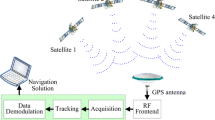
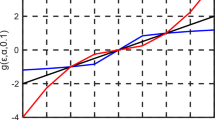
Abstract
The traditional design of tracking loop in global positioning system (GPS), known as the combination of phase-locked loop and delay-locked loop, is fragile under complex environments. With the increasing requirements for tracking performance under more harsh applications, several implementations have emerged in recent years, among which Kalman filter (KF)-based tracking loop is widely used due to its adaptive nature and robust feature, and it could achieve a higher dynamics performance with the aid of inertial navigation system (INS). However, even more critical conditions, such as severe fading, abrupt phase changes, and signal interference coexisting with high user dynamics, are now challenging the traditional carrier tracking architectures, thus calling for the enhancement of robust carrier tracking techniques. A state-constrained Kalman filter-based (SC-KF) approach is proposed to restrict the errors of the tracking loop and to enhance the robustness of the tracking process in high dynamics and signal attenuation environments. In the SC-KF, the system model of INS-aided KF-based tracking loop is built from a perspective of control theory. Based on the ultra-tight GPS/INS integrated scheme, a Doppler-constrained method and moving horizon estimation architecture are introduced to correct the Doppler state and the code, carrier phase states in KF-based tracking loop, respectively. Software and hardware simulations indicate that the proposed architecture has a better performance in tracking and navigation domains comparing with the conventional INS-aided KF-based tracking loop under severe environments.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cong L, Li X, Jin T, Yue S, Xue R (2016) An adaptive INS-aided PLL tracking method for GNSS receivers in harsh environments. Sensors 16(2):146
Gao G, Lachapelle G (2008) A novel architecture for ultra-tight HSGPS-INS integration. J Glob Position Syst 7(1):46–61
Gul HU, Kai YD, Khan M (2017) Multi-sensor integrated filtering for highly dynamic system using recursive moving horizon estimation technique. In: 2017 14th international bhurban conference on applied sciences and technology (IBCAST), Islamabad, January, pp 351–356
Gupta N, Hauser R (2007) Kalman filtering with equality and inequality state constraints. Technical report. Oxford University Computing Laboratory, Oxford
Hsieh GC, Hung JC (1996) Phase-locked loop techniques. A survey. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 43(6):609–615
Hu C, Chen W, Chen Y, Liu D (2003) Adaptive Kalman filtering for vehicle navigation. J Glob Position Syst 2(1):42–47
Hurd WJ, Statman JI, Vilnrotter VA (1985) High dynamic GPS receiver validation demonstration. Final report, publication 85-74, Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), Pasadena
Jwo DJ, Yang CF, Chuang CH, Lee TY (2013) Performance enhancement for ultra-tight GPS/INS integration using a fuzzy adaptive strong tracking unscented Kalman filter. Nonlinear Dyn 73(1–2):377–395
Kaplan ED, Hegarty CJ (2006) Understanding GPS: principles and applications, 2nd edn. Artech House, Boston
Keighobadi J, Vosoughi H, Faraji J (2018) Design and implementation of a model predictive observer for AHRS. GPS Solut 22:29
Kim KH, Jee GI, Song JH (2008) Carrier tracking loop using the adaptive two-stage Kalman filter for high dynamic situations. Int J Control Autom Syst 6(6):948–953
Lashley M (2009) Modeling and performance analysis of GPS vector tracking algorithms. Ph.D. dissertation, Auburn University, December 2009
Legrand F, Macabiau C, Issler JL, Lestarquit L, Mehlen C (2000) Improvement of pseudorange measurements accuracy by using fast adaptive bandwidth lock loops. In: Proceedings of the ION GPS 2000, Institute of Navigation, Salt Lake City, USA, September 19–22, pp 2346–2356
Luo Y, Babu R, Wu WQ, He XF (2012) Double-filter model with modified Kalman filter for baseband signal pre-processing with application to ultra-tight GPS/INS integration. GPS Solut 16(4):463–476
Mao WL, Tsao HW, Chang FR (2004) Intelligent GPS receiver for robust carrier phase tracking in kinematic environments. IEE Proc Radar Sonar Navig 151(3):171–180
Niu X, Li B, Ziedan NI, Guo W, Liu J (2017) Analytical and simulation-based comparison between traditional and Kalman filter-based phase-locked loops. GPS Solut 21(1):123–135
NovAtel Inc (2008) OEM4 family user manual, vol 2
O’Driscoll C, Lachapelle G (2009) Comparison of traditional and Kalman filter based tracking architectures. In: Proceedings of European navigation conference 2009, Naples, May 3–6, 2009
O’Driscoll C, Petovello MG, Lachapelle G (2011) Choosing the coherent integration time for Kalman filter-based carrier-phase tracking of GNSS signals. GPS Solut 15(4):345–356
Petovello MG, Sun D, Lachapelle G, Cannon ME (2007a) Performance analysis of an ultra-tightly integrated GPS and reduced IMU system. In: Proceedings of ION GNSS 2007, Institute of Navigation, Fort Worth, TX, USA, September 25–28, pp 602–609
Petovello MG, O’Driscoll C, Lachapelle G (2007b) Ultra-tight GPS/INS for carrier phase positioning in weak-signal environments. In: Proceedings of NATO RTO SET-104 symposium on military capabilities enabled by advances in navigation Sensors, Antalya, Turkey, 1–2 October 1–2
Qin H, Sun X, Cong L (2014) Using fuzzy logic control for the robust carrier tracking loop in a global positioning system/inertial navigation system tightly integrated system. Trans Inst Meas Control 36(3):354–366
Rao CV, Rawlings JB, Lee JH (2001) Constrained linear state estimation—a moving horizon approach. Automatica 37(10):1619–1628
Simon D (2010) Kalman filtering with state constraints: a survey of linear and nonlinear algorithms. IET Control Theory Appl 4(8):1303–1318
Simon D, Chia TL (2002) Kalman filtering with state equality constraints. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 38(1):128–136
Simon D, El-Sherief H (1995) Fuzzy logic for digital phase-locked loop filter design. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 3(2):211–218
Sircoulomb V, Israel J, Hoblos G, Chafouk H, Ragot J (2008) State estimation under nonlinear state inequality constraints. A tracking application. In: 16th Mediterranean conference on control and automation, Ajaccio, France, pp 1669–1674
Skone S, Lachapelle G, Yao D (2005) Investigating the impact of ionospheric scintillation using a GPS software receiver. In: Proceedings of ION GNSS 2005, Institute of Navigation, Long Beach, CA, USA, September 13–16, pp 1126–1137
Wang Y, Yang R, Ling KV, Poh EK (2015) Robust vector tracking loop using moving horizon estimation. In: Proceedings of ION 2015 Pacific PNT Meeting, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, April 20–23, pp 640–648
Won JH, Dötterböck D, Eissfeller B (2010) Performance comparison of different forms of Kalman filter approaches for a vector-based GNSS signal tracking loop. Navigation 57(3):185–199
Yang C, Blasch E (2009) Kalman filtering with nonlinear state constraints. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 45(1):70–84
Yang R, Ling KV, Poh EK, Morton Y (2017) Generalized GNSS signal carrier tracking—part II: optimization and implementation. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 53(4):1798–1811
Zhang T, Zhang H, Lin T, Yan K, Niu X (2016) Modeling and verifying the impact of time delay on INS-aided GNSS PLLs. GPS Solut 20(4):725–736
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant no. 61471017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, H., Yue, S., Cong, L. et al. A state-constrained tracking approach for Kalman filter-based ultra-tightly coupled GPS/INS integration. GPS Solut 23, 55 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-019-0844-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-019-0844-0