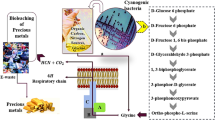
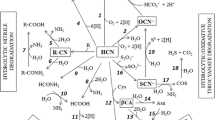
Abstract
Cyanide is a known toxic chemical compound that has an adverse effect on living organisms. Nonetheless, it is one of the active reagents in industries such as mining, pharmaceutical, cosmetics, and food processing companies worldwide. The beneficiation of gold and other precious metals from ore generates great amount of cyanide-bearing contaminants, which is released into the environment. The abundance of cyanide contaminants from these industries have created public health concern since the inception of metal extraction from ore. There are strict regulations on the production, transportation, utilization, and disposal of cyanide-bearing contaminants worldwide. The conventional treatment of cyanide waste is either chemical or physical process. The use of these treatment processes has certain pitfalls like operational challenges, an increase in capital cost, and generation of secondary waste. A number of microorganisms have the potential to utilize cyanide as nitrogen and carbon source and transform it into ammonia and carbon dioxide. Biodetoxification might be efficiently, economically and environmentally safe to detoxify cyanide in contaminants and attractive alternative to conventional detoxification method like chemical or physical. This paper reviews the principles and methods of biodetoxification of cyanide contaminants found in the ecosystem.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith A (1988) Cyanide degradation and detoxification in a heap leach. In: van Zyl JA, Ian H, Kiel J. (eds) Introduction to evaluation, design and operation of precious metal heap leaching projects, 1st edn. Society for Mining Metallurgy, pp 293–305
Nazly N, Knowles CJ (1981) Cyanide degradation by immobilised fungi. Biotechnol Lett 3(7):363–368
Botz MM (2001) Overview of cyanide treatment methods. In: Mudder T (ed) Mining environmental management. Mining Journal Books Ltd., London, pp 28–30
Williamson A, Johnson MS (1981) Reclamation of metalliferous mine wastes. In: Lepp NW (eds) Effect of heavy metal pollution on plants. Pollution Monitoring Series, vol 2. Springer, Dordrecht. pp. 185–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-8099-0_6.
Sinha R, Valani D, Sinha S et al (2010) Bioremediation of contaminated sites: a low-cost nature’s biotechnology for environmental clean up by versatile microbes, plants & earthworms. In: Faerber T, Herzog J (eds) Solid waste management and environmental remediation. Nova Science, USA
Rodger PB (1981) Cyanide degradation by Chromobacterium violaceum. In: Vennesland B, Conn EE, Knowles CJ, Westley J, Wissing F (eds) Cyanide in biology. Academic Press, New York, pp 301–310
Akcil A, Karahan A, Ciftci H et al (2003) Biological treatment of cyanide by natural isolated bacteria (Pseudomonas sp). J Miner Eng 16(7):643–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0892-6875(03)00101-8
Young C, Jordan T (1995) Cyanide remediation: current and past technologies. In: Proceedings of the 10th Annual Conference on Hazardous Waste Research. May 23–24, 1995, Kansas State Univ., Manhattan, Kansas, USA
Cabuk A, Unal AT, Kolankaya N (2006) Biodegradation of cyanide by a white rot fungus Trametes versicolor. Biotechnol Lett 28(16):1313–1317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9090-y
Nelson L (2006) Acute cyanide toxicity: mechanisms and manifestations. J Emerg Nurs 32(4):8–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jen.2006.05.012
Andrews SC, Robinson AK, Rodríguez-Quiñones F (2003) Bacterial iron homeostasis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27(2–3):215–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-6445(03)00055-X
Alexander M (1994) Biodegradation and bioremediation, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York
Ebbs S (2004) Biological degradation of cyanide compounds. Curr Opin Biotechnol 15(3):231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2004.03.006
Ezzi MI, Lynch JM (2005) Biodegradation of cyanide by Trichoderma spp. and Fusarium spp. Enzyme Microbial Technol 36(7):849–854
Figueria M, Ciminelli V, De Andrade M et al (1996) Cyanide degradation by an Escherichia coli strain. Can J Microbiol 42(5):519–523. https://doi.org/10.1139/m96-070
Goncalves M, Pinto A, Granato M (1998) Biodegradation of free cyanide, thiocyanate and metal complexed cyanides in solutions with different compositions. J Environ Technol 19(2):133–142. https://doi.org/10.1080/0959333190861665
Igeño MI, Orovengua E, Guijo MI et al (2007) Biodegradation of cyanide-containing wastes by Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes CECT5344. Commun Curr Res Educ Topics Trends Appl Microbiol 1:100–107
Kuyucak N, Akcil A (2013) Cyanide and removal options from effluents in gold mining and metallurgical processes. Miner Eng 50:13–29
Maniyam MN, Sjahrir F, Ibrahim A et al (2013) Biodegradation of cyanide by Rhodococcus UKMP-5M. Biologia 68(2):177–185. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-013-0158-6
Watts MP, Moreau JW (2018) Thiocyanate biodegradation: harnessing microbial metabolism for mine remediation. Microbiol Aust 39(3):157–161
Baxter J, Cummings S (2006) The impact of bioaugmentation on metal cyanide degradation and soil bacteria community structure. J Biodegrad 17(3):207–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-005-4219-6
Dash RR, Gaur A, Balomajumder C (2009) Cyanide in industrial wastewaters and its removal: a review on biotreatment. J Hazard Mater 163(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.051
Lu Z, Cai M (2012) Disposal methods on solid wastes from mines in transition from open-pit to underground mining. Proc Environ Sci 16:715–721
Akcil A (2002a) Cyanide control in tailings pond: ovacik gold mine, Turkey. In: Proceedings of Seventh International Symposium on Environmental Issues and Waste Management in Energy and Mineral Production (SWEMP), 7–10 october, 2002, Cagliar, sardinia, Italy, 437–441. Kluwer Academic Publishers. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022608213814
Jaszczak E, Polkowska Ż, Narkowicz S, Namieśnik J (2017) Cyanides in the environment, analysis, problems and challenges. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(19):15929–15948
Dzombak DA, Ghosh RS, Young TC (2005) Physical–chemical properties and reactivity of cyanide in water and soil. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 69–104
Anning C, Wang J, Chen P, Batmunkh I et al (2019) Determination and detoxification of cyanide in gold mine tailings: a review. Waste Manag Res 37(11):1117–1126
Borgerding M, Klus H (2005) Analysis of complex mixtures–cigarette smoke. Exp Toxicol Pathol 57:43–73
Raybuck SA (1992) Microbes and microbial enzymes for cyanide degradation. J Biodegrad 3(1):3–18
Baskin SI, Kelly JB, Maliner BI, Rockwood GA et al (2008) Cyanide poisoning. Med Asp Chem Warf 11:372–410
Gail E, Gos S, Kulzer R, Lorösch J, Rubo A et al (2000) Cyano compounds, inorganic. Ullmann's Encycl Ind Chem 5:171–188. https://doi.org/10.1002/14356007.a08_159.pub3
Luque-Almagro VM, Moreno-Vivián C, Roldán MD (2016) Biodegradation of cyanide wastes from mining and jewellery industries. Curr Opin Biotechnol 38:9–13
Luque-Almagro VM, Huertas MJ, Martínez-Luque M et al (2005) Bacterial degradation of cyanide and its metal complexes under alkaline conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(2):940–947. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.2.940-947.2005
Haghighi-Podeh MR, Siyahati-Ardakani G (2000) Fate and toxic effect of cyanide on aerobic treatment system. Water Sci Technol 4(3–4):125–129. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2000.0368
Solomonson LP (1981) Cyanide as a metabolic inhibitor. In: Vannesland B, Conn EE, Knowles CJ, Westly J, Wissing F (eds) Cyanide in biology. Academic press, New York, pp 11–28
Yu X-Z (2015) Uptake, assimilation and toxicity of cyanogenic compounds in plants: facts and fiction. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12(2):763–774. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0571-6
Gleadow RM, Woodrow IE (2002) Mini-review: constraints on effectiveness of cyanogenic glycosides in herbivore defense. J Chem Ecol 28(7):1301–1313. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016298100201
Botz MM, Mudder TI, Akcil A (2005) Cyanide treatment: physical, chemical and biological process. In: Adams M (ed) Advances in gold ore processing. Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam, pp 672–700
Lieberei R, Biehl B, Giesemann A et al (1989) Cyanogenesis inhibits active defense reactions in plants. Plant Physiol 90(1):33–36. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp90.1.33
Kjeldsen P (1999) Behaviour of cyanides in soil and groundwater: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut 115:279–308
Kulig KW, Ballantyne B (1991) Cyanide toxicity. In: Case studies in environmental medicine. Agency for toxic substance and diseases Registry (ATSDR). 15: 5–7
Rubec PJ, Soundararajan R (1990) Chronic toxic effects of cyanide on tropical marine fish. In: Proceedings of the Seventeenth Annual Toxicity Workshop: November 5–7, 1990, Vancouver, BC, Canada.
Leduc G (1984) Cyanides in water: toxicology significance. In: Weber LJ (ed) Aquatic toxicology. Raven Press, New York, pp 153–224
Wiemeyer SN, Hill EF, Carpenter JW et al (1986) Acute oral toxicity of sodium cyanide in birds. J Wildl Dis 22(4):538–546. https://doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-22.4.538
Davis RH (1981) Cyanide detoxification in domestic fowl. In: Vannesland B, Conn EE, Knowles CJ, Westly J, Wissing F (eds) Cyanide in biology. Academic press, New York, NY, pp 57–60
Arya AK, Singh A, Bhatt D (2019) Pesticide applications in agriculture and their effects on birds: an overview. In: Contaminants in agriculture and environment: health risks and remediation 5:10
Kadiri H, Asagba SO (2019) The chronic effects of cyanide on oxidative stress indices in the domestic chicken (Gallus domesticus L.). J Basic Appl Zool 80(1):30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41936-019-0098-y
Oró J (1972) Extraterrestrial organic analysis. Sp Life Sci 3(4):507–550
Jones DA (1962) Selective eating of the acyanogenic form of the plant Lotus corniculatus L. by various animals. Nature 193(4820):1109–1110
Memariani Z, Farzaei MH, Ali A, Momtaz S (2020) Nutritional and bioactive characterization of unexplored food rich in phytonutrients. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 157–175
Süntar I, Yakıncı ÖF (2020) Potential risks of phytonutrients associated with high-dose or long-term use Phytonutrients in food. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 137–155
Reisch MS (2017) Cyanide glitters for some. In: Use of the deadly chemical is on the rise in the gold mining industry. Chem Eng News 95(39):18–19
Cunningham SA (2005) Incident, accident, catastrophe: cyanide on the Danube. Disasters 29(2):99–128
Helwege A (2015) Challenges with resolving mining conflicts in Latin America. Extr Ind Soc 2(1):73–84
Macklin MG, Brewer PA, Hudson-Edwards KA, Bird G et al (2006) A geomorphological approach to the management of rivers contaminated by metal mining. Geomorphology 79(3–4):423–447
Ani E-C, Cristea VM, Agachi PS (2012) Mathematical models to support pollution counteraction in case of accidents. Environ Eng Manag J (EEMJ) 11(1):7–13
Ramraj R (2001) The Omai disaster in Guyana. Geogr Bull Gamma Theta Upsilon 43(2):83–90
Amegbey NA, Adimado AA (2003) Incidents of cyanide spillage in Ghana. Miner Process Extr Metall 112(2):126–130
Kumar R, Saha S, Dhaka S et al (2017) Remediation of cyanide-contaminated environments through microbes and plants: a review of current knowledge and future perspectives. Geosyst Eng 20(1):28–40
Luque-Almagro VM, Cabello P, Sáez LP et al (2018) Exploring anaerobic environments for cyanide and cyano-derivatives microbial degradation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(3):1067–1074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8678-6
Baxter J, Cummings SP, Antonie VL (2006) The current and future applications of microorganism in the bioremediation of cyanide contamination. Springer Neth 90(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-006-9057-y
Gupta N, Balomajumder C, Agarwal V (2010) Enzymatic mechanism and biochemistry for cyanide degradation: a review. J Hazard Mater 176(1–3):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.0388
Fry W, Evans P (1977) Association of formamide hydro-lyase with fungal pathogenicity to cyanogenic plants. Phytopathology 67:1001–1006. https://doi.org/10.1094/Phyto-67-1001
Desai J, Ramakrishna C (1998) Microbial degradation of cyanides and its commercial application. J Sci Ind Res 57:441–453. https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.199904253
Stam H, Stouthamer AH, van Verseveld HW (1985) Cyanide assimilation in Rhizobium ORS 571: influence of the nitrogenase catalyzed hydrogen production on the efficiency of growth. Arch Microbiol 143(2):196–202
Kunz DA, Nagappan O, Silva-Avalos J et al (1992) Utilization of cyanide as nitrogenous substrate by Pseudomonas fluorescens NCIMB 11764: evidence for multiple pathways of metabolic conversion. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(6):2022–2029
Shin D, Park J, Park H et al (2019) Key microbes and metabolic potentials contributing to cyanide biodegradation in stirred-tank bioreactors treating gold mining effluent. Miner Process Extr Metall Rev 41:1–11
Cluness MJ, Turner PD, Clements E et al (1993) Purification and properties of cyanide hydratase from Fusarium lateritium and analysis of the corresponding chy1 gene. J Microbiol 139(8):1807–1815. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-139-8-1807
Siedow JN, Umbach AL (1995) Plant mitochondrial electron transfer and molecular biology. Plant Cell 7(7):821–831. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.7.7821
Ganesan K, Raza S, Vijayaraghavan R (2010) Chemical warfare agents. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 2(3):166. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-7406.68498
Guilloton M, Espie G, Anderson P (2002) What is the role of cyanase in plants. Rev Plant Biochem J Biotechnol 1:57–79
Kao C, Liu J, Lou H et al (2003) Biotransformation of cyanide to methane and ammonia by Klebsiella oxytoca. Chemosphere 50(8):1055–1061
Westley J, Adler H, Westley L et al (1983) The sulfurtransferases. Fundam Appl Toxicol 3(5):377–382. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/3.5.377
Atkinson A (1975) Bacteria cyanide detoxification. J Biotechnol Bioeng 17:457–460
Kelly DP, Baker SC (1990) The organosulphur cycle: aerobic and anaerobic processes leading to turnover of C1-sulphur compounds. FEMS Microbiol Rev 7(3–4):241–246. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04919.x
Berben T, Overmars L, Sorokin DY et al (2017) Comparative genome analysis of three thiocyanate oxidizing Thioalkalivibrio species isolated from soda lakes. Front Microbiol 8:254. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00254
Dursun A, Çalık A, Aksu Z (1999) Degradation of ferrous (II) cyanide complex ions by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Process Biochem 34(9):901–908
Dash RR, Balomajumdar C (2014) Treatment of cyanide bearing effluents by adsorption, biodegradation and combined processes: effect of process parameters. J Desalination Water Treat 52(16–18):3355–3366. https://doi.org/10.1080/1944.2013.800330
Adams D, Komen J, Pickett T (2001) Biological cyanide degradation. In: Young CA (ed) Cyanide: social, industrial and economic aspects. The Mineral Metals & Material Society, Warrendale, pp 203–213
Khamar Z, Makhdoumi-Kakhki A, Gharaie MM (2015) Remediation of cyanide from the gold mine tailing pond by a novel bacterial co-culture. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 99:123–128. https://doi.org/10.1106/j.ibiod.2015.01.009
Adjei MD, Ohta Y (2000) Factors affecting the biodegradation of cyanide by Burkholderia cepacia strain C-3. J Biosci Bioeng 89(3):274–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1389-1723(00)88833-7
Mirizadeh S, Yaghmaei S, Nejad ZG (2014) Biodegradation of cyanide by a new isolated strain under alkaline conditions and optimization by response surface methodology (RSM). J Environ Health Sci Eng 12(1):85
Dwivedi N, Balomajumder C, Mondal P (2016) Comparative evaluation of cyanide removal by adsorption, biodegradation, and simultaneous adsorption and biodegradation (SAB) process using Bacillus cereus and almond shell. J Environ Biol 37(4):551–556
Trapp S, Larsen M, Pirandello A et al (2003) Feasibility of cyanide elimination using plants. Eur J Miner Process Environ Protect 3(1):128–137
Razanamahandry LC, Andrianisa HA, Karoui H et al (2016) Biodegradation of free cyanide by bacterial species isolated from cyanide-contaminated artisanal gold mining catchment area in Burkina Faso. Chemosphere 157:71–78
Moradkhani M, Yaghmaei S, Nejad ZG (2017) Biodegradation of cyanide under alkaline conditions by a strain of Pseudomonas putida isolated from gold mine soil and optimization of process variables through response surface methodology (RSM). Period Polytech Chem Eng 62(3):265–273. https://doi.org/10.3311/ppch.10860
Karamba KI, Ahmad SA, Zulkharnain A et al (2016) Optimisation of biodegradation conditions for cyanide removal by Serratia marcescens strain AQ07 using one-factor-at-a-time technique and response surface methodology. Rend Fis Acc Lincei 27(3):533–545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-016-0516-8
Wu CF, Xu XM, Zhu Q et al (2014) An effective method for the detoxification of cyanide-rich wastewater by Bacillus sp CN-22. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(8):3801–3807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5433-5
Barclay M, Hart A, Knowles CJ et al (1998) Biodegradation of metal cyanides by mixed and pure cultures of fungi. Enzyme Microbial Technol 22(4):223–231
Patil Y, Paknikar K (2000) Development of a process for biodetoxification of metal cyanides from waste waters. Process Biochem 35(10):1139–1151. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(00)00150-3
Mueller JG, Cerniglia CE, Pritchard PH (2005) Bioremediation of environments contaminated. In: Ronald L, Crawford Crawford LD (eds) Bioremediation: principles and applications. Cambridge University Press, New York, p 125. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511608414
Admassu W, Korus RA (1996) Engineering of bioremediation processes: needs and limitations. Biotechnol Res Ser 6:13–34
Akinpelu EA, Adetunji AT, Ntwampe SKO et al (2018) Performance of Fusarium oxysporum EKT01/02 isolate in cyanide biodegradation system. Environ Eng Res 23(2):223–227. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2017.154
Wang X, Wang Q, Wang S et al (2012) Effect of biostimulation on community level physiological profiles of microorganisms in field-scale biopiles composed of aged oil sludge. Biores Technol 111:308–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.158
Hope KM, Knowles CJ (1991) The anaerobic utilisation of cyanide in the presence of sugars by microbial cultures can involve an abiotic process. FEMS Microbiol Lett 8:217–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1097(91)90598-5
Barany S (ed) (2004) Role of interfaces in environmental protection, vol 4. Springer, Dordrecht, p 1564. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0183-0
Crawford RL, Crawford DL (2005) Bioremediation: principles and applications. Cambridge University Press, New York
Azubuike CC, Chikere CB, Okpokwasili GC (2016) Bioremediation techniques-classification based on site of application: principles, advantages, limitations and prospects. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32(11):180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2137-x
Das S (ed) (2014) Microbial biodegradation and bioremediation, 1st edn. Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam, pp 23–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2013-0-13533-7
Brar SK, Verma M, Surampall R et al (2006) Bioremediation of hazardous wastes: a review. Pract Period Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste Manag 10(2):59–72. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-025X(2006)10:2(59)
Sharma S (2012) Bioremediation: features, strategies and applications. Asian J Pharm Life Sci 2(2):2231–4423
Atlas RM, Philp J (2005) Bioremediation: applied aquifers. Applied microbial solutions for real-world environmental cleanup. American Society for Microbiology press, Washington, pp 139–236
Adams GO, Fufeyin PT, Okoro SE et al (2015) Bioremediation, biostimulation and bioaugmention: a review. Int J Environ Bioremediat Biodegrad 3(1):28–39. https://doi.org/10.12691/ijebb-3-1-5
Park D, Lee DS, Kim YM et al (2008) Bioaugmentation of cyanide-degrading microorganisms in a full-scale cokes wastewater treatment facility. Biores Technol 99(6):2092–2096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.03.027
Bushey JT, Small MJ, Dzombak DA et al (2006) Parameter estimation of a plant uptake model for cyanide: application to hydroponic data. Int J Phytorem 8(1):45–62. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226510500507052
Hong L, Banks M, Schwab A (2008) Removal of cyanide contaminants from rhizosphere soil. J Bioremediat 12(4):210–215
Manning K (1988) Detoxification of cyanide by plants and hormone action. Cyanide compounds in biology. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, pp 92–110. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470513712.ch7
Ebbs S, Kosma DK, Nielson EH et al (2010) Nitrogen supply and cyanide concentration influence the enrichment of nitrogen from cyanide in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.). Plant Cell Environ 33(7):1152–1160. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02136.x
Hidayati N, Juhaet T, Syarif F (2009) Mercury and cyanide contaminations in gold mine environment and possible solution of cleaning up by using phytoextraction. HAYATI J Biosci 16(3):88–94. https://doi.org/10.4308/hjb.16.3.88
Mekuto L, Ntwampe SKO, Jackson VA (2015) Biodegradation of free cyanide and subsequent utilisation of biodegradation by-products by Bacillus consortia: optimisation using response surface methodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(14):10434–10443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4221-4
Dias RL, Ruberto L, Calabró A et al (2015) Hydrocarbon removal and bacterial community structure in on-site biostimulated biopile systems designed for bioremediation of diesel-contaminated Antarctic soil. Polar Biol 38(5):677–687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-014-1630-7
Gomez F, Sartaj M (2014) Optimization of field scale biopiles for bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil at low temperature conditions by response surface methodology (RSM). Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 89:103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.01.010
Raymond RL, Hudson JO, Jamison VW (1976) Oil degradation in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 31(4):522–535
Song HG, Bertha R (1990) Effects of jet fuel spills on the microbial community in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 56(3):646–651
Akcil A (2003) Destruction of cyanide in gold mill effluents: biological versus chemical treatments. Biotechnol Adv 21(6):501–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0734-9750(03)00099-5
Jaysankar D, Ramaiah N, Bhosle NB et al (2007) Potential of mercury-resistant marine bacteria for detoxification of chemicals of environmental concern. Microbes Environ 22(4):336–345. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.22.336
Ashraf M, Ahmad MSA, Ozturk M (2010) Plant adaptation and phytoremediation. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-9370-7
Yu X-Z, Zhou PH, Yang YM (2006) The potential for phytoremediation of iron cyanide complex by willows. Ecotoxicology 15(5):461–467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-006-0081-5
Aichi M, Nishida I, Omata T (1998) Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding cyanase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 39:135–135
Das S, Dash HR (2014) Microbial bioremediation: a potential tool for restoration of contaminated areas. In: Das S (ed) Microbial biodegradation and bioremediation. Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam, pp 1–21
Meyers PR, Gokool P, Rawlings DE et al (1991) An efficient cyanide-degrading Bacillus pumilus strain. J Microbiol 137(6):1397–1400
Fedorak PM, Hrudey SE (1989) Cyanide transformation in anaerobic phenol-degradation methanogenic culture. Water Sci Technol 21:67–76
Chakrabortis S, Veeramani H (2006) Effects of HRT and recycle ratio on removal of cyanide, phenol, thiocyanate, and ammonia in an anaerobic–anoxic–aerobic continous system. Process Biochem 4(1):96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2005.03.067
Novak D, Franke-Whittle IH, Pirc ET, Jernan V et al (2013) Biotic and Abiotic process contribute to success anearobic degradation of cyanide by UASB rector biomass treating brewery. Water Res 47(11):3644–3653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.04.027
Nwokoro O, Dibua MEU (2014) Degradation of soil cyanide by single and mixed cultures of Pseudomonas stutzeri and Bacillus subtilis. Arch Ind Hyg Toxicol 65(1):113–119. https://doi.org/10.2478/1004-1254-65-2014-2449
Liu G, Shen J (2004) Effects of culture and medium conditions on hydrogen production from starch using anaerobic bacteria. J Biosci Bioeng 98(4):251–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1389-1723(04)00277-4
Weiland P (2010) Biogas production: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85(4):849–860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2246-7
Song Y-C, Piak B-C, Shin H-S et al (1998) Influence of electron donor and toxic materials on the activity of sulfate reducing bacteria for the treatment of electroplating wastewater. Water Sci Technol 38(4–5):187–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00527-7
Dubey S, Holmes D (1995) Biological cyanide destruction mediated by microorganisms. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11(3):257–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00367095
Kandasamy S, Dananjeyan B, Krishnamurthy K et al (2015) Aerobic cyanide degradation by bacterial isolates from cassava factory wastewater. Braz J Microbiol 46(3):659–666. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-838246320130516
Wang P, VanEtten HD (1992) Cloning and properties of a cyanide hydratase gene from the phytopathogenic fungus Gloeocercospora sorghi. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 187(2):1048–1054
Akopyan TN, Braunstein AE, Goryachenkova EV (1975) Beta-cyanoalanine synthase: purification and characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci 72(4):1617–1621. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.72.4.1617
Gurbuz F, Ciftci H, Akcil A (2009) Biodegradation of cyanide containing effluents by Scenedesmus obliquus. J Hazard Mater 162(1):74–79
Ebel M, Evangelou MW, Schaeffer A (2007) Cyanide phytoremediation by water hyacinths (Eichhornia crassipes). Chemosphere 66(5):816–823
Sankaranarayanan A, Gowthami M (2015) Cyanide degradation by consortium of bacterial species isolated from sago industry effluent. J Environ Treat Tech 3(1):41–46
Tiong B, Bahari ZM, Lee N et al (2015) Cyanide degradation by Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes strain W2 isolated from mining effluent. Sains Malays 44(2):233–238
Acknowledgements
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51674161) and the Major Program of the Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2019BEE075) supported this project.
Funding
The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest concerning the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cosmos, A., Erdenekhuyag, BO., Yao, G. et al. Principles and methods of bio detoxification of cyanide contaminants. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 22, 939–954 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-020-01013-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-020-01013-6