Abstract
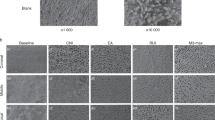
To compare four different techniques for removal of calcium hydroxide from straight root canals. The present study used the design suggested by Lee et al. (Int Endod J 37:607–612, 32) and van der Sluis et al. (Int Endod J 40:52–57, 17). One-hundred and ten extracted human teeth with straight root canals were prepared to ISO-size 50 and split longitudinally. Two lateral grooves were prepared, filled with calcium hydroxide and the root halves reassembled in a muffle. Calcium hydroxide was removed using one of five techniques: (1) passive ultrasonic irrigation, (2) hydrodynamic irrigation using RinsEndo®, (3) sonic irrigation using the EndoActivator®, (4) motor-driven plastic brush (CanalBrush™), and (5) manual irrigation with a syringe as the control group. Distilled water was used as irrigant. Cleanliness of the grooves was scored under a microscope with 40× magnification. For intraindividual reproducibility and interrater agreement, Cohens Kappa was calculated. Results of scoring were analyzed using a non-parametric test. Post hoc pairwise comparisons were used for irrigation techniques (α = 0.05). Passive ultrasonic irrigation performed significantly better than all other groups in the apical groove. Significant differences were found between RinsEndo and CanalBrush (P = 0.01855) and CanalBrush and syringe irrigation (P = 0.00021). In the coronal groove, passive ultrasonic irrigation performed significantly superior and hand irrigation performed significantly worse than all other groups. A statistically significant interaction was shown between irrigation technique and localization of the groove (P = 0.01358). The coronal grooves showed more remaining calcium hydroxide than the apical grooves. Complete removal of calcium hydroxide from the root canal could not be achieved with any of the techniques investigated. The highest degree of cleanliness resulted from the use of passive ultrasonic irrigation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byström A, Claesson R, Sundqvist G. The antibacterial effect of camphorated paramonochlorophenol, camphorated phenol and calcium hydroxide in the treatment of infected root canals. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1985;1:170–5.
Fava LR, Saunders WP. Calcium hydroxide pastes: classification and clinical indications. Int Endod J. 1999;32:257–82.
Siqueira JF Jr, Lopes HP. Mechanisms of antimicrobial activity of calcium hydroxide: a critical review. Int Endod J. 1999;32:361–9.
Guiotti FA, Kuga MC, Duarte MA, Ant’Anna AJ, Fana G. Effect of calcium hydroxide dressing on push-out strength of endodontic sealers to root canal dentin. Braz J Oral Res. 2014;28:1–6.
Barbizam JVB, Trope M, Teixeira ECN, Tanomaru-Filho M, Teixeira FB. Effect of calcium hydroxide intracanal dressing on the bond strength of a resin-based endodontic sealer. Braz Dent J. 2008;19:224–7.
Contardo L, de Luca M, Bevilacqua L, Breschi L, Di Lenarda R. Influence of calcium hydroxide debris on the quality of endodontic apical seal. Minerva Stomatol. 2007;56:509–17.
Kim SK, Kim YO. Influence of calcium hydroxide intracanal medication on apical seal. Int Endod J. 2002;35:623–8.
Böttcher DE, Hirai VH, Silva Neto UX, Grecca FS. Effect of calcium hydroxide dressing on the long-term sealing ability of two different endodontic sealers: an in vitro study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;110:386–9.
Wang C, Debelian GJ, Texeira FB. Effect of intracanal medicament on the sealing ability of root canals filled with Resilon. J Endod. 2006;32:532–6.
Margelos J, Eliades G, Verdelis C, Palaghias G. Interaction of calcium hydroxide with zinc oxide-eugenol type sealers: a potential clinical problem. J Endod. 1997;23:43–8.
Calt S, Serper A. Dentinal tubule penetration of root canal sealers after root canal dressing with calcium hydroxide. J Endod. 1999;25:431–3.
Ricucci D, Langeland K. Incomplete calcium hydroxide removal from the root canal: a case report. Int Endod J. 1997;30:418–31.
Topcuoglu HS, Düzgün S, Ceyhan KT, Akti A, Pala K, Kesim B. Efficacy of different irrigant techniques in the removal of calcium hydroxide from a simulated internal root resorption cavity. Int Endod J. 2015;48:309–16.
Keene DM, Allemang JD, Johnson JD, Hellstein J, Nichol BK. A quantitative assessment of efficacy of various calcium hydroxide removal techniques. J Endod. 2006;32:563–5.
Salgado RJC, Moura-Netto C, Yamazaki AK, Cardoso LN, de Moura AA, Prokopowitsch I. Comparison of different irrigants on calcium hydroxide medication removal: microscopic cleanliness evaluation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;107:580–4.
Rödig T, Vogel S, Zapf A, Hülsmann M. Efficacy of different irrigants in the removal of calcium hydroxide from root canals. Int Endod J. 2010;43:519–27.
van der Sluis LW, Wu MK, Wesselink PR. The evaluation of removal of calcium hydroxide paste from an artificial standardized groove in the apical root canal using different irrigation methods. Int Endod J. 2007;40:52–7.
Balvedi RP, Versiani MA, Manna FF, Biffi JC. A comparison of two techniques for the removal of calcium hydroxide from root canals. Int Endod J. 2010;43:763–8.
Wiseman A, Cox TC, Paranjpe A, Flake NM, Cohenca N, Johnson JD. Efficacy of sonic and ultrasonic activation for removal of calcium hydroxide from mesial canals of mandibular molars: a microtomographic study. J Endod. 2011;37:235–8.
Zorzin J, Wießner J, Wießner T, Lohbauer U, Petschelt A, Ebert J. Removal of radioactively marked calcium hydroxide from the root canal: influence of volume of irrigation and activation. J Endod. 2016;42:637–40.
Gu L, Kim JR, Ling J, Choi KK, Pashley DH, Tay FR. Review of contemporary irrigant agitation techniques and devices. J Endod. 2009;35:791–804.
Karatas E, Ozsu D, Arslan A. Erdogan AS (2014) Comparison of the effect of nonactivated self-adjusting file system, Vibringe, EndoVac, ultrasonic and needle irrigation on apical extrusion of debris. Int Endod J. 2015;48:317–22.
Capar ID, Ozcan E, Arslan H, Ertas H, Aydinbelge HA. Effect of different final irrigation methods on the removal of calcium hydroxide from an artificial standardized grove in the apical third of root canals. J Endod. 2014;40:451–4.
Arslan H, Akcay M, Capar ID, Saygili G, Gok T, Ertas H. An in vitro comparison of irrigation using photon-initiated photoacoustic streaming, ultrasonic, sonic and needle techniques in removing calcium hydroxide. Int Endod J. 2015;48:246–51.
Arslan H, Capar ID, Saygili G, Uysal B, Gok T, Ertas H, Topcuoglu HS. Effiacy of various irrigation protocols on the removal of triple antibiotic paste. Int Endod J. 2014;47:594–9.
Eymirli A, Nagas E, Uyanik MO, Cehreli ZC. Effect of laser-activated irrigation with ethylene diaminetetraacetic acid and phytic acid on the removal of calcium hydroxide and triple antibiotic paste from root dentin. Photomed Laser Surg. 2017;35:43–48.
Chou K, George R, Walsh LJ. Effectiveness of different intracanal irrigation techniques in removing intracanal paste medicaments. Aust Endod J. 2014;40:21–5.
Berkhoff JA, Chen PB, Teixeira FB, Diogenes A. Evaluation of triple antibiotic paste removal by different irrigation procedures. J Endod. 2014;40:1172–7.
Ma J, Shen Y, Yang Y, Gao Y, Wan P, Gan Y, Patel P, Curtis A, Khakpour M, Haapasalo M. In vitro study of calcium hydroxide removal from mandibular molar root canals. J Endod. 2015;41:553–8.
Rödig T, Hirschleb M, Zapf A, Hülsmann M. Comparison of ultrasonic irrigation and RinsEndo for the removal of calcium hydroxide and Ledermix paste from root canals. Int Endod J. 2011;44:1155–61.
Wigler R, Dvir R, Weisman A, Matalon S, Kfir A. Efficacy of XP-endo finisher files in the removal of calcium hydroxide paste from artificial standardized grooves in the apical third of oval root canals. Int Endod J. 2016. doi:10.1111/iej.12668.
Lee S, Wu M, Wesselink PR. The efficacy of ultrasonic irrigation to remove artificially placed dentine debris from different-sized simulated plastic root canals. Int Endod J. 2004;37:607–12.
Brunner E, Domhof S, Langer F. Nonparametric analysis of longitudinal data in factorial experiments. New York: Wiley & Sons; 2002. p. 187–210.
Taşdemir T, Celik D, Er K, Yildirim T, Ceyhanli KT, Yeşilyurt C. Efficacy of several techniques for the removal of calcium hydroxide medicament from root canals. Int Endod J. 2011;44:505–9.
Tay FR, Gu LS, Schoeffel GJ, Wimmer C, Susin L, Zhang K, Arun SN, Kim J, Looney SW, Pashley DH. Effect of vapor lock on root canal debridement by using a side-vented needle for positive-pressure irrigant delivery. J Endod. 2010;36:745–50.
McGill S, Gulabivala K, Mordan N, Ng YL. The efficacy of dynamic irrigation using a commercially available system (RinsEndo) determined by removal of a collagen ‘bio-molecular film’ from an ex vivo model. Int Endod J. 2008;41:602–8.
Lambrianidis T, Margelos J, Beltes P. Removal efficiency of calcium hydroxide dressing from the root canal. J Endod. 1999;25:85–8.
Lambrianidis T, Kosti E, Boutsioukis C, Mazinis M. Removal efficacy of various calcium hydroxide/chlorhexidine medicaments from the root canal. Int Endod J. 2006;39:55–61.
Hosoya N, Kurayama H, Iino F, Arai T. Effects of calcium hydroxide on physical and sealing properties of canal sealers. Int Endod J. 2004;37:178–84.
Nandini S, Velmurugan N, Kandaswamy D. Removal efficiency of calcium hydroxide intracanal medicament with two calcium chelators: volumetric analysis using spiral CT, an in vitro study. J Endod. 2006;32:1097–101.
Goldberg F, Alfie D, Roitman M. Evaluation of the incidence of transportation after placement and removal of calcium hydroxide. J Endod. 2004;30:646–8.
Rödig T, Döllmann S, Konietschke F, Hülsmann M. Effectiveness of different irrigant activation techniques on debris and smear layer removal in curved root canals. A scannning electron microscopy study. J Endod. 2010;36:1983–7.
Hauser V, Braun A, Frentzen M. Penetration depth of a dye marker into dentine using a novel hydrodynamic sytem (RinsEndo). Int Endod J. 2007;40:644–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pabel, AK., Hülsmann, M. Comparison of different techniques for removal of calcium hydroxide from straight root canals: an in vitro study. Odontology 105, 453–459 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10266-017-0293-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10266-017-0293-6