Abstract
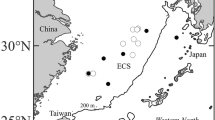
We examined morphological and molecular characteristics of individuals of Macroramphosus in Japanese waters (the East China Sea and the northwestern Pacific). Two morphotypes (M. scolopax-type and M. gracilis-type) that were differentiated based on 10 quantitative morphological characters were not supported by molecular analyses using nuclear and mitochondrial DNA markers, while a genetic deviation was observed between populations of Macroramphosus from the northwestern Pacific and the northeastern Atlantic. Macroramphosus scolopax-type and M. gracilis-type individuals are thought to be intraspecific morphotypes adapted to plankton and benthos feeding, respectively.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson J (2003) Effects of diet-induced resource polymorphism on performance in arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus). Evol Ecol Res 5:213–228
Bandelt H-J, Foster P, Röhl A (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 16:37–48
Bilecenoglu M (2006) Status of the genus Macroramphosus (Syngnathiformes: Centriscidae) in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Zootaxa 1273:55–64
Bleeker P (1852) Bijdrage tot de kennis der ichthyologische fauna van Singapore. Natuurkundig Tijdschrift voor Nederlandsch Indië 3:51–86
Chow S, Hazama K (1998) Universal PCR primers for S7 ribosomal protein gene introns in fish. Mol Ecol 7: 1255–1256
Clarke TA (1984) Diet and morphological variation in snipefishes, presently recognized as Macroramphosus scolopax, from southeast Australia: evidence from two sexually dimorphic species. Copeia 1984:595–608
Ehrich S (1976) On the taxonomy, ecology and growth of Macroramphosus scolopax (Linnaeus, 1758) (Pisces, Syngnathiformes) from the subtropical northeast Atlantic. Ber dt wiss Kommn Meeresforsch 24:251–266
Ehrich S, John H-C (1973) The biology and ecology of Macrorhamphosid fishes off northwest Africa and suggestions to the age-composition of the adult stocks of the Great Meteor Seamount. “Meteor” Forsch-Ergebnisse Ser D 14:87–98
Hasegawa M, Kishino H, Yano T (1985) Dating of the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. J Mol Evol 22:160–174
Kristjánsson BK, Skúlason S, Noakes DLG (2002) Morphological segregation of Icelandic threespine stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus L). Biol J Linn Soc 76:247–257
Kuranaga I, Sasaki K (2000) Larval development in a snipefish (Macroramphosus scolopax) from Japan with notes on eastern Pacific and Mediterranean Macroramphosus larvae (Gasterosteiformes, Macroramphosidae). Ichthyol Res 47:101–106
Lacepède BGE (1803) Histoire naturelle des poissons, vol 5. Chez Plassan, Paris
Linnaeus C (1758) Systema naturae, 10th edition, vol 1. Laurentii Salvii, Holmiae
Lowe RT (1839) A supplement to a synopsis of fishes of Madeira. Proc Zool Soc Lond 7:76–92
Matthiessen B, Fock HO, von Westernhagen H (2003) Evidence for two sympatric species of snipefishes Macroramphosus spp. (Syngnathiformes, Centriscidae) on Great Meteor Seamount. Helgol Mar Res 57:63–72
Miyazaki E, Sasaki K, Mitani T, Ishida M, Uehara S (2004) The occurrence of two species of Macroramphosus (Gasterosteiformes: Macroramphosidae) in Japan: morphological and ecological observations on larvae, juveniles, and adults. Ichthyol Res 51:256–262
Mohr E (1937) Revision of Centriscidae (Acanthopterygii, Centrisciformes). Dana Rep 13:1–69
Okada Y, Suzuki K (1951) A review of the Macroramphosus fishes of Japan. Rep Fac Fish Pref Univ Mie 1:7–11
Oksanen J, Kindt R, Legendre P, O’Hara B, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Wagner H (2008) vegan: Community Ecology Package. http://cran.r-project.org/ and http://vegan.r-forge.r-project.org/. Accessed 12 June 2014
Olsson J, Eklöv P (2005) Habitat structure, feeding mode and morphological reversibility: factors influencing phenotypic plasticity in perch. Evol Ecol Res 7:1109–1123
Ostellari L, Bargelloni L, Penzo E, Patarnello P, Patarnello T (1996) Optimization of single-strand conformation polymorphism and sequence analysis of the mitochondrial control region in Pagellus bogaraveo (Sparidae, Teleostei): Rationalized tools in fish population biology. Anim Genet 27:423–427
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
R Development Core Group (2008) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria
Robalo JI, Sousa-Santos C, Cabral H, Castilho R, Almada VC (2009) Genetic evidence fails to discriminate between Macroramphosus gracilis Lowe 1839 and Macroramphosus scolopax Linnaeus 1758 in Portuguese waters. Mar Biol 156:1733–1737
Rodríguez F, Oliver JF, Marín A, Medina JR (1990) The general stochastic model of nucleotide substitution. J Theor Biol 142:485–501
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MRBAYES 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Smith TB, Skúlason S (1996) Evolutionary significance of resource polymorphisms in fishes, amphibians, and birds. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 27:111–133
Stamatakis A (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22:2688–2690
Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J (2008) A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML web-servers. Syst Biol 57:758–771
Swanson BO, Gibb AC, Marks JC, Hendrickson DA (2003) Trophic polymorphism and behavioral differences decrease intraspecific competition in a cichlid, Herichthys minckleyi. Ecology 84:1441–1446
Swofford DL (2002) PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Whiteley AR (2007) Trophic polymorphism in a riverine fish: morphological, dietary, and genetic analysis of a mountain whitefish. Biol J Linn Soc 92:253–267
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Prof. K. Sasaki, Kochi University, and Mr. K. Shimizu and Mr. N. Yamawaki, Nagasaki University for providing the specimens. We thank the captains, officers, and crew members of T/V Nagasaki-maru of Nagasaki University and R/V Wakataka-maru of Tohoku National Fisheries Research Institute, Fisheries Research Agency, for their support in specimen sampling. We also thank Prof. J. Pabalo and the anonymous reviewers for many helpful comments on our manuscript. All experiments comply with the current laws of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article was registered in the Official Register of Zoological Nomenclature (ZooBank) as DDF0EB17-0748-49F5-8E5D-C1E95ACF1669.
This article was published as an Online First article on the online publication date shown on this page. The article should be cited by using the doi number.
About this article
Cite this article
Noguchi, T., Sakuma, K., Kitahashi, T. et al. No genetic deviation between two morphotypes of the snipefishes (Macroramphosidae: Macroramphosus) in Japanese waters. Ichthyol Res 62, 368–373 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-014-0443-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-014-0443-6