Abstract
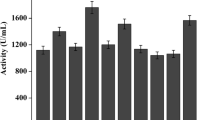
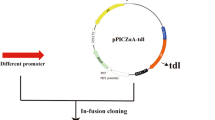
This study attempted to enhance the expression level of Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase (TLL) in Pichia pastoris using a series of strategies. The tll gene was first inserted into the expression vector pPIC9 K and transformed into P. pastoris strain GS115. The maximum hydrolytic activity of TLL reached 4,350 U/mL under the optimal culture conditions of a 500 mL shaking flask containing 20 mL culture medium with the addition of 1.2 % (w/v) methanol, cultivation for 144 h at pH 7.0 and 27 °C. To further increase the TLL expression and copy number, strains containing two plasmids were obtained by sequential electroporation into GS115/9k-TLL #3 with a second vector, either pGAPZαA-TLL, pFZα-TLL, or pPICZαA-TLL. The maximum activity of the resultant strains GS115/9KTLL-ZαATLL #40, GS115/9KTLL-FZαATLL #46 and GS115/9KTLL-GAPTLL #45 was 6,600 U/mL, 6,000 U/mL and 4,800 U/mL, respectively. The tll copy number in these strains, as assessed by real-time quantitative PCR, was demonstrated to be seven, five, and three, respectively, versus two copies in GS115/9k-TLL #3. When a co-feeding strategy of sorbitol/methanol was adopted in a 3-L fermenter, the maximum TLL activity of GS115/9k-TLL #3 increased to 27,000 U/mL after 130 h of fed-batch fermentation, whereas, the maximum TLL activity was 19,500 U/mL after 145 h incubation when methanol was used as the sole carbon source.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad S, Kitz K, Hörmann A, Schreiner U, Hartner FS, Glieder A (2010) Real time PCR based determination of gene copy numbers in Pichia pastoris. Biotech J 5:413–420
Andualema B, Gessesse A (2012) Microbial lipases and their industrial applications: review. Biotech 11(3):100–118
Bornscheuer UT, Huisman GW, Kazlauskas RJ, Lutz S, Moore JC, Robins K (2012) Engineering the thirdwave of biocatalysis. Nature 485:185–194
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brzozowski AM, Derewenda U, Derewenda ZS, Dodson GG, Lawson DM, Turkenburg JP, Bjorkling F, Huge-Jensen B, Patkar SA, Thim L (1991) A model for interfacial activation in lipases from the structure of a fungal lipase-inhibitor complex. Nature 351:491–496
Çelik E, Çalık P, Oliver SG (2009) Fed-batch methanol feeding strategy for recombinant protein production by Pichia pastoris in the presence of co-substrate sorbitol. Yeast 26:473–484
Cereghino JL, Cregg JM (2006) Heterologous protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24:45–66
Cregg JM, Vedvick TS, Raschke WC (1993) Recent advances in the expression of foreign genes in Pichia pastoris. Nat Biotechnol 11:905–910
Damasceno LM, Huang C, Batt CA (2012) Protein secretion in Pichia pastoris and adnances in protein production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(1):31–39
Datta S, Christena LR, Rajaram YRS (2013) Enzyme immobilization: an overview on techniques and support materials. 3 Biotech 3:1–9
Duan H, Umar S, Hu Y, Chen J (2009) Both the AOX1 promoter and the FLD1 promoter work together in a Pichia pastoris expression vector. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1779–1783
Davis BG (2003) Chemical modification of biocatalysts. Curr Opinion Biotechnol 14:379–386
Fernandez-Lafuente R (2010) Lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus: uses and prospects as an industrial biocatalyst. J Mol Catal B Enzym 62:197–212
Hasan F, Shah AA, Hameed A (2006) Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme Microb Tech 39:235–251
Iyer PV, Ananthanarayan L (2008) Enzyme stability and stabilization—Aqueous and non-aqueous environment. Process Biochem 43(10):1019-1032
Jaeger K, Reetz MT (1998) Microbial lipases form versatile tools for biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 16:396–403
Jahic M, Veide A, Charoenrat T, Teeri T, Enfors SO (2006) Process technology for production and recovery of heterologous proteins with Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Progr 22:1465–1473
Laemmli UK (1970) Most commonly used discontinuous buffer system for SDS electrophoresis. Nature 227:680–685
Lee C, Kim J, Shin SG, Hwang S (2006) Absolute and relative QPCR quantification of plasmid copy number in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 123:273–280
Maruyamaa T, Maruyama Tatsuo, Nakajima M, Ichikawa S, Nabetani H, Furusaki S, Seki M (2000) Oil-water interfacial activation of lipase for interesterification of triglyceride and fatty acid. J Am Oil Chem Soc 77:1121–1126
Mateo C, Palomo JM, Fernandez-Lorente G, Guisan JM, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2007) Improvement of enzyme activity, stability and selectivity via immobilization techniques. Enzyme Microb Tech 40(6):1451–1463
Niu HX, Jost L, Pirlot N, Sassi H, Daukandt M, Rodriguez C, Fickers P (2013) A quantitative study of methanol/sorbitol co-feeding process of a Pichia pastoris Mut+/pAOX1-lacZ strain. Microb Cell Fact 12:33
Palomo JM, Filice M, Romero O, Guisan JM (2013) Improving lipase activity by immobilization and post-immobilization strategies. Methods Mol Biol 1051:255–273
Pan XX, Xu L, Zhang Y, Xiao X, Wang XF, Liu Y, Zhang HJ, Yan YJ (2012) Efficient display of active Geotrichum sp. lipase on Pichia pastoris cell wall and its application as a whole-cell biocatalyst to enrich EPA and DHA in fish oil. J Agric Food Chem 60:9673–9679
Resina D, Maurer M, Cos O, Arnau C, Carnicer M, Marx H, Gasser B, Valero F, Mattanovich D, Ferrer P (2009) Engineering of bottlenecks in Rhizopus oryzae lipase production in Pichia pastoris using the nitrogen source-regulated FLD1 promoter. New Biotechnol 25:396–403
Rodrigues RC, Godoy CA, Volpato G, Ayub MAZ, Fernandez-Lafuente R, Guisan JM (2009) Immobilization-stabilization of the lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus: critical role of chemical amination. Process Biochem 44(9):963–968
Schmid RD, Verger R (1998) Lipases: interfacial enzymes with attractive applications. Angew Chem Int Ed 37:1608–1633
Sharma R, Thakur V, Sharma M, Birkeland N (2013) Biocatalysis through thermostable lipases: adding flavor to chemistry. In: Satyanarayana T (ed) Thermophilic Microbes in Environmental and Industrial Biotechnology, 2nd edn. Springer, Netherlands, pp 905–927
Singh AK, Mukhopadhyay M (2012) Overview of fungal lipase: a review. Appl Biochem Biotech 166:486–520
Sreekrishna K, Brankamp RG, Kropp KE, Blankenship DT, Tsay JT, Smith PL, Wierschke JD, Subramaniam A, Birkenberger LA (1997) Strategies for optimal synthesis and secretion of heterologous proteins in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Gene 190:55–62
Stratton J, Chiruvolu V, Meagher M (1998) High cell-density fermentation. In: Higgins DR, Cregg JM (eds) Methods in molecular biology: Pichia protocols. Humana, Totowa, pp 107–120
Thorpe ED, D’Anjou MC, Daugulis AJ (1999) Sorbitol as a non-repressing carbon source for fed-batch fermentation of recombinant Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Lett 21:669–672
Tilbeurgh HV, Egloff MP, Martinez C, Rugani N, Verger R, Cambillau C (1993) Interfacial activation of the lipase–procolipase complex by mixed micelles revealed by X-ray crystallography. Nature 362:814–820
Wang XF, Shen XG, Sun YQ, Ke F, Zhao HY, Xu L, Liu Y, Yan YJ (2012) Production of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase LIP2 in Pichia pastoris using the nitrogen source-regulated FLD1 promoter. J Chem Technol Biot 87:553–558
Wang XF, Sun YQ, Ke F, Zhao HY, Liu T, Xu L, Liu Y, Yan YJ (2012) Constitutive expression of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase LIP2 in Pichia pastoris using GAP as promoter. Appl Biochem Biotech 166:1355–1367
Williams KE, Jiang J, Ju J, Olsen DR (2008) Novel strategies for increased copy number and expression of recombinant human gelatin in Pichia pastoris with two antibiotic markers. Enzyme Microb Tech 43:31–34
Wu JM, Lin JC, Chieng LL, Lee CK, Hsu TA (2003) Combined use of GAP and AOX1 promoter to enhance the expression of human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in Pichia pastoris. Enzyme Microb Tech 33:453–459
Yan JY, Yan YJ (2009) Combined strategy for preparation of a bioimprinted Geotrichum sp. lipase biocatalyst effective in non-aqueous media. Process Biochem 44:1128–1132
Yan YJ, Xu L, Dai M (2012) A synergetic whole-cell biocatalyst for biodiesel production. RSC Advances 2(15):6170–6173
Yu H, Yan X, Shen W, Hong Q, Zhang J, Shen Y, Li S (2009) Expression of methyl parathion hydrolase in Pichia pastoris. Curr Microbiol 59:573–578
Yu X, Wang L, Xu Y (2009) Rhizopus chinensis lipase: gene cloning, expression in Pichia pastoris and properties. J Mol Catal B Enzym 57:304–311
Zhang W, Hywood Potter KJ, Plantz BA, Schlegel VL, Smith LA, Meagher MM (2003) Pichia pastoris fermentation with mixed-feeds of glycerol and methanol: growth kinetics and production improvement. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30:210–215
Zhao W, Wang J, Deng R, Wang X (2008) Scale-up fermentation of recombinant Candida rugosa lipase expressed in Pichia pastoris using the GAP promoter. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:189–195
Zheng YY, Guo XH, Song NN, Li DC (2011) Thermophilic lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus: gene cloning, expression and characterization. J Mol Catal B Enzym 69:127–132
Zhu J, Liu H, Zhang J, Wang P, Liu S, Liu G, Wu L (2014) Effects of Asn-33 glycosylation on the thermostability of Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase. J Appl Microbiol 117(1):151–159
Zhu T, Guo M, Tang Z, Zhang M, Zhuang Y, Chu J, Zhang S (2009) Efficient generation of multi-copy strains for optimizing secretory expression of porcine insulin precursor in yeast Pichia pastoris. J Appl Microbiol 107:954–963
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge financial support by the National High Technology Research Development Program of P. R. China (863 Program) (Nos. 2014AA093510 and 2011AA02A204), the National Natural Science Foundation of P. R. China (NSFC) (Nos. 31170078, 31070089 and J1103514), the R and D Special Foundation of the ShengZhen Municipal Government (No. JCYJ20120831111657864), the Innovation Foundation of HUST (Nos. 2014QN119 and 2014NY007), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities HUST (No. 2172012SHYJ004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Z., Xu, L., Pan, D. et al. Enhanced production of Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase in Pichia pastoris via genetic and fermentation strategies. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41, 1541–1551 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1491-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1491-7