Abstract
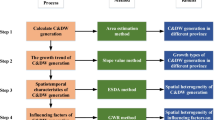
Urban planners require an understanding of the spatial patterns of municipal solid waste generation to design policies for various locales within the city. Many of the previous studies used demographic and socioeconomic factors as the determinants, but few of them focused on the influential spatial factors such as land use and building coverage. In this study, we used global and local spatial autocorrelation tools to reveal the spatial pattern of MSW generation inside an island city in China. Correlation analysis and linear regression were then applied to identify influential factors including population, land use and building coverage. Results showed that (1) there were significant mirror global spatial autocorrelations for MSW quantities and densities; (2) local spatial autocorrelations revealed that the MSW hot spots were concentrated in the early industrial zones and the old downtown; and (3) total and seasonal MSW was predominantly determined by people’s socioeconomic activities better reflected by C&R land or commercial land and vacant land. Different sources of MSW had some distinctive significant influential factors which reflect their differences in socioeconomic activities. We believe that those significant models constructed from the identified influential spatial factors could provide quick, useful and low-cost decision support for MSW management.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vergara SE, Tchobanoglous G (2012) Municipal solid waste and the environment: a global perspective. Annu Rev Environ Resour 37:277–310
GPWN (2012) The global garbage crisis: no time to waste. http://new.unep.org/gpwm/News/GPWMconference/tabid/106686/Default.aspx. Accessed 7 Jan 2013
Hoornweg D, Bhada-Tata P (2012) What a waste: a global review of solid waste management. The World Bank. http://go.worldbank.org/BCQEP0TMO0. Accessed 7 Jan 2013
CNBS (2011) China statistical yearbook 2011. China Statistics Press, Beijing
Li RS (2013) Interpretation of suggestion on further strengthening the work of Municipal Solid Waste Treatment (in Chinese). China Architecture & Building Press, Beijing
Pan LY, Lin T, Xiao LS, Zhao Y, Cui SH (2010) Household waste management for a peri-urban area based on analysing greenhouse gas emissions for Jimei District, Xiamen, China. Int J Sust Dev World 17:342–349
Beigl P, Lebersorger S, Salhofer S (2008) Modelling municipal solid waste generation: a review. Waste Manag 28:200–214
Bandara N, Hettiaratchi J, Wirasinghe SC, Pilapiiya S (2007) Relation of waste generation and composition to socio-economic factors: a case study. Environ Monit Assess 135:31–39
Beigl P, Wassermann G, Schneider F, Salhofer S (2004) Forecasting municipal solid waste generation in major European cities. Paper presented at the IEMSs International Conference: Complexity and Integrated Resources Management
Dennison GJ, Dodd VA, Whelan B (1996) A socio-economic based survey of household waste characteristics in the city of Dublin, Ireland. 1. Waste composition. Resour Conserv Recy 17:227–244
Keser S, Duzgun S, Aksoy A (2012) Application of spatial and non-spatial data analysis in determination of the factors that impact municipal solid waste generation rates in Turkey. Waste Manag 32:359–371
Purcell M, Magette WL (2009) Prediction of household and commercial BMW generation according to socio-economic and other factors for the Dublin region. Waste Manag 29:1237–1250
Seco Pon JP, Becherucci ME (2012) Spatial and temporal variations of urban litter in Mar del Plata, the major coastal city of Argentina. Waste Manag 32:343–348
Xiamen Statistics Bureau (2011) Year book of Xiamen Special Economic Zone 2011 (in Chinese). China Statistics Press, Beijing
Lin T, Xue XZ, Shi LY, Gao LJ (2013) Urban spatial expansion and its impacts on island ecosystem services and landscape pattern: a case study of the island city of Xiamen, Southeast China. Ocean Coast Manag 81:90–96
Li XH, Lin T, Zhang GQ, Xiao LS, Zhao QJ, Cui SH (2011) Dynamic analysis of urban spatial expansion and its determinants in Xiamen Island. J Geog Sci 21:503–520
Zhang GQ, Li XQ, Zhao QJ (2010) Resource consumption and city size: a case study of Xiamen and implications for sustainable urbanisation. Int J Sust Dev World 17:350–355
ESRI (2009) ArcGIS Desktop, Version 9.3. Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc, Redland, CA, USA
Xiamen City Chronicles Edition Board (ed.) (2004) Chronicles of Xiamen City (in Chinese). Chronicle Press, Beijing
Wang JF (2006) Spatial analysis (in Chinese). Science Press, Beijing
IBM (2010) IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 19.0. International Business Machines Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA
Zhang, GQ (2011) Urban Residential Space Change and its Effect on Commuting: a Case Study of Xiamen under Housing Marketization (in Chinese). Dissertation, Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
Acknowledgments
Thanks for Environmental Sanitation Administration of Xiamen City, Project 41201155, 41201598, 41101551, 41301621 and 41371535 supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, Project 2010I0014 supported by Fujian Science & Technology Program, and Project 3502Z20111049 supported by Xiamen Science & Technology Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Lin, T., Chen, S. et al. Spatial characteristics of municipal solid waste generation and its influential spatial factors on a city scale: a case study of Xiamen, China. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 17, 399–409 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-014-0257-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-014-0257-7