Abstract
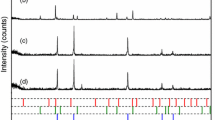
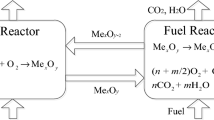
Chemical looping hydrogen generation using iron oxides as oxygen carriers is a novel technology to convert carbonaceous substances into hydrogen. The reduction characteristics of oxygen carriers greatly impact the process efficiency. In this work, the oxygen carriers of Fe2O3 60wt%/Al2O3 were prepared by physical mixing method. The stepwise reduction kinetics of this material was investigated at 800–1000 °C in a TGA with a thermodynamics-controlled method. For this method, CO/CO2 mixture gases at the volume ratios of 0.11, 1, and 5.67 were selected as fuels to decouple the continuous reduction of Fe2O3→Fe into independent reductions, including Fe2O3→Fe3O4, Fe3O4→FeO and FeO→Fe with little mutual influences. The kinetic mechanisms of Fe2O3→Fe3O4, Fe3O4→FeO and FeO→Fe were well represented by the nucleation and grain-growth function, the diffusion-controlled function and the phase-boundary-controlled function, respectively. Fe3O4→FeO was determined as the rate-limiting step with a lower reaction rate constant (8.89 × 10−6–5.60 × 10−4 s−1) and a higher activation energy (234 kJ/mol). By means of XRD analysis, it was also found that Al2O3, usually regarded as the supported component, became active by forming FeAl2O4 with FeO. At 900–1000 °C, FeAl2O4 impacted on the reduction rate of Fe2+→Fe due to its lower reactivity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalinci Y, Hepbasli A, Dincer I (2009) Biomass-based hydrogen production: a review and analysis. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:8799–8817. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.08.078
Balat H, Kırtay E (2010) Hydrogen from biomass– Present scenario and future prospects. Int J Hydrogen Energy 35:7416–7426. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.04.137
Saxena RC, Seal D, Kumar S, Goyal HB (2008) Thermo-chemical routes for hydrogen rich gas from biomass: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 12:1909–1927. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2007.03.005
Kobayashi N, Fan L-S (2011) Biomass direct chemical looping process: a perspective. Biomass Bioenergy 35:1252–1262. doi:10.1016/j.biombioe.2010.12.019
Li F, Zeng L, Fan L-S (2010) Biomass direct chemical looping process: process simulation. Fuel 89:3773–3784. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2010.07.018
Fan L-S (2010) Chemical looping systems for fossil energy. Wiley, Hoboken
Barin L (2003) Thermochemical properties of inorganic substances. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Li F, Kim HR, Sridhar D, Wang F, Zeng L, Chen J, Fan LS (2009) Syngas chemical looping gasification process: oxygen carrier particle selection and performance. Energy Fuels 23:4182–4189. doi:10.1021/ef900236x
Mondal K, Lorethova H, Hippo E, Wiltowski T, Lalvani SB (2004) Reduction of iron oxide in carbon monoxide atmosphere—reaction controlled kinetics. Fuel Process Technol 86:33–47. doi:10.1016/j.fuproc.2003.12.009
Monazam ER, Breault RW, Siriwardane R (2014) Reduction of hematite (Fe2O3) to wüstite (FeO) by carbon monoxide (CO) for chemical looping combustion. Chem Eng J 242:204–210. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2013.12.040
Monazam ER, Breault RW, Siriwardane R (2014) Kinetics of hematite to Wüstite by hydrogen for chemical looping combustion. Energy Fuels 28:5406–5414. doi:10.1021/ef501100b
Go KS, Son SR, Kim SD (2008) Reaction kinetics of reduction and oxidation of metal oxides for hydrogen production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 33:5986–5995. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.05.039
Luo M, Wang S, Wang L, Lv M (2014) Reduction kinetics of iron-based oxygen carriers using methane for chemical-looping combustion. J Power Sources 270:434–440. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.07.100
Bohn CD, Cleeton JP, Müller CR, Davidson JF, Hayhurst AN, Scott SA, Dennis JS (2010) The kinetics of the reduction of iron oxide by carbon monoxide mixed with carbon dioxide. AIChE J 56:1016–1029. doi:10.1002/aic.12084
Sridhar D, Tong A, Kim H, Zeng L, Li F, Fan L-S (2012) Syngas chemical looping process: design and construction of a 25kWth subpilot unit. Energy Fuels 26:2292–2302. doi:10.1021/ef202039y
Ishida M, Takeshita K, Suzuki K, Ohba T (2005) Application of Fe2O3 − Al2O3 composite particles as solid looping material of the chemical-loop combustor. Energy Fuels 19:2514–2518. doi:10.1021/ef0500944
Cabello A, Dueso C, García-Labiano F, Gayán P, Abad A, de Diego LF, Adánez J (2014) Performance of a highly reactive impregnated Fe2O3/Al2O3 oxygen carrier with CH4 and H2S in a 500Wth CLC unit. Fuel 121:117–125. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2013.12.027
Bao J, Liu W, Cleeton JPE, Scott SA, Dennis JS, Li Z, Cai N (2013) Interaction between Fe-based oxygen carriers and n-heptane during chemical looping combustion. Proc Combust Inst 34:2839–2846. doi:10.1016/j.proci.2012.07.079
Ping-Chin Chiu YK, You-Lin Wu, Hsuan-Chih Wu, Kuo Yu-Lin, Tseng Yao-Hsuan (2014) Characterization and evaluation of prepared Fe2O3/Al2O3 oxygen carriers for chemical looping process. Aerosol Air Quality Res 14:981–990. doi:10.4209/aaqr.2013.04.0135
Cabello A, Abad A, García-Labiano F, Gayán P, de Diego LF, Adánez J (2014) Kinetic determination of a highly reactive impregnated Fe2O3/Al2O3 oxygen carrier for use in gas-fueled chemical looping combustion. Chem Eng J 258:265–280. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.083
Adanez J, Abad A, Garcia-Labiano F, Gayan P, de Diego LF (2012) Progress in chemical-looping combustion and reforming technologies. Prog Energy Combust Sci 38:215–282. doi:10.1016/j.pecs.2011.09.001
Bohn CD, Cleeton JP, Müller CR, Chuang SY, Scott SA, Dennis JS (2010) Stabilizing iron oxide used in cycles of reduction and oxidation for hydrogen production. Energy Fuels 24:4025–4033. doi:10.1021/ef100199f
Kidambi PR, Cleeton JPE, Scott SA, Dennis JS, Bohn CD (2012) Interaction of iron oxide with alumina in a composite oxygen carrier during the production of hydrogen by chemical looping. Energy Fuels 26:603–617. doi:10.1021/ef200859d
Hancock JD, Sharp JH (1972) Method of comparing solid-state kinetic data and its application to the decomposition of kaolinite, brucite, and BaCO3. J Am Ceram Soc 55:74–77. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1972.tb11213.x
Son SR, Go KS, Kim SD (2009) Thermogravimetric analysis of copper oxide for chemical-looping hydrogen generation. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:380–387. doi:10.1021/ie800174c
Chiron F-X, Patience GS (2012) Kinetics of mixed copper–iron based oxygen carriers for hydrogen production by chemical looping water splitting. Int J Hydrogen Energy 37:10526–10538. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.04.052
Chen S, Shi Q, Xue Z, Sun X, Xiang W (2011) Experimental investigation of chemical-looping hydrogen generation using Al2O3 or TiO2-supported iron oxides in a batch fluidized bed. Int J Hydrogen Energy 36:8915–8926. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.04.204
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial assistance from the National Key Technology R&D Program of China (2010BAC66B03) and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (2011CB201502) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21477061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Wang, W., Lian, S. et al. Stepwise reduction kinetics of iron-based oxygen carriers by CO/CO2 mixture gases for chemical looping hydrogen generation. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 19, 453–462 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-015-0443-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-015-0443-2