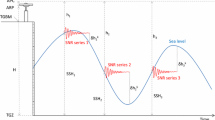
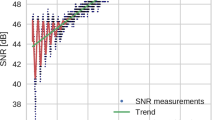
Abstract
We further developed a new approach using GNSS reflectometry to determine the leveling connection between a tide gauge and a GNSS antenna. This approach includes the optimization of the unknown receiver bandwidth and the estimation of frequency changes in the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) oscillation through an extended Kalman filter/smoother algorithm. We also corrected the geometric bending of the GNSS signals due to tropospheric refraction using local meteorological observations. Using 3 weeks of SNR data in Spring Bay, Australia, from a GNSS antenna placed sideways (i.e., ground plane orientated vertically and directed in azimuth toward the sea surface) to improve the SNR interference near the horizon, we obtained mean leveling differences of approximately 5 mm, with an RMS of approximately 3 cm level with respect to the nominal leveling from classical surveying techniques. SNR data from three different receiver manufacturers, coupled to the same antenna, provided similar leveling results. With a second antenna in the usual upright configuration, we obtained mean leveling differences of 1–2 cm and a RMS of about 10 cm. In the upright configuration, the leveling differences may include errors in the GNSS antenna phase center calibration, which are avoided in our technique but not in the classical surveying techniques. These results demonstrate the usefulness of the reflectometry technique to obtain precisely and remotely the leveling between a GNSS antenna and a tide gauge. In addition, this technique can be applied continuously, providing an independent and economical means to monitor the stability of the tide gauge zero.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
http://www.bom.gov.au/oceanography/projects/abslmp/data/index.shtml last accessed January 2016.
References
Anderson KD (2000) Determination of water level and tides using interferometric observations of GPS signals. J Atmos Oceanic Technol 17:1118–1127. doi:10.1175/1520-0426(2000)017<1118:DOWLAT>2.0.CO;2
Bennett GG (1982) The calculation of astronomical refraction in marine navigation. J Navig 35:255–259. doi:10.1017/S0373463300022037
Benton CJ, Mitchell CN (2011) Isolating the multipath component in GNSS signal-to-noise data and locating reflecting objects. Radio Science 46:n/a-n/a doi:10.1029/2011RS004767
Dee DP et al (2011) The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q J R Meteorol Soc 137:553–597. doi:10.1002/qj.828
Hunter JR (2003) On the temperature correction of the aquatrak acoustic tide gauge. J Atmos Oceanic Technol 20:1230–1235. doi:10.1175/1520-0426(2003)020<1230:OTTCOT>2.0.CO;2
Jazwinski AH (1966) Filtering for nonlinear dynamical systems. Autom Control IEEE Trans 11:765–766
Larson KM, Nievinski FG (2013) GPS snow sensing: results from the EarthScope plate boundary observatory. GPS Solut 17:41–52. doi:10.1007/s10291-012-0259-7
Larson KM, Löfgren JS, Haas R (2013a) Coastal sea level measurements using a single geodetic GPS receiver. Adv Space Res 51:1301–1310. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2012.04.017
Larson KM, Ray RD, Nievinski FG, Freymueller JT (2013b) The accidental tide gauge: a gps reflection case study from Kachemak Bay, Alaska. Geosci Rem Sens Lett IEEE 10:1200–1204. doi:10.1109/LGRS.2012.2236075
Löfgren JS, Haas R, Scherneck H-G (2014) Sea level time series and ocean tide analysis from multipath signals at five GPS sites in different parts of the world. J Geodyn 80:66–80. doi:10.1016/j.jog.2014.02.012
Nievinski FG, Larson KM (2014) Inverse modeling of GPS multipath for snow depth estimation—part I: formulation and simulations. Geosci Rem Sens IEEE Trans 52:6555–6563. doi:10.1109/TGRS.2013.2297681
Roussel N, Frappart F, Ramillien G, Desjardins C, Gegout P, Pérosanz F, Biancale R (2014) Simulations of direct and reflected waves trajectories for in situ GNSS-R experiments. Geosci Model Dev Discuss 7:1001–1062. doi:10.5194/gmdd-7-1001-2014
Santamaría-Gómez A, Watson C, Gravelle M, King M, Wöppelmann G (2015) Levelling co-located GNSS and tide gauge stations using GNSS reflectometry. J Geod 89:241–258. doi:10.1007/s00190-014-0784-y
Scargle JD (1982) Studies in astronomical time series analysis. II—statistical aspects of spectral analysis of unevenly spaced data. Astrophys J. doi:10.1086/160554
Shih HH, Rogers D (1981) Error analysis for tide measurement systems utilizing stilling wells. NOAA Tech Rep, US Department of Commerce, NOAA, Office of Ocean Technology and Engineering Services
Acknowledgments
A.S.G. is a recipient of a FP7 Marie Curie International Outgoing Fellowship (Project Number 330103). We acknowledge Geoscience Australia for providing the three GNSS receivers and the GPS data at Spring Bay, and Lachlan Nicholls (Bureau of Meteorology, Australia) for providing and discussing the tide gauge and meteorological data. We acknowledge comments provided by M.A. King. Kristine M Larson and an anonymous reviewer provided comments that helped to improve the manuscript. Google Earth provided the satellite image of Fig. 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santamaría-Gómez, A., Watson, C. Remote leveling of tide gauges using GNSS reflectometry: case study at Spring Bay, Australia. GPS Solut 21, 451–459 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-016-0537-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-016-0537-x