Abstract
Objectives
To find the economic burden of COPD and to identify the key cost drivers in the management of COPD patients across different European countries.
Background
COPD is a major cause of mortality and morbidity and is associated with considerable economic burden on the individual and society. It limits the daily activities and working ability of the patients.
Methodology
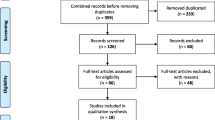
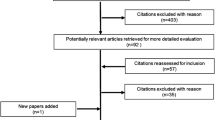
We conducted a systematic search of PUBMED, SCIENCE DIRECT, Cochrane CENTRAL, SCOPUS, Google Scholar and SAGE Premier Databases to find scientific research articles evaluating the cost of COPD management from patient and societal perspective.
Results
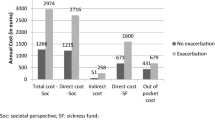
Estimated per patient per year direct cost in Norway, Denmark, Germany, Italy, Sweden, Greece, Belgium, and Serbia was €10,701, €9580, €7847, €7448, €7045, €2896, €1963, and €2047, respectively. Annual per patient cost of work productivity loss was highest in Germany as €5735 and lowest in Greece as €998. It was estimated as €4824, €2033 and €1298 in Bulgaria, Denmark and Sweden, respectively. Several factors found associated with increasing cost of COPD management that include but not limited to late diagnosis, severity of disease, frequency of exacerbation, hospital readmissions, non-adherence to the therapy and exposure to COPD risk factors.
Conclusion
Minimizing the COPD exacerbations and controlling the worsening of symptoms may potentially reduce the cost of COPD management at any stage.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vogelmeier, C.F., Criner, G.J., Martinez, F.J., Anzueto, A., Barnes, P.J., Bourbeau, J., et al.: Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease 2017 report. GOLD executive summary. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 195(5), 557–582 (2017)
Blanco, I., Diego, I., Bueno, P., Fernández, E., Casas-Maldonado, F., Esquinas, C., et al.: Geographical distribution of COPD prevalence in Europe, estimated by an inverse distance weighting interpolation technique. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 13, 57 (2018)
World Health Organization http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs315/en/.. 2018. Accessed 21 August 2018
Molinari, N., Chanez, P., Roche, N., Ahmed, E., Vachier, I., Bourdin, A.: Rising total costs and mortality rates associated with admissions due to COPD exacerbations. Respir. Res. 17(1), 149 (2016)
ur Rehman A, Hassali MAA, Abbas S, Ali IABH, Harun SN, Muneswarao J et al. Pharmacological and non-pharmacological management of COPD; limitations and future prospects: a review of current literature. Journal of Public Health. 2019:1-10
Polatli, M., Kheder, A.B., Wali, S., Javed, A., Khattab, A., Mahboub, B., et al.: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and associated healthcare resource consumption in the Middle East and North Africa: the BREATHE study. Respir. Med. 106, S75–S85 (2012)
Rothnie, K.J., Müllerová, H., Thomas, S.L., Chandan, J.S., Smeeth, L., Hurst, J.R., et al.: Recording of hospitalizations for acute exacerbations of COPD in UK electronic health care records. Clin. Epidemiol. 8, 771 (2016)
European lung white book. https://www.erswhitebook.org/chapters/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease/. 2013. Accessed September 16 2018
May SM, Li JT, editors. Burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: healthcare costs and beyond. Allergy and asthma proceedings; 2015: OceanSide Publications
Thornton Snider, J., Romley, J.A., Wong, K.S., Zhang, J., Eber, M., Goldman, D.P.: The disability burden of COPD. COPD: Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 9(5), 513–521 (2012)
Soriano, J.B., Abajobir, A.A., Abate, K.H., Abera, S.F., Agrawal, A., Ahmed, M.B., et al.: Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine 5(9), 691–706 (2017)
Srivastava, K., Thakur, D., Sharma, S., Punekar, Y.S.: Systematic review of humanistic and economic burden of symptomatic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pharmacoeconomics 33(5), 467–488 (2015)
Bustacchini, S., Chiatti, C., Furneri, G., Lattanzio, F., Mantovani, L.G.: The economic burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the elderly: results from a systematic review of the literature. Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine 17(Suppl 1), S35–S41 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mcp.0000410746.82840.79
Miravitlles, M., Vogelmeier, C., Roche, N., Halpin, D., Cardoso, J., Chuchalin, A.G., et al.: A review of national guidelines for management of COPD in Europe. Eur. Respir. J. 47(2), 625–637 (2016)
Liberati, A., Altman, D.G., Tetzlaff, J., Mulrow, C., Gøtzsche, P.C., Ioannidis, J.P., et al.: The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Medicine 6(7), e1000100 (2009)
Higgins, J.P., Green, S.: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Wiley, Hoboken (2011)
Larg, A., Moss, J.R.: Cost-of-illness studies. Pharmacoeconomics 29(8), 653–671 (2011)
Official Data Foundation. CPI inflation Calculator. http://www.in2013dollars.com/Euro-inflation. 2018. Accessed October 15 2018
Punekar, Y.S., Shukla, A., Müllerova, H.: COPD management costs according to the frequency of COPD exacerbations in UK primary care. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 9, 65 (2014)
Souliotis, K., Kousoulakou, H., Hillas, G., Tzanakis, N., Toumbis, M., Vassilakopoulos, T.: The direct and indirect costs of managing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Greece. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 12, 1395 (2017)
Stafyla, E., Geitona, M., Kerenidi, T., Economou, A., Daniil, Z., Gourgoulianis, K.I.: The annual direct costs of stable COPD in Greece. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 13, 309 (2018)
Blasi, F., Cesana, G., Conti, S., Chiodini, V., Aliberti, S., Fornari, C., et al.: The clinical and economic impact of exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a cohort of hospitalized patients. PLoS ONE 9(6), e101228 (2014)
Dal Negro, R.W., Bonadiman, L., Turco, P., Tognella, S., Iannazzo, S.: Costs of illness analysis in Italian patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): an update. ClinicoEconomics and Outcomes Research: CEOR 7, 153 (2015)
Jakovljevic, M., Lazic, Z., Verhaeghe, N., Jankovic, S., Gajovic, O., Annemans, L.: Direct medical costs of COPD diagnosis and treatment, Eastern vs Western European country: examples of Serbia and Belgium. Farmeconomia, Health Economics and Therapeutic pathways 14(4), 161–168 (2013)
Jansson, S.-A., Backman, H., Stenling, A., Lindberg, A., Rönmark, E., Lundbäck, B.: Health economic costs of COPD in Sweden by disease severity–has it changed during a 10 years period? Respir. Med. 107(12), 1931–1938 (2013)
Jensen, M.B., Fenger-Gron, M., Fonager, K., Omland, O., Vinding, A.L., Hansen, J.G.: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease involves substantial health-care service and social benefit costs. Danish Medical Journal 60(1), A4557 (2013)
Karl, F.M., Holle, R., Bals, R., Greulich, T., Jörres, R.A., Karch, A., et al.: Costs and health-related quality of life in Alpha-1-Antitrypsin Deficient COPD patients. Respir. Res. 18(1), 60 (2017)
Lisspers, K., Larsson, K., Johansson, G., Janson, C., Costa-Scharplatz, M., Gruenberger, J.-B., et al.: Economic burden of COPD in a Swedish cohort: the ARCTIC study. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 13, 275 (2018)
Løkke, A., Hilberg, O., Tønnesen, P., Ibsen, R., Kjellberg, J., Jennum, P.: Direct and indirect economic and health consequences of COPD in Denmark: a national register-based study: 1998–2010. BMJ Open 4(1), e004069 (2014)
Menn, P., Heinrich, J., Huber, R.M., Jörres, R.A., John, J., Karrasch, S., et al.: Direct medical costs of COPD–an excess cost approach based on two population-based studies. Respir. Med. 106(4), 540–548 (2012)
Nielsen, R., Johannessen, A., Omenaas, E.R., Bakke, P.S., Askildsen, J.E., Gulsvik, A.: Excessive costs of COPD in ever-smokers. A longitudinal community study. Respir. Med. 105(3), 485–493 (2011)
Wacker, M., Jörres, R., Schulz, H., Heinrich, J., Karrasch, S., Karch, A., et al.: Direct and indirect costs of COPD and its comorbidities: results from the German COSYCONET study. Respir. Med. 111, 39–46 (2016)
Geitona, M., Hatzikou, M., Steiropoulos, P., Alexopoulos, E.C., Bouros, D.: The cost of COPD exacerbations: a university hospital–based study in Greece. Respir. Med. 105(3), 402–409 (2011)
Kayyali, R., Odeh, B., Frerichs, I., Davies, N., Perantoni, E., D’arcy, S., et al.: COPD care delivery pathways in five European Union countries: mapping and health care professionals’ perceptions. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 11, 2831 (2016)
Byng, D., Lutter, J.I., Wacker, M.E., Jörres, R.A., Liu, X., Karrasch, S., et al.: Determinants of healthcare utilization and costs in COPD patients: first longitudinal results from the German COPD cohort COSYCONET. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 14, 1423 (2019)
Pavlovic R, Stojkov S, Binakaj Z. Costs of treatment of severe COPD exacerbation in Serbia. Serbian Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research. 2018
Merino, M., Villoro, R., Hidalgo-Vega, Á., Carmona, C.: social economic costs of COPD in extremadura (spain): an observational study. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 13, 2501 (2018)
Ding, B., Small, M., Bergström, G., Holmgren, U.: COPD symptom burden: impact on health care resource utilization, and work and activity impairment. International journal of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 12, 677 (2017)
Foo, J., Landis, S.H., Maskell, J., Oh, Y.-M., van der Molen, T., Han, M.K., et al.: Continuing to confront COPD international patient survey: economic impact of COPD in 12 countries. PLoS ONE 11(4), e0152618 (2016)
Tachkov, K., Kamusheva, M., Pencheva, V., Mitov, K.: Evaluation of the economic and social burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 31(4), 855–861 (2017)
Mulpuru, S., McKay, J., Ronksley, P.E., Thavorn, K., Kobewka, D.M., Forster, A.J.: Factors contributing to high-cost hospital care for patients with COPD. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 12, 989 (2017)
Ke, X., Marvel, J., Yu, T.-C., Wertz, D., Geremakis, C., Wang, L., et al.: Impact of lung function on exacerbations, health care utilization, and costs among patients with COPD. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 11, 1689 (2016)
Hurst, J.R., Vestbo, J., Anzueto, A., Locantore, N., Müllerova, H., Tal-Singer, R., et al.: Susceptibility to exacerbation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 363(12), 1128–1138 (2010)
Fuhrman, C., Roche, N., Vergnenègre, A., Zureik, M., Chouaid, C., Delmas, M.-C.: Hospital admissions related to acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in France, 1998–2007. Respir. Med. 105(4), 595–601 (2011)
Larsson KÅ, Janson C, Ställberg B, Lisspers K, Olsson P, Kostikas K et al. Extent and impact of late vs early stage COPD diagnosis in the Swedish ARCTIC study. Eur Respiratory Soc; 2016
Yin H-L, Yin S-Q, Lin Q-Y, Xu Y, Xu H-W, Liu T. Prevalence of comorbidities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients: a meta-analysis. Medicine. 2017;96(19)
Eurostat. Eurostat regional yearbook. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Healthcare_expenditure_statistics. 2018. Accessed October 18 2018
Statistics Norway. Prices and Prices Indices in Norway. https://www.ssb.no/en/omssb/om-oss. 2018. Accessed October 10 2018
TEO WSK, TAN WS, CHONG WF, Abisheganaden J, LEW YJ, LIM TK et al. Economic burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respirology. 2012;17(1):120-6
Tsiachristas, A., Burgers, L., Rutten-van Mölken, M.P.: Cost-effectiveness of disease management programs for cardiovascular risk and COPD in the Netherlands. Value in Health 18(8), 977–986 (2015)
Ruparel M, Lopez-Campos JL, Castro-Acosta A. Understanding variation in length of hospital stay for COPD exacerbation: European COPD audit. European Respitatory Journal Open Research. 2016;2(1)
Vogler, S., Zimmermann, N., Babar, Z.U.: Price comparison of high-cost originator medicines in European countries. Expert review of pharmacoeconomics & outcomes research. 17(2), 221–230 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/14737167.2016.1223543
de Oca, M.M., Aguirre, C., Varela, M.V.L., Laucho-Contreras, M.E., Casas, A., Surmont, F.: exacerbations and health care resource utilization in patients with airflow limitation diseases attending a primary care setting: the PUMa study. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 11, 3059 (2016)
Mapel, D.W., Dalal, A.A., Blanchette, C.M., Petersen, H., Ferguson, G.T.: Severity of COPD at initial spirometry-confirmed diagnosis: data from medical charts and administrative claims. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 6, 573 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to the teaching faculty of school of pharmaceutical science, University Sains Malaysia, who gave their valuable feedback on the systematic review and library staff for searching and requesting the full-text articles from the authors.
Funding
No funding was received from any source for the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rehman, A.u., Hassali, M.A.A., Muhammad, S.A. et al. The economic burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in Europe: results from a systematic review of the literature. Eur J Health Econ 21, 181–194 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-019-01119-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10198-019-01119-1