Bornet A, Vuichoud B, Milani J, Gajan D, Rossini AJ, Emsley L, Bodenhausen G, Jannin S (2017) Transportable hyperpolarized metabolites. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/Ncomms13975
Capozzi A, Cheng T, Boero G, Roussel C, Comment A (2017) Thermal annihilation of photo-induced radicals following dynamic nuclear polarization to produce transportable frozen hyperpolarized 13C-substrates. Nat Commun 8:15757
Eichhorn TR, Takado Y, Salameh N, Capozzi A, Cheng T, Hyacinthe JN, Mishkovsky M, Roussel C, Comment A (2013) Hyperpolarization without persistent radicals for in vivo real-time metabolic imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:18064–18069
van der Wel PCA, Hu K-N, Lewandowski J, Griffin RG (2006) Dynamic nuclear polarization of amyloidogenic peptide nanocrystals: GNNQQNY, a core segment of the yeast prion protein Sup35p. J Am Chem Soc 128:10840–10846
Rossini AJ, Zagdoun A, Hegner F, Schwarzwälder M, Gajan D, Copéret C, Lesage A, Emsley L (2012) Dynamic nuclear polarization NMR spectroscopy of microcrystalline solids. J Am Chem Soc 134:16899–16908
Pinon AC, Schlagnitweit J, Berruyer P, Rossini AJ, Lelli M, Socie E, Tang M, Pham T, Lesage A, Schantz S, Emsley L (2017) Measuring nano- to microstructures from relayed dynamic nuclear polarization NMR. J Phys Chem C 121:15993–16005
Pinon AC (2018) Spin diffusion in dynamic nuclear polarization nuclear magnetic resonance. https://doi.org/10.5075/EPFL-THESIS-8519
Pines A, Gibby MG, Waugh JS (1972) Proton-enhanced nuclear induction spectroscopy 13$C chemical shielding anisotropy in some organic solids. Chem Phys Lett 15:373–376
Suter D, Ernst RR (1985) Spin diffusion in resolved solid-state NMR spectra. Phys Rev B 32:5608–5627
Szeverenyi NM, Sullivan MJ (1969) Maciel GE (1982) Observation of spin exchange by two-dimensional fourier transform 13C cross polarization-magic-angle spinning. J Magn Reson 47:462–475
Silverio DL, van Kalkeren HA, Ong T-C, Baudin M, Yulikov M, Veyre L, Berruyer P, Chaudhari S, Gajan D, Baudouin D, Cavaillès M, Vuichoud B, Bornet A, Jeschke G, Bodenhausen G, Lesage A, Emsley L, Jannin S, Thieuleux C, Copéret C (2017) Tailored polarizing hybrid solids with nitroxide radicals localized in mesostructured silica walls. Helv Chim Acta 100:e1700101
Capozzi A, Hyacinthe JN, Cheng T, Eichhorn TR, Boero G, Roussel C, van der Klink JJ, Comment A (2015) Photoinduced nonpersistent radicals as polarizing agents for X-nuclei dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization. J Phys Chem C 119:22632–22639
Capozzi A, Karlsson M, Petersen JR, Lerche MH, Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH (2018) Liquid-state 13 C polarization of 30% through photoinduced nonpersistent radicals. J Phys Chem C 122:7432–7443
Capozzi A, Patel S, Gunnarsson CP, Marco-Rius I, Comment A, Karlsson M, Lerche MH, Ouari O, Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH (2019) Efficient hyperpolarization of U-(13) C-glucose using narrow-line UV-generated labile free radicals. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 58:1334–1339
Marco-Rius I, Cheng T, Gaunt AP, Patel S, Kreis F, Capozzi A, Wright AJ, Brindle KM, Ouari O, Comment A (2018) Photogenerated radical in phenylglyoxylic acid for in vivo hyperpolarized (13)C MR with photosensitive metabolic substrates. J Am Chem Soc 140:14455–14463
Carravetta M, Johannessen OG, Levitt MH (2004) Beyond the T 1 Limit: singlet nuclear spin states in low magnetic fields. Phys Rev Lett 92:153003
Carravetta M, Levitt MH (2004) Long-lived nuclear spin states in high-field solution NMR. J Am Chem Soc 126:6228–6229
Vasos PR, Comment A, Sarkar R, Ahuja P, Jannin S, Ansermet J-P, Konter JA, Hautle P, van den Brandt B, Bodenhausen G (2009) Long-lived states to sustain hyperpolarized magnetization. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:18469–18473
Eills J, Cavallari E, Kircher R, Di Matteo G, Carrera C, Dagys L, Levitt MH, Ivanov K, Aime S, Reineri F, Münnemann K, Budker D, Buntkowsky G, Knecht S (2020) Singlet-Contrast. Magn Reson Imaging. https://doi.org/10.26434/chemrxiv.12863639.v1
Dubroca T, Wi S, van Tol J, Frydman L, Hill S (2019) Large volume liquid state scalar Overhauser dynamic nuclear polarization at high magnetic field. Phys Chem Chem Phys 21:21200–21204
Denysenkov V, Prandolini MJ, Gafurov M, Sezer D, Endeward B, Prisner TF (2010) Liquid state DNP using a 260 GHz high power gyrotron. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:5786
Bachert P, Brunner H, Hausser KH, Colpa JP (1984) Microwave-induced optical nuclear polarization (MI ONP) of benzophenone in dibromodiphenylether. Chem Phys 91:435–447
Bargon J, Fischer H, Johnsen U (1967) Kernresonanz-Emissionslinien während rascher Radikalreaktionen. Z Für Naturforschung A 22:1551–1555
Ward HR, Lawler RG (1967) Nuclear magnetic resonance emission and enhanced absorption in rapid organometallic reactions. J Am Chem Soc 89:5518–5519
Iinuma M, Takahashi Y, Shaké I, Oda M, Masaike A, Yabuzaki T, Shimizu HM (2000) High proton polarization by microwave-induced optical nuclear polarization at 77 K. Phys Rev Lett 84:171–174
Eichhorn TR, Haag M, van den Brandt B, Hautle P, Wenckebach WTh (2013) High proton spin polarization with DNP using the triplet state of pentacene-. Chem Phys Lett 555:296–299
Eichhorn TR, Niketic N, van den Brandt B, Filges U, Panzner T, Rantsiou E, Wenckebach WTh, Hautle P (2014) Proton polarization above 70% by DNP using photo-excited triplet states, a first step towards a broadband neutron spin filter. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect Accel Spectrometers Detect Assoc Equip 754:10–14
Tateishi K, Negoro M, Nishida S, Kagawa A, Morita Y, Kitagawa M (2014) Room temperature hyperpolarization of nuclear spins in bulk. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:7527–7530
Tateishi K, Negoro M, Kagawa A, Kitagawa M (2013) Dynamic nuclear polarization with photoexcited triplet electrons in a glassy matrix. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:13307–13310
Kouno H, Orihashi K, Nishimura K, Kawashima Y, Tateishi K, Uesaka T, Kimizuka N, Yanai N (2020) Triplet dynamic nuclear polarization of crystalline ice using water-soluble polarizing agents. Chem Commun 56:3717–3720
Negoro M, Kagawa A, Tateishi K, Tanaka Y, Yuasa T, Takahashi K, Kitagawa M (2018) Dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization at room temperature using photoexcited triplet electrons. J Phys Chem A 122:4294–4297
Keshari KR, Kurhanewicz J, Macdonald JM, Wilson DM (2012) Generating contrast in hyperpolarized 13C MRI using ligand–receptor interactions. The Analyst 137:3427
Can TV, Weber RT, Walish JJ, Swager TM, Griffin RG (2017) Frequency-swept integrated solid effect. Angew Chem Int Ed 56:6744–6748
Henstra A, Dirksen P, Wenckebach WTh (1988) Enhanced dynamic nuclear polarization by the integrated solid effect. Phys Lett A 134:134–136
Quan Y, van den Brandt B, Kohlbrecher J, Wenckebach WTh, Hautle P (2019) A transportable neutron spin filter. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect Accel Spectrometers Detect Assoc Equip 921:22–26
King JP, Jeong K, Vassiliou CC, Shin CS, Page RH, Avalos CE, Wang H-J, Pines A (2015) Room-temperature in situ nuclear spin hyperpolarization from optically pumped nitrogen vacancy centres in diamond. Nat Commun 6:8965
Comment A, van den Brandt B, Uffmann K, Kurdzesau F, Jannin S, Konter JA, Hautle P, Wenckebach WT, Gruetter R, van der Klink JJ (2016) Principles of operation of a DNP prepolarizer coupled to a rodent MRI scanner. Appl Magn Reson 34:313–319
Comment A, van den Brandt B, Uffmann K, Kurdzesau F, Jannin S, Konter JA, Hautle P, Wenckebach WTH, Gruetter R, van der Klink JJ (2007) Design and performance of a DNP prepolarizer coupled to a rodent MRI scanner. Concepts Magn Reson Part B-Magn Reson Eng 31B:255–269
Jahnig F, Kwiatkowski G, Dapp A, Hunkeler A, Meier BH, Kozerke S, Ernst M (2017) Dissolution DNP using trityl radicals at 7 T field. Phys Chem Chem Phys 19:19196–19204
Jannin S, Comment A, Kurdzesau F, Konter JA, Hautle P, van den Brandt B, van der Klink JJ (Jun 28) A 140 GHz prepolarizer for dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization. J Chem Phys 128:241102 1–4
Ardenkjaer‐Larsen JH (2017) Cryogen‐free dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization at 10 T (and other instrumental developments for dDNP). Asilomar, p 30
Bowen S, Rybalko O, Petersen JR, Ardenkaer-Larsen JH (2017) Multi‐field cryogen free dissolution‐DNP at 3.35, 6.70, and 10.05 T
Baudin M, Vuichoud B, Bornet A, Bodenhausen G, Jannin S (2018) A cryogen-consumption-free system for dynamic nuclear polarization at 9.4 T. J Magn Reson 294:115–121
Bornet A, Pinon A, Jhajharia A, Baudin M, Ji X, Emsley L, Bodenhausen G, Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH, Jannin S (2016) Microwave-gated dynamic nuclear polarization. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18:30530–30535
Batel M, Krajewski M, Weiss K, With O, Däpp A, Hunkeler A, Gimersky M, Pruessmann KP, Boesiger P, Meier BH, Kozerke S, Ernst M (2012) A multi-sample 94 GHz dissolution dynamic-nuclear-polarization system. J Magn Reson 214:166–174
Capozzi A, Kilund, J., Karlsson M, Lerche MH, Ardenkaer-Larsen JH (2020) Transportable hyperpolarized glucose samples: towards remote dissolution DNP. ISMRM 2020 New Front. Hyperpolarization Program Number 0693
Bowen S, Hilty C (2010) Rapid sample injection for hyperpolarized NMR spectroscopy. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:5766–5770
Kouřil K, Kouřilová H, Bartram S, Levitt MH, Meier B (2019) Scalable dissolution-dynamic nuclear polarization with rapid transfer of a polarized solid. Nat Commun 10:1733
Gadian DG, Panesar KS, Perez Linde AJ, Horsewill AJ, Köckenberger W, Owers-Bradley JR (2012) Preparation of highly polarized nuclear spin systems using brute-force and low-field thermal mixing. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:5397
Peat DT, Hirsch ML, Gadian DG, Horsewill AJ, Owers-Bradley JR, Kempf JG (2016) Low-field thermal mixing in [1- 13 C] pyruvic acid for brute-force hyperpolarization. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18:19173–19182
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Danish National Research Foundation (DNRF124), the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie Grant Agreement No. 713683 (COFUNDfellowsDTU), and the Swiss National Fund under the SPARK Grant Agreement No. CRSK-2_190547.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JA review article conception; ACP drafting of manuscript; AC and JA critical revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
JA is an employee of GE Healthcare and the owner of the company Polarize. We have no further potential conflicts of interest. This review does not involve any human participants or animal research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pinon, A.C., Capozzi, A. & Ardenkjær-Larsen, J.H. Hyperpolarization via dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization: new technological and methodological advances. Magn Reson Mater Phy 34, 5–23 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-020-00894-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-020-00894-w