Abstract
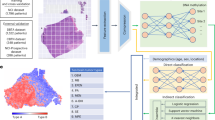
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common primary malignant brain tumor in adults. The standard treatment for GBM consists of surgical resection followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy and adjuvant temozolomide. O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation status is an important prognostic biomarker that predicts the response to temozolomide and guides treatment decisions. At present, the only reliable way to determine MGMT promoter methylation status is through the analysis of tumor tissues. Considering the complications of the tissue-based methods, an imaging-based approach is preferred. This study aimed to compare three different deep learning-based approaches for predicting MGMT promoter methylation status. We obtained 576 T2WI with their corresponding tumor masks, and MGMT promoter methylation status from, The Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) 2021 datasets. We developed three different models: voxel-wise, slice-wise, and whole-brain. For voxel-wise classification, methylated and unmethylated MGMT tumor masks were made into 1 and 2 with 0 background, respectively. We converted each T2WI into 32 × 32 × 32 patches. We trained a 3D-Vnet model for tumor segmentation. After inference, we constructed the whole brain volume based on the patch’s coordinates. The final prediction of MGMT methylation status was made by majority voting between the predicted voxel values of the biggest connected component. For slice-wise classification, we trained an object detection model for tumor detection and MGMT methylation status prediction, then for final prediction, we used majority voting. For the whole-brain approach, we trained a 3D Densenet121 for prediction. Whole-brain, slice-wise, and voxel-wise, accuracy was 65.42% (SD 3.97%), 61.37% (SD 1.48%), and 56.84% (SD 4.38%), respectively.



Similar content being viewed by others
Code Availability
A link to the code will be shared after peer review.
Data Availability
The raw data required to reproduce the above findings are available to download from http://braintumorsegmentation.org/.
Abbreviations
- BraTS:
-
Brain Tumor Segmentation
- CCR:
-
Concurrent chemoradiation therapy
- TMZ:
-
Temozolomide
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma
- MGMT:
-
O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase
- AUCROC:
-
Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve
- TCIA:
-
The Cancer Imaging Archive
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
References
Tamimi AF, Juweid M. Epidemiology and outcome of glioblastoma. In: De Vleeschouwer S, editor. Glioblastoma. Brisbane (AU): Codon Publications; 2017.
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Truitt G, Boscia A, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2011–2015. Neuro Oncol. 2018;20: iv1–iv86.
Egaña L, Auzmendi-Iriarte J, Andermatten J, Villanua J, Ruiz I, Elua-Pinin A, et al. Methylation of MGMT promoter does not predict response to temozolomide in patients with glioblastoma in Donostia Hospital. Sci Rep. 2020;10: 18445.
Tesileanu CMS, Dirven L, Wijnenga MMJ, Koekkoek JAF, Vincent AJPE, Dubbink HJ, et al. Survival of diffuse astrocytic glioma, IDH1/2 wildtype, with molecular features of glioblastoma, WHO grade IV: a confirmation of the cIMPACT-NOW criteria. Neuro Oncol. 2020;22: 515–523.
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJB, Janzer RC, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10: 459–466.
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJB, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352: 987–996.
Hombach-Klonisch S, Mehrpour M, Shojaei S, Harlos C, Pitz M, Hamai A, et al. Glioblastoma and chemoresistance to alkylating agents: involvement of apoptosis, autophagy, and unfolded protein response. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;184: 13–41.
Vlachostergios PJ, Hatzidaki E, Befani CD, Liakos P, Papandreou CN. Bortezomib overcomes MGMT-related resistance of glioblastoma cell lines to temozolomide in a schedule-dependent manner. Invest New Drugs. 2013;31: 1169–1181.
Hegi ME, Diserens A-C, Gorlia T, Hamou M-F, de Tribolet N, Weller M, et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352: 997–1003.
Tierling S, Jürgens-Wemheuer WM, Leismann A, Becker-Kettern J, Scherer M, Wrede A, et al. Bisulfite profiling of the MGMT promoter and comparison with routine testing in glioblastoma diagnostics. Clin Epigenetics. 2022;14: 26.
Brigliadori G, Goffredo G, Bartolini D, Tosatto L, Gurrieri L, Mercatali L, et al. Influence of intratumor heterogeneity on the predictivity of MGMT gene promoter methylation status in glioblastoma. Front Oncol. 2020;10: 533000.
Hamilton MG, Roldán G, Magliocco A, McIntyre JB, Parney I, Easaw JC. Determination of the methylation status of MGMT in different regions within glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol. 2011;102: 255–260.
Grasbon-Frodl EM, Kreth FW, Ruiter M, Schnell O, Bise K, Felsberg J, et al. Intratumoral homogeneity of MGMT promoter hypermethylation as demonstrated in serial stereotactic specimens from anaplastic astrocytomas and glioblastomas. Int J Cancer. 2007;121: 2458–2464.
Singh G, Manjila S, Sakla N, True A, Wardeh AH, Beig N, et al. Radiomics and radiogenomics in gliomas: a contemporary update. Br J Cancer. 2021; 1–17.
Kickingereder P, Bonekamp D, Nowosielski M, Kratz A, Sill M, Burth S, et al. Radiogenomics of glioblastoma: machine learning-based classification of molecular characteristics by using multiparametric and multiregional MR imaging features. Radiology. 2016;281: 907–918.
Drabycz S, Roldán G, de Robles P, Adler D, McIntyre JB, Magliocco AM, et al. An analysis of image texture, tumor location, and MGMT promoter methylation in glioblastoma using magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage. 2010;49: 1398–1405.
Ellingson BM, Cloughesy TF, Pope WB, Zaw TM, Phillips H, Lalezari S, et al. Anatomic localization of O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylated and unmethylated tumors: a radiographic study in 358 de novo human glioblastomas. Neuroimage. 2012;59: 908–916.
Fathi Kazerooni A, Bakas S, Saligheh Rad H, Davatzikos C. Imaging signatures of glioblastoma molecular characteristics: a radiogenomics review. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020;52: 54–69.
Xi Y-B, Guo F, Xu Z-L, Li C, Wei W, Tian P, et al. Radiomics signature: a potential biomarker for the prediction of MGMT promoter methylation in glioblastoma. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018;47: 1380–1387.
Han L, Kamdar MR. MRI to MGMT: predicting methylation status in glioblastoma patients using convolutional recurrent neural networks. Biocomputing 2018. WORLD SCIENTIFIC; 2017. pp. 331–342.
Yogananda CGB, Shah BR, Nalawade SS, Murugesan GK, Yu FF, Pinho MC, et al. MRI-based deep-learning method for determining glioma MGMT promoter methylation status. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021;42: 845–852.
Korfiatis P, Kline TL, Coufalova L, Lachance DH, Parney IF, Carter RE, et al. MRI texture features as biomarkers to predict MGMT methylation status in glioblastomas. Med Phys. 2016;43: 2835–2844.
Chang P, Grinband J, Weinberg BD, Bardis M, Khy M, Cadena G, et al. Deep-learning convolutional neural networks accurately classify genetic mutations in gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018;39: 1201–1207.
Korfiatis P, Kline TL, Lachance DH, Parney IF, Buckner JC, Erickson BJ. Residual deep convolutional neural network predicts MGMT methylation status. J Digit Imaging. 2017;30: 622–628.
Kihira S, Tsankova NM, Bauer A, Sakai Y, Mahmoudi K, Zubizarreta N, et al. Multiparametric MRI texture analysis in prediction of glioma biomarker status: added value of MR diffusion. Neurooncol Adv. 2021;3: vdab051.
Wei J, Yang G, Hao X, Gu D, Tan Y, Wang X, et al. A multi-sequence and habitat-based MRI radiomics signature for preoperative prediction of MGMT promoter methylation in astrocytomas with prognostic implication. Eur Radiol. 2019;29: 877–888.
Mikkelsen VE, Dai HY, Stensjøen AL, Berntsen EM, Salvesen Ø, Solheim O, et al. MGMT promoter methylation status is not related to histological or radiological features in IDH wild-type glioblastomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2020;79: 855–862.
Li Z-C, Bai H, Sun Q, Li Q, Liu L, Zou Y, et al. Multiregional radiomics features from multiparametric MRI for prediction of MGMT methylation status in glioblastoma multiforme: a multicentre study. Eur Radiol. 2018;28: 3640–3650.
Clark K, Vendt B, Smith K, Freymann J, Kirby J, Koppel P, et al. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): maintaining and operating a public information repository. J Digit Imaging. 2013;26: 1045–1057.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, Weinstein JN, Collisson EA, Mills GB, Shaw KRM, Ozenberger BA, et al. The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-Cancer analysis project. Nat Genet. 2013;45: 1113–1120.
Baid U, Ghodasara S, Mohan S, Bilello M, Calabrese E, Colak E, et al. The RSNA-ASNR-MICCAI BraTS 2021 Benchmark on Brain Tumor Segmentation and Radiogenomic Classification. arXiv [cs.CV]. 2021. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2107.02314
Menze BH, Jakab A, Bauer S, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Farahani K, Kirby J, et al. The Multimodal Brain Tumor Image Segmentation Benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2015;34: 1993–2024.
Bakas S, Akbari H, Sotiras A, Bilello M, Rozycki M, Kirby JS, et al. Advancing The Cancer Genome Atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci Data. 2017;4: 170117.
RSNA-MICCAI Brain Tumor Radiogenomic Classification. [cited 8 Apr 2022]. Available: https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/rsna-miccai-brain-tumor-radiogenomic-classification/overview
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O, et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J Mach Learn Res. 2011;12: 2825–2830.
Rouzrokh P, Khosravi B, Faghani S, Moassefi M, Vera Garcia DV, Singh Y, et al. Mitigating bias in radiology machine learning: 1. Data handling. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence. 2022;4: e210290.
MONAI Consortium. MONAI: Medical Open Network for AI. Zenodo; 2022.
Zhang K, Khosravi B, Vahdati S, Faghani S, Nugen F, Rassoulinejad-Mousavi SM, et al. Mitigating bias in radiology machine learning: 2. Model development. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence. 2022;4: e220010.
Jocher G, Stoken A, Borovec J, NanoCode, ChristopherSTAN, Changyu L, et al. ultralytics/yolov5: v3.1 - Bug Fixes and Performance Improvements. 2020.
Faghani S, Khosravi B, Zhang K, Moassefi M, Jagtap JM, Nugen F, et al. Mitigating bias in radiology machine learning: 3. Performance metrics. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence. 2022; e220061.
The MONAI Consortium. Project MONAI. 2020. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4323059
Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi S-A. V-Net: Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv [cs.CV]. 2016. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1606.04797
Kingma DP, Ba J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv [cs.LG]. 2014. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980
Bakas S, Reyes M, Jakab A, Bauer S, Rempfler M, Crimi A, et al. Identifying the Best Machine Learning Algorithms for Brain Tumor Segmentation, Progression Assessment, and Overall Survival Prediction in the BRATS Challenge. arXiv [cs.CV]. 2018. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1811.02629
Saeed N, Hardan S, Abutalip K, Yaqub M. Is it Possible to Predict MGMT Promoter Methylation from Brain Tumor MRI Scans Using Deep Learning Models? arXiv [eess.IV]. 2022. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2201.06086
Pálsson S, Cerri S, Van Leemput K. Prediction of MGMT Methylation Status of Glioblastoma Using Radiomics and Latent Space Shape Features. arXiv [eess.IV]. 2021. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2109.12339
Kanas VG, Zacharaki EI, Thomas GA, Zinn PO, Megalooikonomou V, Colen RR. Learning MRI-based classification models for MGMT methylation status prediction in glioblastoma. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2017;140: 249–257.
Le NQK, Do DT, Chiu F-Y, Yapp EKY, Yeh H-Y, Chen C-Y. XGBoost improves classification of MGMT promoter methylation status in IDH1 wildtype glioblastoma. J Pers Med. 2020;10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10030128
Crisi G, Filice S. Predicting MGMT promoter methylation of glioblastoma from dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion: a radiomic approach. J Neuroimaging. 2020;30: 458–462.
Jiang C, Kong Z, Liu S, Feng S, Zhang Y, Zhu R, et al. Fusion radiomics features from conventional MRI predict MGMT promoter methylation status in lower grade gliomas. Eur J Radiol. 2019;121: 108714.
Hajianfar G, Shiri I, Maleki H, Oveisi N, Haghparast A, Abdollahi H, et al. Noninvasive O6 methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase status prediction in glioblastoma multiforme cancer using magnetic resonance imaging radiomics features: univariate and multivariate radiogenomics analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;132: e140–e161.
Lu Y, Patel M, Natarajan K, Ughratdar I, Sanghera P, Jena R, et al. Machine learning-based radiomic, clinical and semantic feature analysis for predicting overall survival and MGMT promoter methylation status in patients with glioblastoma. Magn Reson Imaging. 2020;74: 161–170.
Calabrese E, Villanueva-Meyer JE, Cha S. A fully automated artificial intelligence method for non-invasive, imaging-based identification of genetic alterations in glioblastomas. Sci Rep. 2020;10: 11852.
Malmström A, Łysiak M, Kristensen BW, Hovey E, Henriksson R, Söderkvist P. Do we really know who has an MGMT methylated glioma? Results of an international survey regarding use of MGMT analyses for glioma. Neurooncol Pract. 2020;7: 68–76.
Calabrese E, Rudie JD, Rauschecker AM, Villanueva-Meyer JE, Clarke JL, Solomon DA, et al. Combining radiomics and deep convolutional neural network features from preoperative MRI for predicting clinically relevant genetic biomarkers in glioblastoma. Neurooncol Adv. 2022;4: vdac060.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported in part by funding from the Mayo Clinic Center for Individualized Medicine (CIM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Gian Marco Conte and Bradley J. Erickson are co-senior authors.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Faghani, S., Khosravi, B., Moassefi, M. et al. A Comparison of Three Different Deep Learning-Based Models to Predict the MGMT Promoter Methylation Status in Glioblastoma Using Brain MRI. J Digit Imaging 36, 837–846 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-022-00757-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-022-00757-x