Abstract
Objectives
We evaluated diffusion imaging measures of the corticospinal tract obtained with a probabilistic tractography algorithm applied to data of two acquisition protocols based on different numbers of diffusion gradient directions (NDGDs).
Materials and methods
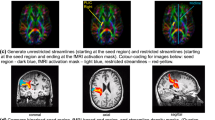
The corticospinal tracts (CST) of 18 healthy subjects were delineated using 22 and 66-NDGD data. An along-tract analysis of diffusion metrics was performed to detect possible local differences due to NDGD.
Results
FA values at 22-NDGD showed an increase along the central portion of the CST. The mean of partial volume fraction of the orientation of the second fiber (f2) was higher at 66-NDGD bilaterally, because for 66-NDGD data the algorithm more readily detects dominant fiber directions beyond the first, thus the increase in FA at 22-NDGD is due to a substantially reduced detection of crossing fiber volume. However, the good spatial correlation between the tracts drawn at 22 and 66 NDGD shows that the extent of the tract can be successfully defined even at lower NDGD.
Conclusions
Given the spatial tract localization obtained even at 22-NDGD, local analysis of CST can be performed using a NDGD compatible with clinical protocols. The probabilistic approach was particularly powerful in evaluating crossing fibers when present.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mori S, van Zijl PC (2002) Fiber tracking: principles and strategies—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:468–480
Ciccarelli O, Behrens TE, Altmann DR, Orrell RW, Howard RS, Johansen-Berg H, Miller DH, Matthews PM, Thompson AJ (2006) Probabilistic diffusion tractography: a potential tool to assess the rate of disease progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 129:1859–1871
Bastin ME, Pettit LD, Bak TH, Gillingwater TH, Smith C, Abrahams S (2013) Quantitative tractography and tract shape modeling in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 38(5):1140–1145
Mori S, Crain B, Chacko VP, van Zijl PCM (1999) Three dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 45:265–269
Basser PJ, Pajevic S, Pierpaoli C, Duda J, Aldroubi A (2000) In vivo fiber tractography using DT-MRI data. Magn Reson Med 44:625–632
Wahl M, Li YO, Ng J, Lahue SC, Cooper SR, Sherr EH, Mukherjee P (2010) Microstructural correlations of white matter tracts in the human brain. Neuroimage 51(2):531–541
Tournier JD, Calamante F, Connelly A (2012) MRtrix: diffusion tractography in crossing fiber regions. Int J Imag Syst Tech 22(1): 53–66
Garyfallidis E, Brett M, Amirbekian B, Rokem A, Van Der Walt S, Descoteaux M, Nimmo-Smith I (2014) Dipy, a library for the analysis of diffusion MRI data. Front Neuroinform 8:1–17
Jones DK, Knösche TR, Turner R (2013) White matter integrity, fiber count, and other fallacies: the do’s and don’ts of diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 73:239–254
Pujol S, Wells W, Pierpaoli C, Brun C, Gee J, Cheng G, Vemuri B, Commowick O, Prima S, Stamm A, Goubran M, Khan A, Peters T, Neher P, Maier-Hein KH, Shi Y, Tristan-Vega A, Veni G, Whitaker R, Styner M, Westin CF, Gouttard S, Norton I, Chauvin L, Mamata H, Gerig G, Nabavi A, Golby A, Kikinis R (2015) The DTI challenge: toward standardized evaluation of diffusion tensor imaging tractography for neurosurgery. J Neuroimaging 25(6): 875–882
O’Donnell LJ, Westin CF, Golby AJ (2009) Tract-based morphometry for white matter group analysis. Neuroimage 45(3):832–844
Gong G, Jiang T, Zhu C, Zang Y, Wang F, Xie S, Xiao J, Guo X (2005) Asymmetry analysis of cingulum based on scale-invariant parameterization by diffusion tensor imaging. Hum Brain Mapp 24(2):92–98
Lin F, Yu C, Jiang T, Li K, Li X, Qin W, Sun H, Chan P (2006) Quantitative analysis along the pyramidal tract by length-normalized parameterization based on diffusion tensor tractography: application to patients with relapsing neuromyelitis optica. Neuroimage 33(1):154–160
Reich DS, Smith SA, Jones CK, Zackowski KM, van Zijl PC, Calabresi PA, Mori S (2006) Quantitative characterization of the corticospinal tract at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27(10):2168–2178
Oh JS, Song IC, Lee JS, Kang H, Park KS, Kang E, Lee DS (2007) Tractography-guided statistics (TGIS) in diffusion tensor imaging for the detection of gender difference of fiber integrity in the midsagittal and parasagittal corpora callosa. Neuroimage 36:606–616
Oh JS, Kubicki M, Rosenberger G, Bouix S, Levitt JJ, McCarley RW, Westin CF, Shenton ME (2009) Thalamo-frontal white matter alterations in chronic schizophrenia: a quantitative diffusion tractography study. Hum Brain Mapp 30(11):3812–3825
Hong JH, Son SM, Jang SH (2010) Somatotopic location of corticospinal tract at pons in human brain: a diffusion tensor tractography study. Neuroimage 51:952–955
Hong YH, Lee KW, Sung JJ, Chang KH, Song IC (2004) Diffusion tensor MRI as a diagnostic tool of upper motor neuron involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 227:73–78
Toosy AT, Werring DJ, Orrell RW, Howard RS, King MD, Barker GJ et al (2003) Diffusion tensor imaging detects corticospinal tract involvement at multiple levels in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:1250–1257
Abe O, Yamada H, Masutani Y, Aoki S, Kunimatsu A, Yamasue H, Fukuda R, Kasai K, Hayashi N, Masumoto T et al (2004) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: diffusion tensor tractography and voxelbased analysis. NMR Biomed 17:411–416
Ni H, Kavcic V, Zhu T, Ekholm S, Zhong J (2006) Effects of number of diffusion gradient directions on derived diffusion tensor imaging indices in human brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1776–1781
Jones D (2004) The Effect of gradient sampling schemes on measures derived from diffusion tensor MRI: a Monte Carlo study. Magn Reson Med 51:807–815
Landman BA, Farrell JA, Jones CK, Smith SA, Prince JL, Mori S (2007) Effects of diffusion weighting schemes on the reproducibility of DTI-derived fractional anisotropy, mean diffusivity, and principal eigenvector measurements at 1.5T. Neuroimage 36(4):1123–1138
Lebel C, Benner T, Beaulieu C (2012) Six is enough? Comparison of diffusion parameters measured using six or more diffusion-encoding gradient directions with deterministic tractography. Magn Reson Med 68(2):474–483
Behrens T, Johansen Berg H, Jbabdi S, Rushworth M, Woolrich M (2007) Probabilistic diffusion tractography with multiple fibre orientations: what can we gain? NeuroImage 34:144–155
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9:97–113
Jenkinson M, Smith SM (2001) A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Med Image Anal 5(2):143–156
Ardekani BA, Braun M, Hutton BF, Kanno I, Iida H (1995) A fully automatic multimodality image registration algorithm. J Comput Assist Tomogr 19(4):615–623
Fischl B (2012) FreeSurfer. Neuroimage 62(2):774–781
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, Rueckert D, Nichols TE, Mackay CE, Watkins KE, Ciccarelli O, Cader MZ, Matthews PM et al (2006) Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 31:1487–1505
Anderson VM, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Abdel-Aziz K, Miller DH, Toosy A, Thompson AJ, Ciccarelli O (2011) A comprehensive assessment of cerebellar damage in multiple sclerosis using diffusion tractography and volumetric analysis. Mult Scler 17(9):1079–1087
Guye M, Parker GJ, Symms M, Boulby P, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Salek-Haddadi A, Barker GJ, Duncan JS (2003) Combined functional MRI and tractography to demonstrate the connectivity of the human primary motor cortex in vivo. Neuroimage 19(4):1349–1360
Yasmin H, Aoki S, Abe O, Nakata Y, Hayashi N, Masutani Y, Goto M, Ohtomo K (2009) Tract-specific analysis of white matter pathways in healthy subjects: a pilot study using diffusion tensor MRI. Neuroradiology 51:831–840
Hattori T, Yuasa T, Aoki S, Sato R, Sawaura H, Mori T, Mizusawa H (2011) Altered microstructure in corticospinal tract in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: comparison with Alzheimer Disease and Parkinson Disease with dementia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:1681–1687
Surova Y, Szczepankiewicz F, Lätt J, Nilsson M, Eriksson B, Leemans A, Hansson O, van Westen D, Nilsson C (2013) Assessment of global and regional diffusion changes along white matter tracts in parkinsonian disorders by MR tractography. PLoS One 8(6):e66022
Colby J, Soderbergc L, Lebel C, Dinova I, Thompson P, Sowel E (2012) Along-tract statistics allow for enhanced tractography analysis. Neuroimage 59(4):3227–3242
Holodny AI, Watts R, Korneinko VN, Pronin IN, Zhukovskiy ME, Gor DM, Ulug A (2005) Diffusion tensor tractography of the motor white matter tracts in man: Current controversies and future directions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1064:88–97 (Review)
Jellison BJ, Field AS, Medow J, Lazar M, Salamat MS, Alexander AL (2004) Diffusion tensor imaging of cerebral white matter: a pictorial review of physics, fiber tract anatomy, and tumor imaging patterns. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25(3):356–369
King MD, Gadian DG, Clark CA (2009) A random effects modelling approach to the crossing-fibre problem in tractography. Neuroimage 44(3):753–768
Thiebaut de Schotten M, Ffytche DH, Bizzi A, Dell’Acqua F, Allin M, Walshe M, Murray R, Williams SC, Murphy DG, Catani M (2011) Atlasing location, asymmetry and inter-subject variability of white matter tracts in the human brain with MR diffusion tractography. Neuroimage 54(1):49–59
Jones DK, Cercignani M (2010) Twenty-five pitfalls in the analysis of diffusion MRI data. NMR Biomed 23(7):803–820
Barrio-Arranz G, de Luis-García R, Tristán-Vega A, Martín-Fernández M, Aja-Fernández S (2015) Impact of MR acquisition parameters on DTI scalar indexes: a tractography based approach. PLoS One 10(10):e0137905
Al Masri O (2011) An essay on the human corticospinal tract: history, development, anatomy, and connections. Neuroanatomy 10:1–4
Nathan PW, Smith MC, Deacon P (1990) The corticospinal tracts in man. Course and location of fibres at different segmental levels. Brain 113:303–324
Rademacher J, Bürgel U, Geyer S, Schormann T, Schleicher A, Freund HJ, Zilles K (2001) Variability and asymmetry in the human precentral motor system. A cytoarchitectonic and myeloarchitectonic brain mapping study. Brain 124(Pt 11):2232–2258
Lebel C, Beaulieu C (2009) Lateralization of the arcuate fasciculus from childhood to adulthood and its relation to cognitive abilities in children. Hum Brain Mapp 30(11):3563–3573
Herve PY, Leonard G, Perron M, Pike B, Pitiot A, Richer L, Veillette S, Pausova Z, Paus T (2009) Handedness, motor skills and maturation of the corticospinal tract in the adolescent brain. Hum Brain Mapp 30:3151–3162
Westerhausen R, Huster RJ, Kreuder F, Wittling W, Schweiger E (2007) Corticospinal tract asymmetries at the level of the internal capsule: is there an association with handedness? Neuroimage 37: 379–386
Papadakis NG, Xing D, Houston GC, Smith JM, Smith MI, James MF, Parsons AA, Huang CL, Hall LD, Carpenter TA (1999) A study of rotationally invariant and symmetric indices of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Imaging 17(6):881–892
Skare S, Hedehus M, Moseley ME, Li TQ (2000) Condition number as a measure of noise performance of diffusion tensor data acquisition schemes with MRI. J Magn Reson 147(2):340–352
Papadakis NG, Murrills CD, Hall LD, Huang CL, Adrian Carpenter T (2000) Minimal gradient encoding for robust estimation of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Imaging 18(6):671–679
Yao X, Yu T, Liang B, Xia T, Huang Q, Zhuang S (2015) Effect of increasing diffusion gradient direction number on diffusion tensor imaging fiber tracking in the human brain. Korean J Radiol 16(2):410–418
Acknowledgements
We thank Claudio Bianchini for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Testa, C., Evangelisti, S., Popeo, M. et al. The effect of diffusion gradient direction number on corticospinal tractography in the human brain: an along-tract analysis. Magn Reson Mater Phy 30, 265–280 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-016-0600-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-016-0600-1