Abstract
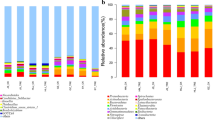
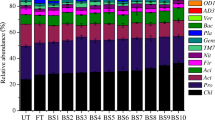
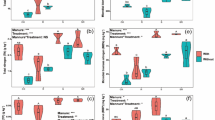
A 6-year field experiment was conducted to assess the effects of biogas slurry (BS) application on rice yield, soil nutrients, soil microbial activity (MicroResp™) and community composition (16S rRNA gene sequencing) in paddy field in southeast China. The experiment included five treatments: (1) 270 kg N ha−1 from urea (mineral fertilizers only, MF); (2) 135 kg N ha−1 from urea and 135 kg N ha−1 from BS (BS1); (3) 270 kg N ha−1 from BS (BS2); (4) 405 kg N ha−1 from BS (BS3) and (5) 540 kg N ha−1 from BS (BS4). Results showed that no significant differences were found in average rice yield between the MF and BS treatments (BS1–BS4). Both soil available phosphorus (AP) and soil available potassium (AK) increased with an increasing application rate of BS. The average substrate-induced respiration was significantly higher in the treatment with lower rate of BS (BS1 and BS2) than in other treatments and then decreased with increasing application rate of BS. Soil microbial communities were affected by BS application. Chloroflexi, Proteobacteria and Acidobacteria were the dominant bacterial phyla across all soil samples. The BS application resulted in a relative abundance of Nitrospirae 2.6–3.7 times than that in MF. Our results also indicated that AP and AK were the two main factors affecting soil microbial activity and community. Overall, the results suggest that the replacement of chemical fertilizer with BS may be an alternative management practice for improving soil quality, soil fertility and nutrient balance in paddy field.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abubaker J, Risberg K, Pell M (2012) Biogas residues as fertilisers—effects on wheat growth and soil microbial activities. Appl Energy 99:126–134
Abubaker J, Cederlund H, Arthurson V, Pell M (2013) Bacterial community structure and microbial activity in different soils amended with biogas residues and cattle slurry. Appl Soil Ecol 72:171–180
Abubaker J, Risberg K, Jönsson E, Dahlin AS, Cederlund H, Pell M (2015) Short-term effects of biogas digestates and pig slurry application on soil microbial activity. Appl Environ Soil Sci 2015:1–15
Abujabhah IS, Doyle R, Bound SA, Bowman JP (2016) The effect of biochar loading rates on soil fertility, soil biomass, potential nitrification, and soil community metabolic profiles in three different soils. J Soils Sediments 16:2211–2222
An J, Liu C, Wang Q, Yao M, Rui J, Zhang S, Li X (2019) Soil bacterial community structure in Chinese wetlands. Geoderma 337:290–299
Bachmann S, Gropp M, Eichler-Löbermann B (2014) Phosphorus availability and soil microbial activity in a 3 year field experiment amended with digested dairy slurry. Biomass Bioenergy 70:429–439
Bérard A, Mazzia C, Sappin-Didier V, Capowiez L, Capowiez Y (2014) Use of the MicroResp™ method to assess pollution-induced community tolerance in the context of metal soil contamination. Ecol Indic 40:27–33
Bian B, Wu H, Lv L, Fan Y, Lu H (2015) Health risk assessment of metals in food crops and related soils amended with biogas slurry in Taihu Basin: perspective from field experiment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:14358–14366
Campbell CD, Chapman SJ, Cameron CM, Davidson MS, Potts JM (2003) A rapid microtiter plate method to measure carbon dioxide evolved from carbon substrate amendments so as to determine the physiological profiles of soil microbial communities by using whole soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3593–3599
Cao Y, Wang J, Wu H, Yan S, Guo D, Wang G, Ma Y (2016) Soil chemical and microbial responses to biogas slurry amendment and its effect on Fusarium wilt suppression. Appl Soil Ecol 107:116–123
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Caracciolo AB, Bustamante MA, Nogues I, Di Lenola M, Luprano ML, Grenni P (2015) Changes in microbial community structure and functioning of a semiarid soil due to the use of anaerobic digestate derived composts and rosemary plants. Geoderma 245–246:89–97
Chapman SJ, Campbell CD, Artz RRE (2007) Assessing CLPPs using MicroResp™. J Soils Sediments 7:406–410
Chen D, Jiang L, Huang H, Toyota K, Dahlgren RA, Lu J (2013) Nitrogen dynamics of anaerobically digested slurry used to fertilize paddy fields. Biol Fertil Soils 49:647–659
Chen C, Zhang J, Lu M, Qin C, Chen Y, Yang L, Huang Q, Wang J, Shen Z, Shen Q (2016) Microbial communities of an arable soil treated for 8 years with organic and inorganic fertilizers. Biol Fertil Soils 52:455–467
Chen D, Yuan L, Liu Y, Ji J, Hou H (2017a) Long-term application of manures plus chemical fertilizers sustained high rice yield and improved soil chemical and bacterial properties. Eur J Agron 90:34–42
Chen G, Zhao G, Zhang H, Shen Y, Fei H, Cheng W (2017b) Biogas slurry use as N fertilizer for two-season Zizania aquatica Turcz. in China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 107:303–320
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OUT sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998
Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:626–631
Fierer N, Bradford MA, Jackson RB (2007) Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 88:1354–1364
Ge T, Chen X, Yuan H, Li B, Zhu H, Peng P, Li K, Jones DL, Wu J (2013) Microbial biomass, activity, and community structure in horticultural soils under conventional and organic management strategies. Eur J Soil Biol 58:122–128
Guo J, Liu W, Zhu C, Luo G, Kong Y, Ling N, Wang M, Dai J, Shen Q, Guo S (2017) Bacterial rather than fungal community composition is associated with microbial activities and nutrient-use efficiencies in a paddy soil with short-term organic amendments. Plant Soil 424:335–349
Hou H, Zhou S, Hosomi M, Toyota K, Yosimura K, Mutou Y, Nisimura T, Takayanagi M, Motobayashi T (2007) Ammonia emissions from anaerobically-digested slurry and chemical fertilizer applied to flooded forage rice. Water Air Soil Poll 183:37–48
Hupfauf S, Bachmann S, Fernandez-Delgado Juarez M, Insam H, Eichler-Lobermann B (2016) Biogas digestates affect crop P uptake and soil microbial community composition. Sci Total Environ 542:1144–1154
Ji Y, Liu G, Ma J, Zhang G, Xu H, Yagi K (2013) Effect of controlled-release fertilizer on mitigation of N2O emission from paddy field in South China: a multi-year field observation. Plant Soil 371:473–486
Jin H, Chang Z (2011) Distribution of heavy metal contents and chemical fractions in anaerobically digested manure slurry. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 164:268–282
Lagomarsino A, Grego S, Kandeler E (2012) Soil organic carbon distribution drives microbial activity and functional diversity in particle and aggregate-size fractions. Pedobiologia 55:101–110
Li P, Lu J, Hou W, Pan Y, Wang Y, Khan MR, Ren T, Cong R, Li X (2017) Reducing nitrogen losses through ammonia volatilization and surface runoff to improve apparent nitrogen recovery of double cropping of late rice using controlled release urea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:11722–11733
Lin H, Sun W, Zhang Z, Chapman SJ, Freitag TE, Fu J, Zhang X, Ma J (2016) Effects of manure and mineral fertilization strategies on soil antibiotic resistance gene levels and microbial community in a paddy-upland rotation system. Environ Pollut 211:332–337
Liu X, Vitousek P, Chang Y, Zhang W, Matson P, Zhang F (2016) Evidence for a historic change occurring in China. Environ Sci Technol 50:505–506
Long XE, Wang J, Huang Y, Yao H (2016) Microbial community structures and metabolic profiles response differently to physiochemical properties between three landfill cover soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:15483–15494
Lu LK (1999) Analytical methods of soil and agricutural chemistry. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Lu J, Jiang L, Chen D, Toyota K, Strong PJ, Wang H, Hirasawa T (2012) Decontamination of anaerobically digested slurry in a paddy field ecosystem in Jiaxing region of China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 146:13–22
Manzoni S, Taylor P, Richter A, Porporato A, Agren GI (2012) Environmental and stoichiometric controls on microbial carbon-use efficiency in soils. New Phytol 196:79–91
Moreno-García B, Guillén M, Quílez D (2017) Response of paddy rice to fertilisation with pig slurry in northeast Spain: strategies to optimise nitrogen use efficiency. Field Crop Res 208:44–54
National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC) (2017) China statistical yearbook. China Statistics Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Olsen S, Sommers L (1982) Phosphorus. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. SSSA, Madison
Pan F, Li Y, Chapman SJ, Yao H (2016) Effect of rice straw application on microbial community and activity in paddy soil under different water status. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:5941–5948
Peng S, Buresh RJ, Huang J, Zhong X, Zou Y, Yang J, Wang G, Liu Y, Hu R, Tang Q, Cui K, Zhang F, Dobermann A (2010) Improving nitrogen fertilization in rice by sitespecific N management. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 30:649–656
Roberts TL, Ross WJ, Norman RJ, Slaton NA, Wilson CE (2011) Predicting nitrogen fertilizer needs for rice in Arkansas using alkaline hydrolyzable-nitrogen. Soil Sci Soc Am J 75:1161–1171
Sasada Y, Win KT, Nonaka R, Win AT, Toyota K, Motobayashi T, Hosomi M, Dingjiang C, Lu J (2011) Methane and N2O emissions, nitrate concentrations of drainage water, and zinc and copper uptake by rice fertilized with anaerobically digested cattle or pig slurry. Biol Fertil Soils 47:949–956
Terhoeven-Urselmans T, Scheller E, Raubuch M, Ludwig B, Joergensen RG (2009) CO2 evolution and N mineralization after biogas slurry application in the field and its yield effects on spring barley. Appl Soil Ecol 42:297–302
USDA/NRCS (1999) Soil taxonomy. A basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys, 2nd edn. U. S. Government Printing Office, Washington
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Wang J, Chapman SJ, Yao H (2014) The effect of storage on microbial activity and bacterial community structure of drained and flooded paddy soil. J Soils Sediments 15:880–889
Wang J, Song Y, Ma T, Raza W, Li J, Howland JG, Huang Q, Shen Q (2017) Impacts of inorganic and organic fertilization treatments on bacterial and fungal communities in a paddy soil. Appl Soil Ecol 112:42–50
Wentzel S, Schmidt R, Piepho HP, Semmler-Busch U, Joergensen RG (2015) Response of soil fertility indices to long-term application of biogas and raw slurry under organic farming. Appl Soil Ecol 96:99–107
Win KT, Nonaka R, Win AT, Sasada Y, Toyota K, Motobayashi T (2013) Effects of water saving irrigation and rice variety on greenhouse gas emissions and water use efficiency in a paddy field fertilized with anaerobically digested pig slurry. Paddy Water Environ, 13:51–60
Xiong J, Liu Y, Lin X, Zhang H, Zeng J, Hou J, Yang Y, Yao T, Knight R, Chu H (2012) Geographic distance and pH drive bacterial distribution in alkaline lake sediments across Tibetan Plateau. Environ Microbiol 14:2457–2466
Xu X, He P, Zhao S, Qiu S, Johnston AM, Zhou W (2016) Quantification of yield gap and nutrient use efficiency of irrigated rice in China. Field Crop Res 186:58–65
Yao Y, Zhang M, Tian Y, Zhao M, Zhang B, Zhao M, Zeng K, Yin B (2018) Urea deep placement for minimizing NH3 loss in an intensive rice cropping system. Field Crop Res 218:254–266
Zhang J, Wang M, Cao Y, Liang P, Wu S, Leung AO, Christie P (2017a) Replacement of mineral fertilizers with anaerobically digested pig slurry in paddy fields: assessment of plant growth and grain quality. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:8916–8923
Zhang M, Yao Y, Zhao M, Zhang B, Tian Y, YinB ZhuZ (2017b) Integration of urea deep placement and organic addition for improving yield and soil properties and decreasing N loss in paddy field. Agric Ecosyst Environ 247:236–245
Zhao J, Ni T, Li Y, Xiong W, Ran W, Shen B, Shen Q, Zhang R (2014a) Responses of bacterial communities in arable soils in a rice–wheat cropping system to different fertilizer regimes and sampling times. PLoS ONE 9:e85301
Zhao J, Zhang R, Xue C, Xun W, Sun L, Xu Y, Shen Q (2014b) Pyrosequencing reveals contrasting soil bacterial diversity and community structure of two main winter wheat cropping systems in China. Microb Ecol 67:443–453
Zhao J, Ni T, Li J, Lu Q, Fang Z, Huang Q, Zhang R, Li R, Shen B, Shen Q (2016) Effects of organic–inorganic compound fertilizer with reduced chemical fertilizer application on crop yields, soil biological activity and bacterial community structure in a rice–wheat cropping system. Appl Soil Ecol 99:1–12
Zheng X, Fan J, Cui J, Wang Y, Zhou J, Ye M, Sun M (2016) Effects of biogas slurry application on peanut yield, soil nutrients, carbon storage, and microbial activity in an Ultisol soil in southern China. J Soils Sediments 16:449–460
Zhu ZL, Chen DL (2002) Nitrogen fertilizer use in China-contributions to food production, impacts on the environment and best management strategies. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 63:117–127
Zhu K, Choi HL, Yao HQ, Suresh A, Oh DI (2009) Effects of anaerobically digested pig slurry application on runoff and leachate. Chem Ecol 25:359–369
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0200800 and 2016YFD0200102), the Major Scientific and Technological Project of Zhejiang Province (2015C02013), the Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (2015C03013/001) and the Public Welfare Technology Application Research Plan Project of Zhejiang Province (LGN18D010005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Wang, Q., Ma, J. et al. Soil microbial activity and community composition as influenced by application of pig biogas slurry in paddy field in southeast China. Paddy Water Environ 18, 15–25 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-019-00761-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-019-00761-y