Abstract
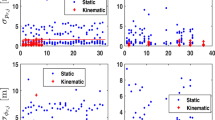
The GPS-precise point positioning (PPP) is still not as popular as network-based real-time kinematic (N-RTK) for engineering kinematic applications based on differential positioning principles for several reasons. One is the fact that the accuracy of kinematic GPS-PPP is lower than N-RTK solutions. The second reason is that GPS-PPP requires a comparatively long initialization period. In order to overcome such shortcomings, a new PPP approach augmented by a ground-based positioning system such as “Locata” is proposed in this paper. The new approach is referred to as Locata/GPS-PPP. Locata’s ground-based technology has rapid geometry change for kinematic applications; thus, the proposed approach is able to provide high-accuracy solutions with faster initialization. In the proposed Locata/GPS-PPP approach, the Locata and GPS carrier phase measurements are processed simultaneously in a tightly combined mode and the carrier phase ambiguities are resolved as floating-point values on an epoch-by-epoch basis in order to avoid the need for cycle-slip repair. In order to evaluate the system performance, a kinematic field trial was conducted on Sydney Harbor. A Locata transmitter network was setup on the fringes of Sydney’s CBD. The experiment demonstrated that the initial convergence time of the integrated Locata/GPS-PPP filter is only 10 s, which is significantly faster than the conventional GPS-PPP method. Comparison of the proposed method with the GPS-PPP and Locata-single point positioning (SPP) approaches was conducted. The results confirm that the Locata/GPS-PPP approach can achieve centimeter-level accuracy for horizontal positioning which improves 36.4 and 68.8 % over Locata-SPP and GPS-PPP. The results validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach for high-accuracy maritime applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashby N (2003) Chapter 1: the Sagnac effect in the global positioning system. In: Rizzi G, Ruggiero ML (eds) Relativity in rotating frames: relativistic physics in rotating reference frames (fundamental theories of physics), Springer, ISBN: 1-4020-1805-3
Barnes J, Rizos C, Wang J, Small D, Voight G, Gambale N (2003) LocataNet: the positioning technology of the future? In: 6th Int. Symp. on Satellite navigation technology including mobile positioning & location services, Melbourne, Australia, 22–25 July, CD-ROM proc, paper 49
Bertsch J, Choudhury M, Rizos C, Kahle H-G (2009) On-the-fly ambiguity resolution for Locata. In: International Symposium on GPS/GNSS, Gold Coast, Australia, 1–3 December, CD-ROM procs
Boehm J, Werl B, Schuh H (2006) Troposphere mapping functions for GPS and very long baseline interferometry from European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts operational analysis data. J Geophys Res 111:B02406
Boehm J, Heinkelmann R, Schuh H (2007) Short note: a global model of pressure and temperature for geodetic applications. J Geod 81(2):679–683
Chen X, Allison T, Cao W, Ferguson K, Grünig S, Gomez V, Kipka A, Köhler J, Landau H, Leandro R, Lu G, Stolz R, Talbot N (2011) Trimble RTX, an innovative new approach for network RTK. In: Proceedings of the ION-GNSS-2011, Institute of Navigation, Portland, Oregon, USA, 20–23 Sept, pp 2214–2219
Choudhury M, Rizos C, Harvey BR (2009a) A survey of techniques and algorithms in deformation monitoring applications and the use of the Locata technology for such applications. In: Proceedings of the ION-GNSS-2009, Institute of Navigation, Savannah, Georgia, USA, 22–25 Sept, pp 668–678
Choudhury M, Harvey BR, Rizos C (2009b) Tropospheric correction for Locata when known point ambiguity resolution technique is used in static survey—is it required? In: Proceedings of the international symposium on GPS/GNSS, Gold Coast, Australia, 1–3 Dec, CD-ROM procs
Collins P (2008) Isolating and estimating undifferenced GPS integer ambiguities. ION-NTM-2008, Institute of Navigation, San Diego, California, USA, 28–30 Jan, pp 720–732
Fotopoulos G, Cannon ME (2001) An overview of multi-reference station methods for cm-level positioning. GPS Solut 4(3):1–10
Gao S, Chen W, Hu C, Chen Y, Ding X (2004) Analysis of regional ionospheric disturbance with HK GPS Network. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on GPS/GNSS, Sydney, Australia, 6–8 Dec, CD-ROM procs
Ge M, Gendt G, Rothacher M, Shi C, Liu J (2008) Resolution of GPS carrier-phase ambiguities in precise point positioning (PPP) with daily observations. J Geod 82(7):389–399
Ge M, Dousa J, Li X, Ramatschi M, Wickert J (2012) A novel real-time precise positioning service system: global precise point positioning with regional augmentation. J Glob Position Syst 11(1):2–10
Geng J, Teferle FN, Meng X, Dodson AH (2010) Towards PPP-RTK: ambiguity resolution in real-time precise point positioning. Adv Space Res 47(10):1664–1673
ICD-GPS-200C (1993) Interface control document, NAVSTAR GPS space segment. 10 Oct. http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/icd200c123.pdf
IERS: IERS Conventions (2010) Petit G, Luzum B (eds) (IERS technical note 36) Verlag des Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Frankfurt am Main, ISBN 3-89888-989-6
Jiang W, Li Y, Rizos C (2013) On-the-fly Locata/inertial navigation system integration for precise maritime application. Meas Sci Technol 24(10):105104
Kouba J (2009) A guide to using International GNSS Service (IGS) products [online]. IGS Central Bureau, May. http://igscb.jpl.nasa.gov/igscb/resource/pubs/UsingIGSProductsVer21.pdf
Landau H, Chen X, Klose S, Leandro R, Vollath U (2007) Trimble’s RTK and DGPS solutions in comparison with precise point positioning, observing our changing earth. International Association of Geodesy Symposia 133. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IAG General Assembly, Perugia, Italy, 2–13 July, pp 709–718
Li Y, Rizos C (2010) Seamless navigation through a Locata-enhanced GPS and INS integrated system. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on GPS/GNSS, Taipei, Taiwan, 26–28 Oct, pp 40–45
Locata Corporation (2012) LocataNet positioning signal interface control document. http://www.locata.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/02/Locata-ICD-100B.pdf
Montillet J, Roberts G, Hancock C, Meng X, Ogundipe O, Barnes J (2009) Deploying a Locata network to enable precise positioning in urban canyons. J Geod 83(2):91–103
Rizos C, Grejner-Brzezinska DA, Toth CK, Dempster AG, Li Y, Politi N, Barnes J (2008) A hybrid system for navigation in GPS-challenged environments: Case study. In: Proceedings of the ION-GNSS-2008, Institute of Navigation, Savannah, Georgia, USA, 16–19 Sept 2008, pp 1418–1428
Rizos C, Roberts GW, Barnes J, Gambale N (2010) Locata: a new high accuracy indoor positioning system. In: Mautz R, Kunzand M, Ingensand H (eds) 1st international conference on indoor positioning and indoor navigation (IPIN), Zurich, Switzerland, 15–17 September, pp 441–447
Zumberge JF, Heflin MB, Jefferson DC, Watkins MM, Webb FH (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res 102(B3):5005–5017
Zumberge JF, Watkins MM, Webb FH (1998) Characteristics and applications of precise GPS clock solutions every 30 seconds. J Navig 44(4):449–456
Acknowledgments
The first author wishes to thank the Chinese Scholarship Council (CSC) for supporting her studies at the University of New South Wales. The authors acknowledge the valuable assistance provided by Locata Corporation and Land and Property Information NSW.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, W., Li, Y. & Rizos, C. Locata-based precise point positioning for kinematic maritime applications. GPS Solut 19, 117–128 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0373-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0373-9