Abstract
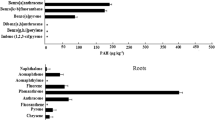
While pollution of the environment by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons has been rather well studied, the fate of substituted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ecosystems is less understood, notably in soil–plant systems. Here we hypothesized that substituted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons could enter wheat and induce phytotoxicity. We studied the accumulation, root-shoot translocation and phytotoxicity of α-tetralone, 1-nitronaphthalene, 1-nitropyrene, and 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene in wheat using hydroponic experiments. We deciphered the accumulation and translocation mechanisms by inhibition with sodium vanadate, glycerol and silver nitrate. Results show that pollutant concentrations increased rapidly in roots, reaching maximum of 38.3 μg/g for α-tetralone, 268.7 μg/g for 1-nitronaphthalene, 3566.1 μg/g for 1-nitropyrene, and 3632.7 μg/g for 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene. In contrast, the root-shoot translocation factors of α-tetralone, 1-nitronaphthalene, 1-nitropyrene and 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene were 2.4, 1.6, 0.1, and 0.1, respectively, thus decreasing significantly with increasing compound hydrophobicity. This could be explained by preferential adsorption for hydrophobic compounds, whereas less hydrophobic compounds could be partly translocated in a soluble form through plant water channels. The accumulated substituted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in wheat induced the decrease of the total chlorophyll contents by 19.0–30.1%, yet did not cause lipid peroxidation damage. Overall, our findings indicates the bioaccumulation potential and toxicity of substituted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in terrestrial plants.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali S, Rizwan M, Hussain A, Rehman MZU, Ali B, Yousaf B, Wijaya L, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2019) Silicon nanoparticles enhanced the growth and reduced the cadmium accumulation in grains of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Physiol Bioch 140:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.04.041
Bandowe BAM, Meusel H (2017) Nitrated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (nitro-PAHs) in the environment-a review. Sci Total Environ 581:237–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.115
Barbier-Brygoo H, Vinauger M, Colcombet J, Ephritikhine G, Frachisse JM, Maurel C (2000) Anion channels in higher plants: functional characterization, molecular structure and physiological role. BBA-Biomembranes 1465(1–2):199–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2736(00)00139-5
Baroudi F, Al-Alam J, Chimjarn S, Delhomme O, Fajloun Z, Millet M (2020) Conifers as environmental biomonitors: a multi-residue method for the concomitant quantification of pesticides, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls by LC-MS/MS and GC-MS/MS. Microchem J 154:104593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104593
Belykh LI (2009) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the soil-plant system. Eurasian Soil Sci 42(9):1005–1011. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229309090075
Brasher AMD, Wolff RH (2004) Relations between land use and organochlorine pesticides, PCBs, and semi-volatile organic compounds in streambed sediment and fish on the Island of Oahu Hawaii. Arch Environ Con Tox 46(3):385–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-003-3019-4
Deng S, Ke T, Wu Y, Zhang C, Hu Z, Yin H, Guo L, Chen L, Zhang D (2018) Heavy metal exposure alters the uptake behavior of 16 priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by Pak Choi (Brassica chinensis L.). Environ Sci Technol 52(22):13457–13468. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b01405
Diblasi CJ, Li H, Davis AP, Ghosh U (2009) Removal and fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutants in an urban stormwater bioretention facility. Environ Sci Technol 43(2):494–502. https://doi.org/10.1021/es802090g
Fan Y, Zhao Z, Shi R, Li X, Yang Y, Lan J (2021) Urbanization-related changes over the last 20 years in occurrence, sources, and human health risks of soil PAHs in rural Tianjin China. Environ Chem Lett 19(6):3999–4008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01264-0031
Felizeter S, McLachlan MS, de Voogt P (2012) Uptake of perfluorinated alkyl acids by hydroponically grown lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Environ Sci Technol 46(21):11735–11743. https://doi.org/10.1021/es302398u
Finch BE, Marzooghi S, Di Toro DM, Stubblefield WA (2017) Evaluation of the phototoxicity of unsubstituted and alkylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to mysid shrimp (Americamysis bahia): validation of predictive models. Environ Toxicol Chem 36(8):2043–2049. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3733
Gao M, Guo Z, Dong Y, Song Z (2019) Effects of di-n-butyl phthalate on photosynthetic performance and oxidative damage in different growth stages of wheat in cinnamon soils. Environ Pollut 250:357–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.04.022
Honda M, Suzuki N (2020) Toxicities of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons for aquatic animals. Int J Env Res Pub He 17(4):1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041363
Huang XD, McConkey BJ, Babu TS, Greenberg BM (1997) Mechanisms of photoinduced toxicity of photomodified anthracene to plants: inhibition of photosynthesis in the aquatic higher plant Lemna gibba (duckweed). Environ Toxicol Chem 16(8):1707–1715. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620160819
Jesus F, Pereira JL, Campos I, Santos M, Re A, Keizer J, Nogueira A, Goncalves FJM, Abrantes N, Serpa D (2022) A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons distribution in freshwater ecosystems and their toxicity to benthic fauna. Sci Total Environ 820:153282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153282
Kang F, Chen D, Gao Y, Zhang Y (2010) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in subcellular root tissues of ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.). BMC Plant Biol 10:210. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-210
Kaushik D, Aryadeep R (2014) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front Environ Sci 2:53. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2014.00053
Krzyszczak A, Czech B (2021) Occurrence and toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons derivatives in environmental matrices. Sci Total Environ 788:147738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147738
Kurade MB, Kim JR, Govindwar SP, Jeon BH (2016) Insights into microalgae mediated biodegradation of diazinon by Chlorella vulgaris: microalgal tolerance to xenobiotic pollutants and metabolism. Algal Res 20:126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.10.003
Lan Z, Zhou M, Yao Y, Sun H (2018) Plant uptake and translocation of perfluoroalkyl acids in a wheat-soil system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(31):30907–30916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3070-3
Liu H, Weisman D, Ye YB, Cui B, Huang YH, Colon-Carmona A, Wang ZH (2009) An oxidative stress response to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure is rapid and complex in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci 176(3):375–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2008.12.002
Liu Q, Wang X, Yang R, Yang L, Sun B, Zhu L (2019) Uptake kinetics, accumulation, and long-distance transport of organophosphate esters in plants: impacts of chemical and plant properties. Environ Sci Technol 53(9):4940–4947. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b07189
Liu Q, Liu M, Wu S, Xiao B, Wang X, Sun B, Zhu L (2020) Metabolomics reveals antioxidant stress responses of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) exposed to chlorinated organophosphate esters. J Agr Food Chem 68(24):6520–6529. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c01397
Liu Q, Liu Y, Dong F, Sallach JB, Wu X, Liu X, Xu J, Zheng Y, Li Y (2021) Uptake kinetics and accumulation of pesticides in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): impact of chemical and plant properties. Environ Pollut 275:116637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116637
Lofroth G, Nilsson L, Sugiyama AE, T, (1985) Salmonella/microsome mutagenicity of monochloro derivatives of some di-, tri-and tetracyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Mutat Res 155(3):91–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1218(85)90123-5
Meharg AA, Jardine L (2003) Arsenite transport into paddy rice (Oryza sativa) roots. New Phytol 157(1):39–44. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00655.x
Miller EL, Nason SL, Karthikeyan KG, Pedersen JA (2016) Root uptake of pharmaceuticals and personal care product ingredients. Environ Sci Technol 50(2):525–541. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01546
Mueller CE, LeFevre GH, Timofte AE, Hussain FA, Sattely ES, Luthy RG (2016) Competing mechanisms for perfluoroalkyl acid accumulation in plants revealed using an arabidopsis model system. Environ Toxicol Chem 35(5):1138–1147. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3251
Niemietz CM, Tyerman SD (2002) New potent inhibitors of aquaporins: silver and gold compounds inhibit aquaporins of plant and human origin. Febs Lett 531(3):443–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03581-0
Paskova V, Hilscherova K, Feldmannova M, Blaha L (2006) Toxic effects and oxidative stress in higher plants exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their N-heterocyclic derivatives. Environ Toxicol Chem 25(12):3238–3245. https://doi.org/10.1897/06-162R.1
Qiao M, Qi W, Liu H, Qu J (2013) Simultaneous determination of typical substituted and parent polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and solid matrix by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1291:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.03.044
Qiao M, Qi W, Liu H, Bai Y, Qu J (2016) Formation of oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons during aerobic activated sludge treatment and their removal process. Chem Eng J 302:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.139
Qiao M, Fu L, Li Z, Liu D, Bai Y, Zhao X (2020) Distribution and ecological risk of substituted and parent polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface waters of the Bai, Chao, and Chaobai rivers in northern China. Environ Pollut 257:113600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113600
Sanchez-Pinero J, Gomez-Meijide P, Concha-Grana E, Moreda-Pineiro J, Muniategui-Lorenzo S, Lopez-Mahia P (2022) Oral bioavailability reveals an overestimation of the toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric particulate matter. Environ Chem Lett 20(1):49–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01354-0
Seth CS, Misra CPK, V, (2008) The role of phytochelatins and antioxidants in tolerance to Cd accumulation in Brassica juncea L. Ecotox Environ Safe 71:76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.10.030
Sun Z, Zhu Y, Zhuo S, Liu W, Zeng EY, Wang X, Xing B, Tao S (2017) Occurrence of nitro-and oxy-PAHs in agricultural soils in eastern China and excess lifetime cancer risks from human exposure through soil ingestion. Environ Int 108:261–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.09.001
Tao Y, Zhang S, Zhu YG, Christie P (2009) Uptake and acropetal translocation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in field-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Technol 43(10):3556–3560. https://doi.org/10.1021/es803368y
Tfouni SAV, Reis RM, Kamikata K, Gomes FML, Morgano MA, Furlani RPZ (2018) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in teas using QuEChERS and HPLC-FLD. Food Addit Contam B 11(2):146–152. https://doi.org/10.1080/19393210.2018.1440638
Titaley IA, Chlebowski A, Truong L, Tanguay RL, Simonich SLM (2016) Response to correspondence on identification and toxicological evaluation of unsubstituted PAHs and novel PAH derivatives in pavement sealcoat products. Environ Sci Technol Let 3(11):406–408. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.6b00400
Wan W, Huang H, Lv J, Han R, Zhang S (2017) Uptake, translocation, and biotransformation of organophosphorus esters in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ Sci Technol 51(23):13649–13658. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b01758
Wang X, Zhu L, Zhong W, Yang L (2018) Partition and source identification of organophosphate esters in the water and sediment of Taihu Lake, China. J Hazard Mater 360:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.07.082
Wild E, Dent J, Thomas GO, Jones KC (2005) Direct observation of organic contaminant uptake, storage, and metabolism within plant roots. Environ Sci Technol 39(10):3695–3702. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048136a
Wu Y, Shi Y, Zhang N, Wang Y, Ren Y (2021) Pollution levels, characteristics, and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric particulate matter across the Hu line in China. A review. Environ Chem Lett 19(5):3821–3836. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01258-z
Xu G, Lin X, Yu Y (2023) Different effects and mechanisms of polystyrene micro-and nano-plastics on the uptake of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Pb and Cd) by lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Environ Pollut 316:120656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120656
Yu Y, Huang J, Jin L, Yu M, Yu X, Zhu X, Sun J, Zhu L (2023) Translocation and metabolism of tricresyl phosphate in rice and microbiome system: isomer-specific processes and overlooked metabolites. Environ Int 172:107793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2023.107793
Yun Y, Liang L, Wei Y, Luo Z, Yuan F, Li G, Sang N (2019) Exposure to Nitro-PAHs interfere with germination and early growth of Hordeum vulgare via oxidative stress. Ecotox Environ Safe 180:756–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.05.032
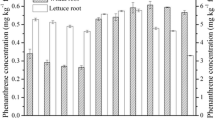
Zhan XH, Ma HL, Zhou LX, Liang JR, Jiang TH, Xu GH (2010) Accumulation of phenanthrene by roots of intact wheat (Triticum acstivnm L.) seedlings: Passive or active uptake? BMC Plant Biol 10:52. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-52
Zhan X, Yi X, Yue L, Fan X, Xu G, Xing B (2015) Cytoplasmic pH-Stat during phenanthrene uptake by wheat roots: a mechanistic consideration. Environ Sci Technol 49(10):6037–6044. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00697
Zhan X, Zhu M, Shen Y, Yue L, Li J, Gardea-Torresdey JL, Xu G (2018) Apoplastic and symplastic uptake of phenanthrene in wheat roots. Environ Pollut 233:331–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.056
Zhou J, Yang Z, Liu Q, Liu Y, Liu M, Wang T, Zhu L (2020) Insights into uptake, translocation, and transformation mechanisms of perfluorophosphinates and perfluorophosphonates in wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Environ Sci Technol 54(1):276–285. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b05656
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Shaanxi Public Welfare Special Project of geological prospecting “Comprehensive Study and Investigation and Evaluation of Land Quality in Ankang Area of Shaanxi Province (No. 201908), Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (No. 2022JQ-245), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41877126, 42007303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HY: conceptualization, investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft. ZZ: methodology, writing—review and editing. JZ: writing—review and editing. JL: writing—review and editing. JC: conceptualization, resources, supervision, writing—review and editing. AL: writing—review and editing. CW: writing—review and editing. CZ: writing—review and editing. YD: writing—review and editing. HJ: conceptualization, resources, supervision, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Zhu, Z., Zhou, J. et al. Accumulation, root-shoot translocation and phytotoxicity of substituted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in wheat. Environ Chem Lett 21, 2509–2517 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01614-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01614-1