Abstract
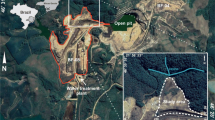
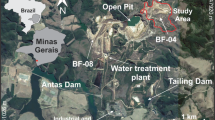
The Osamu Utsumi mine was the first to economically mine uranium ore in Brazil. During its operation, a river valley was buried for the construction of the waste rock pile. The original stream was diverted to the northwest side of the pile and has since flowed into a diversion channel devoid of basal waterproofing, while an acid mine drainage (AMD) source flows at the base of this waste rock pile. This research aims to evaluate the possible relationship between water infiltration of the diversion channel and the AMD resurgence at the base of the pile using electrical resistivity tomography and induced polarization. 2D inversion models and pseudo-3D maps allowed the recognition of low resistivity zones (< 100 Ω·m) with high chargeability areas (10 mV/V). Some of these low-resistivity areas have been interpreted as infiltration zones in segments of the diversion channel into the pile, and in one of them, the flow intercepts a high chargeability area interpreted as a sulfide-rich zone that is expected to contribute to AMD at the base of the pile. Understanding the hydrogeochemical process will help select effective actions to mitigate the generation of AMD at the mine, which is currently in the decommissioning phase.
Zusammenfassung
Der Bergbau Osamu Utsumi war die erste, in dem Uranerz in Brasilien wirtschaftlich abgebaut wurde. Während des Betriebs wurde ein Flusstal für den Bau der Halde verkippt. Der ursprüngliche Fluss wurde auf die nordwestliche Seite der Halde umgeleitet und fließt seitdem in einen Umleitungskanal ohne Basisabdichtung, während am Fuß der Halde saure Grubenwässer (AMD) austreten. Ziel dieser Untersuchung ist es, den möglichen Zusammenhang zwischen der Versickerung im Umleitungskanal und dem Wiederauftreten von AMD am Fuß der Halde mit Hilfe der Widerstandstomographie und der induzierten Polarisation zu bewerten. 2D-Inversionsmodelle und Pseudo-3D-Karten ermöglichten die Erkennung von Zonen mit niedrigem spezifischen Widerstand (< 100 Ωm) und Bereichen mit hoher Aufladbarkeit (>10 mV/V). Einige dieser Bereiche mit niedrigem Widerstand wurden als Versickerungszonen aus Abschnitten des Umleitungskanals in die Halde interpretiert. In einem dieser Bereiche durchschneidet der Fluss einen Bereich mit hoher Wiederaufladbarkeit, der als sulfidreiche Zone interpretiert wird, von der angenommen wird, dass sie zur AMD am Fuß der Halde beiträgt. Das Verständnis des hydrogeochemischen Prozesses wird dazu beitragen, wirksame Maßnahmen zur Minimierung der Entstehung von AMD im Bergbau, der sich derzeit in der Stilllegungsphase befindet, auszuwählen.
Resumen
La mina de Osamu Utsumi fue la primera en explotar económicamente el mineral de uranio en Brasil. Durante su explotación, se enterró un valle fluvial para la construcción de la pila de roca estéril. El arroyo original fue desviado hacia el lado noroeste de la pila y desde entonces fluye hacia un canal de desviación desprovisto de impermeabilización basal, mientras que una fuente de drenaje ácido de mina (DAM) fluye en la base de esta pila de roca residual. Esta investigación tiene como objetivo evaluar la posible relación entre la infiltración de agua del canal de desvío y el resurgimiento de DAM en la base de la pila utilizando la tomografía de resistividad eléctrica y la polarización inducida. Los modelos de inversión 2D y los mapas pseudo-3D permitieron reconocer zonas de baja resistividad (< 100 Ω-m) con zonas de alta cargabilidad (10 mV/V). Algunas de estas zonas de baja resistividad se han interpretado como zonas de infiltración en segmentos del canal de desviación hacia la pila, y en uno de ellos, el flujo intercepta una zona de alta cargabilidad interpretada como una zona rica en sulfuro que se espera que contribuya a la DAM en la base de la pila. La comprensión del proceso hidrogeoquímico ayudará a seleccionar acciones eficaces para mitigar la generación de AMD en la mina, que actualmente se encuentra en fase de desmantelamiento.
抽象的
Osamu Utsumi矿是巴西第一个实现铀矿经济开采的铀矿。铀矿生产期间, 废石堆填埋了一条河谷。虽然原河谷溪流已被改道至废石堆西北侧, 流向了无基底防渗的分流河道, 但是废石堆底却有一个酸性矿山废水 (AMD) 排放源。研究旨在用电阻率层析成像法和诱发极化法分析分流河道水入渗和废石堆底部酸性矿山废水 (AMD) 释放的关系。由二维反演模型和拟三维图形识别出了低电阻率区 (< 100 Ω·m) 与高荷电率区 (10 mV/V) 。一些低电阻率区被解释为分流河道河水渗入废石堆的入渗区; 而且, 其中一个低阻区的水流截断了解译的产生酸性矿山废水 (AMD) 的富硫化物高荷电率区。水文地球化学过程的了解将有助于采取有效措施, 减少目前闭坑矿山产生酸性矿山废水 (AMD) 的产生。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABEM (2012) Terrameter LS—Instruction manual. ABEM Instrument, Sundbyberg, Sweden
Akcil A, Koldas S (2006) Acid Mine Drainage (AMD): causes, treatment and case studies. J Clean Prod 14:1139–1145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2004.09.006
Alberti HL (2017) Estudo hidroquímico e isotópico das águas subterrâneas impactadas pela drenagem ácida da mina de urânio—Osamu Utsumi, Planalto de Poços de Caldas (MG). State Univ of Campinas, Thesis ((in Portuguese))
Anterrieu O, Chouteau M, Aubertin M (2010) Geophysical characterization of the large-scale internal structure of a waste rock pile from a hard rock mine. Bull Eng Geol Environ 69:533–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-010-0264-4
Capovilla MNGM (2001) Urânio nos hidrotermalitos potássicos (“rocha potássica”) da Mina Osamu Utsumi, Complexo Alcalino de Poços de Caldas. PhD Diss, Univ of São Paulo (in Portuguese), MG
Casagrande MFS, Moreira CA, Targa DA (2020) Study of generation and underground flow of acid mine drainage in waste rock pile in uranium mine using electrical resistivity tomography. Pure Appl Geophys 77:703–721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-019-02351-9
Castro M, Lima H, Flôres J (2011) Overview of mine closure in Minas Gerais. Brazil Revista Escola De Minas 64(2):205–211. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0370-44672011000200012
Cipriani M (2002) Mitigação dos impactos sociais e ambientais decorrentes do fechamento definitivo de minas de urânio. Thesis, State Univ of Campinas (in Portuguese)
Côrtes ARP, Moreira CA, Veloso DIK, Vieira LB, Bergonzoni FA (2016) Geoelectrical prospecting for a coppersulfide mineralization in the Camaquã sedimentary basin, southern Brazil. Geofís Int 55:107–117
Costa PCG (2001) Projeto hidrogeoambiental das estâncias hidrominerais da Companhia Mineradora de Minas Gerais–COMIG – Estância Hidromineral de Poços de Caldas. Technical Report, COMIG/Fundação Gorceix (Portuguese)
Dimech A, Chouteau M, Aubertin M, Bussière B, Martin V, Plante B (2019) Three-dimensional time-lapse geoelectrical monitoring of water infiltration in an experimental mine waste rock pile. Vadose Zone J 18(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2018.05.0098
Edokpayi JN, Makungo R, Mathivha F, Rivers N, Volenzo T, Odiyo JO (2020) Influence of global climate change on water resources in South Africa: toward an adaptive management approach. In: Ch 5, Water Conservation and Wastewater Treatment in BRICS Nations, Elsevier, pp 83–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818339-7.00005-9
Fagundes JRT (2005) Balanço hídrico do bota-fora BF4 da mina de Urânio Osamu Utsumi, como subsídio para projetos de remediação de drenagem ácida. In: MS Diss, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Engenharia Civil, Escola de Minas, Federal Univ of Ouro Preto, Brazil 59 (in Portuguese)
Federative Republic of Brazil (2010) Constitution of the Federative Republic of Brazil, 3rd Edition. https://www.oas.org/es/sla/ddi/docs/acceso_informacion_base_dc_leyes_pais_b_1_en.pdf
Fraenkel MO, Santos RC, Loureiro FEVL, Muniz WS (1985) Jazidas de urânio no Planalto de Poços de Caldas—Minas Gerais. In: Principais minerais do Brasil, vol 1. MMe, DNPM e CVRD, pp 89–103 (in Portuguese)
Franklin MR (2007) Modelagem numérica do escoamento hidrológico e dos processos geoquímicos aplicados à previsão da drenagem ácida em uma pilha de estéril da mina de urânio de Poços de Caldas—MG. Thesis, Federal Univ of Rio de Janeiro (in Portuguese)
Geotomo software (2003) Geoelectrical imaging 2D & 3D. https:// www.geotomosoft.com/downloads.php
Greer BM, Burbey TJ, Zipper CE, Hester ET (2017) Electrical resistivity imaging of hydrologic flow through surface coal mine valley fills with comparison to other landforms. Hydrol Process 31(12):2244–2260. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.11180
Gurin G, Tarasov A, Ilyin Y, Titotv K (2013) Time domain spectral induced polarization of disseminated electronic conductor: laboratory data analysis through the Debye decomposition approach. J Appl Geophys 98:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2013.07.008
Haddaway NR, Cooke SJ, Lesser P, Macura B, Nilsson AE, Taylor JJ, Raito K (2019) Evidence of the impacts of metal mining and the effectiveness of mining mitigation measures on social–ecological systems in Arctic and boreal regions: a systematic map protocol. Environ Evid 8:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13750-019-0152-8
Hester ET, Little KL, Buckwalter JD, Zipper CE, Burbey TJ (2019) Variability of subsurface structure and infiltration hydrology among surface coal mine valley fills. Sci Total Environ 651:2648–2661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.169
Leite JSM (2010) Previsão de drenagem ácida por meio de testes estáticos do material do bota fora 4 da mina Osamu Utsumi –Caldas/MG. Master’s diss, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Evolução Crustal e Recursos Naturais, Dept de Geologia, Escola de Minas, Federal Univ of Ouro Preto, Brazil. 59 (in Portuguese)
Lghoul M, Sbihi K, Maqsoud A, Hakkou R, Kchikach A (2021) Remediation scenario of the abandoned Kettara mine site (Morocco): acid mine drainage (AMD) transport modeling. SN Appl Sci 3:702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04690-6
Loke MH, Baker RD (1996) Rapid least squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections by quasi-Newton method. Geophys Prospect 44:131–152. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2478.1996.tb00142.x
Martín-Crespo T, Gómes-Ortiz D, Marín-Velázquez S, Martínez-Pagán P, Ignacio C, Lillo J, Faz A (2018) Geoenvironmental characterization of unstable abandoned mine waste rocks combining geophysical and geochemical methods (Cartagena-La Union district, Spain). Eng Geol 232:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.11.018
Martínez-Pagán P, Gómez-Ortiz D, Martín-Crespo T, Martín-Velázquez S, Martínez-Segura M (2021) Electrical resistivity imaging applied to waste rocks ponds: an overview. Mine Water Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-020-00741-3
Moon CJ, Whateley MEG, Evans AM (2006) Introduction to mineral exploration. Backwell Publishing, Oxford
Moreira CA, Carrara A, Helene LPI, Hansen MAF, Malagutti Filho W, Dourado JC (2017a) Electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) applied in the detection of inorganic contaminants in suspended aquifer in Leme city (Brazil). Rev Brasil De Geofís 35:213–225. https://doi.org/10.22564/rbgf.v35i3.848
Moreira CA, Helene LPI, Côrtes ARP (2017b) DC resistivity method applied in the monitoring of diesel leakage in a railway accident in São Manuel city, São Paulo State (Brazil). Rev Brasil De Geofís 35:5–14. https://doi.org/10.22564/rbgf.v35i1.969
Moreira CA, Casagrande MFS, Büchi FMS, Targa DA (2020) Hydrogelogical characterization of a waste rock pile and bedrock affected by acid mine drainage from geophysical survey. SN Appl Sci 2:1236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-3021-8
Moreira CA, Lapola MM, Carrara A (2016) Comparative analyzes among electrical resistivity tomography arrays in the characterization of flow structure in free aquifer. Geofís Int, 55(2):119–129. http://revistagi.geofisica.unam.mx/index.php/RGI/article/view/1716/1592
Morin KA, Gerencher E, Jones CE, Konasewich DE (1991) Critical literature review of acid drainage from waste rock. MEND Rep 1(11):1
Moyé J, Picard-Lesteven T, Zouhri L, Amari KE, Hibti M, Benkaddour A (2017) Groundwater assessment and environmental impact in the abandoned mine of Kettara (Morocco). Environ Pollut 231:899–907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.044
Nobes DC (1996) Troubled waters: environmental applications of electrical and electromagnetic methods. Surv Geophys 17:393–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01901640
Nordstrom DK, Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ (2015) Hydrogeochemistry and microbiology of mine drainage: an update. Appl Geochem 57:3–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.02.008
Okpoli CC (2013) Sensitivity and resolution capacity of electrode configurations. Int J Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/608037
Pardo Abad CJ (2019) Environmental recovery of abandoned mining areas in Spain: sustainability and new landscapes in some case studies. J Sustain Res 1:e190003. https://doi.org/10.20900/jsr20190003
Pearce S, Lehane S, Pearce J (2016) Waste material placement options during construction and closure risk reduction—quantifying the how, the why and the how much. In: AB Fourie & M Tibbett (eds). Mine Closure, Australian Centre for Geomechanics. https://doi.org/10.36487/ACG_rep/1608_51_Pearce
Poisson J, Chouteau M, Aubertin M, Campos D (2009) Geophysical experiments to image the shallow internal structure and the moisture distribution of a mine waste rock pile. J Appl Geophys 67:179–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2008.10.011
Power C, Tsourlos P, Ramasamy M, Nivorlis A, Mkandawire M (2018) Combined DC resistivity and induced polarization (DC-IP) for mapping the internal composition of a mine waste rock pile in Nova Scotia, Canada. J Appl Geophys 150:40–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2018.01.009
Rey J, Martínez J, Hidalgo MC, Mendoza R, Sandoval S (2021) Assessment of tailings ponds by a combination of electrical (ERT and IP) and hydrochemical techniques (Linares, southern Spain). Mine Water Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-020-00709-3
Rubio RF (2012) Mining: the challenge knocks on our door. Mine Water Environ 31:69–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-012-0169-5
Schorscher HD, Shea ME (1992) The regional geology of the Poços de Caldas alkaline complex: mineralogy and geochemistry of selected nepheline syenites and phonolites. J Geochem Explor 45:25–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6742(92)90121-N
Skousen JG, Ziemkiewicz PF, McDonald LM (2018) Acid mine drainage formation, control and treatment: approaches and strategies. Extractive Ind Soc 6(1):241–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exis.2018.09.008
Smith FW, Underwood B (2000) Mine closure: the environmental challenge. Min Technol 109(3):202–209. https://doi.org/10.1179/mnt.2000.109.3.202
Targa DA, Moreira CA, Camarero PL, Casagrande MFC, Alberti HLC (2019) Structural analysis and geophysical survey for hydrogeological diagnosis in uranium mine, Poços de Caldas (Brazil). SN Appl Sci 1:299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0309-7
Targa DA, Moreira CA, Casagrande MFS (2021) Hydrogeological analysis of sulfide waste rocks at a uranium mine using geophysical and hydrochemical methods. Mine Water Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-021-00791-1
Valeton I, Schumann A, Vinx R, Wieneke M (1997) Supergene alteration since the upper cretaceous on alkaline igneous and metasomatic rocks of the Poços de Caldas ring complex, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Appl Geochem 12:133–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(96)00060-1
Veloso DIK, Moreira CA, Côrtes ARP (2015) Integration of geoelectrical methods in the diagnostic of a diesel contaminated site in Santa Ernestina (SP, Brazil). Rev Brasil De Geofís 33(4):667–676. https://doi.org/10.22564/rbgf.v33i4.760
Vieira LB, Moreira CA, Côrtes ARP, Luvizotto GL (2016) Geophysical modeling of the manganese deposit for induced polarization method in Itapira (Brazil). Geofís In 55:107–117. http://revistagi.geofisica.unam.mx/index.php/RGI/article/view/1715/1591
Waber N, Schorscher HD, Tj P (1992) Hydrothermal and supergene uranium mineralization at the Osamu Utsumi mine, Poços de Ca1das, Minas Gerais, Brazil. J Geochem Explor 45:53–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6742(92)90122-O
Warhate SR, Yenkie MKN, Chaudhari MD, Pokale WK (2006) Impacts of mining activities on water and soil. J Environ Sci Eng 48(2):81–90
Wilson GW (2011) Rock dump hydrology: an overview of full-scale excavations and scale-up experiments conducted during the last two decades. In: Bell LC, Braddock B (Eds), Proc, 7th Australian Workshop on Acid and Metalliferous Drainage, pp 307–322
Wolkersdorfer C, Bowell R (2005) Contemporary reviews of mine water studies in Europe, Part 3. Mine Water Environ 24:58–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-005-0074-2
Younger PL, Wolkersdorfer C (2004) Mining impacts on the fresh water environment: technical and managerial guidelines for catchment scale management. Mine Water Environ 23:s2–s80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-004-0028-0
Yuval D, Oldenburg W (1996) DC resistivity and IP methods in acid mine drainage problems: results from the Copper Clif mine waste rocks impoundments. J Appl Geophys 34:187–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-9851(95)00020-8
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) for funding the project “Sustainable decommissioning: analysis of hydrogeological behaviour in rock massifs and their influence on geotechnical stability in open pit mine slopes and acid mine drainage generation” (2020/14647-0), the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) for financial support, and the INB for collaborating and allowing the fieldwork, with technical support and access to data and the study area.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
do Nascimento, M.M.P.F., Moreira, C.A., Duz, B.G. et al. Geophysical Diagnosis of Diversion Channel Infiltration in a Uranium Waste Rock Pile. Mine Water Environ 41, 704–720 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-022-00878-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-022-00878-3