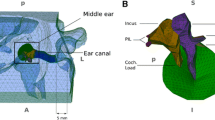
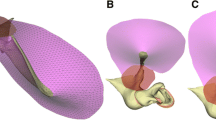
Abstract
The anatomical differences between the newborn ear and the adult one result in different input admittance responses in newborns than those in adults. Taking into account fluid-structure interactions, we have developed a finite-element model to investigate the wideband admittance responses of the ear canal and middle ear in newborns for frequencies up to 10 kHz. We have also performed admittance measurements on a group of 23 infants with ages between 14 and 28 days, for frequencies from 250 to 8000 Hz with 1/12-octave resolution. Sensitivity analyses of the model were performed to investigate the contributions of the ear canal and middle ear to the overall admittance responses, as well as the effects of the material parameters, measurement location and geometrical variability. The model was validated by comparison with our new data and with data from the literature. The model provides a quantitative understanding of the canal and middle-ear resonances around 500 and 1800 Hz, respectively, and also predicts the effects of the first resonance mode of the middle-ear cavity (around 6 kHz) as well as the first and second standing-wave modes in the ear canal (around 7.2 and 9.6 kHz, respectively), which may explain features seen in our high-frequency-resolution clinical measurements.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdala C, Keefe DH (2012) Morphological and functional ear development, Hum Audit Dev (Springer), pp 19–59
Anson BJ, Donaldson JA (1992) Surgical anatomy of the temporal bone and ear, 4th edn. Saunders Philadelphia, New York
Bergevin C, Olson ES (2014) External and middle ear sound pressure distribution and acoustic coupling to the tympanic membrane. J Acoust Soc Am 135:1294–1312
Charlebois M, Motallebzadeh H, Funnell WRJ (2013) Visco-hyperelastic law for finite deformations: a frequency analysis. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 12:705–715
Cinamon U (2009) The growth rate and size of the mastoid air cell system and mastoid bone: a review and reference. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266:781–786
Day J, Funnell WRJ (1990) An approach to finite-element modelling of the structural-acoustic interaction between the ear canal and eardrum. Proc 16th Can Med Biol Eng Conf Winnipeg. pp. 155-156
Decraemer WF, Khanna, SM (2004) Measurement, visualization and quantitative analysis of complete three-dimensional kinematical data sets of human and cat middle ear. In: Middle Ear Mechanics in Research and Otology. World Scientific, Singapore, pp. 3-10
Feldman AS (1974) Eardrum abnormality and the measurement of middle ear function. Arch Otolaryngol 99:211–217
Funnell WRJ, Laszlo CA (1978) Modeling of the cat eardrum as a thin shell using the finite-element method. J Acoust Soc Am 63:1461–1467
Gan RZ, Feng B, Sun Q (2004) Three-dimensional finite element modeling of human ear for sound transmission. Ann Biomed Eng 32:847–859
Gan RZ, Sun Q, Feng B, Wood MW (2006) Acoustic–structural coupled finite element analysis for sound transmission in human ear—pressure distributions. Med Eng Phys 28:395–404
Gan RZ, Reeves BP, Wang X (2007) Modeling of sound transmission from ear canal to cochlea. Ann Biomed Eng 35:2180–2195
Gan RZ, Cheng T, Dai C, Yang F, Wood MW (2009) Finite element modeling of sound transmission with perforations of tympanic membrane. J Acoust Soc Am 126:243–253
Gilman S, Dirks DD (1986) Acoustics of ear canal measurement of eardrum SPL in simulators. J Acoust Soc Am 80:783–793
Greffet N (2013) Éléments vibro-acoustiques, Retrieved from http://www.code-aster.org/V2/doc/default/fr/man_r/r4/r4.02.02.pdf
Holte L, Cavanaugh RM, Margolis RH (1990) Ear canal wall mobility and tympanometric shape in young infants. J Pediatr 117:77–80
Holte L, Margolis RH, Cavanaugh RM Jr (1991) Developmental changes in multifrequency tympanograms. Audiology 30:1–24
Ihrle S, Lauxmann M, Eiber A, Eberhard P (2013) Nonlinear modelling of the middle ear as an elastic multibody system—applying model order reduction to acousto-structural coupled systems. J Comput Appl Math 246:18–26
Keefe DH (2015) Acoustical transmission-line model of the middle-ear cavities and mastoid air cells. J Acoust Soc Am 137:1877–1887
Keefe DH, Levi E (1996) Maturation of the middle and external ears: acoustic power-based responses and reflectance tympanometry. Ear Hear 17:361–373
Keefe DH, Bulen JC, Arehart KH, Burns EM (1993) Ear-canal impedance and reflection coefficient in human infants and adults. J Acoust Soc Am 94:2617–2638
Khaleghi M, Puria S (2017) Attenuating the ear canal feedback pressure of a laser-driven hearing aid. J Acoust Soc Am 141:1683-1693
Kuypers LC, Decraemer WF, Dirckx JJ (2006) Thickness distribution of fresh and preserved human eardrums measured with confocal microscopy. Otol Neurotol 27:256–264
Lee C-F, Chen P-R, Lee W-J, Chou Y-F, Chen J-H, Liu T-C (2010) Computer aided modeling of human mastoid cavity biomechanics using finite element analysis. EURASIP J Adv Signal Proc 2010:6
Liu Y-W, Sanford CA, Ellison JC, Fitzpatrick DF, Gorga MP, Keefe DH (2008) Wideband absorbance tympanometry using pressure sweeps: system development and results on adults with normal hearing. J Acoust Soc Am 124:3708–3719
Maftoon N, Funnell WRJ, Daniel SJ, Decraemer WF (2015) Finite-element modelling of the response of the gerbil middle ear to sound. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 16:547–567
McLellan MS, Webb CH (1950) Ear studies in the newborn infant. J Pediatr 51:672–677
Merchant GR, Horton NJ, Voss SE (2010) Normative reflectance and transmittance measurements on healthy newborn and 1-month-old infants. Ear Hear 31:746–754
Motallebzadeh H, Gariepy B, Maftoon N, Funnell WRJ, Daniel SJ (2013a) Finite-element modelling of the newborn ear canal and middle ear. Proc Meet Acoust (Acoust Soc Am) 19:030101
Motallebzadeh H, Charlebois M, Funnell WRJ (2013b) A non-linear viscoelastic model for the tympanic membrane. J Acoust Soc Am 134:4427–4434
Motallebzadeh H, Maftoon N, Pitaro J, Funnell WRJ, Daniel SJ (2017) Finite-element modelling of the acoustic input admittance of the newborn ear canal and middle ear. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 18:25–48
Nakajima HH, Ravicz ME, Rosowski JJ, Peake WT, Merchant SN (2005) Experimental and clinical studies of malleus fixation. Laryngoscope 115:147–154
Paradise JL (1982) Editorial retrospective: tympanometry. N Engl J Med 307:1074–1076
Paradise JL, Smith CG, Bluestone CD (1976) Tympanometric detection of middle ear effusion in infants and young children. Pediatrics 58:198–210
Pitaro J, Al Masaoudi L, Motallebzadeh H, Funnell WRJ, Daniel SJ (2016) Wideband reflectance measurements in newborns: relationship to otoscopic findings. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 86:156–160
Qi L, Liu H, Lutfy J, Funnell WRJ, Daniel SJ (2006) A nonlinear finite-element model of the newborn ear canal. J Acoust Soc Am 120:3789
Qi L, Funnell WRJ, Daniel SJ (2008) A nonlinear finite-element model of the newborn middle ear. J Acoust Soc Am 124:337
Rabbitt RD (1988) High-frequency plane waves in the ear canal: application of a simple asymptotic theory. J Acoust Soc Am 84:2070–2080
Ruah CB, Schachern PA, Zelterman D, Paparella MM, Yoon TH (1991) Age-related morphologic changes in the human tympanic membrane. A light and electron microscopic study. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 117:627–634
Sanford CA, Feeney MP (2008) Effects of maturation on tympanometric wideband acoustic transfer functions in human infants. J Acoust Soc Am 124:2106–2122
Shahnaz N, Polka L (1997) Standard and multifrequency tympanometry in normal and otosclerotic ears. Ear Hear 18:326–341
Shanks JE, Lilly DJ (1981) An evaluation of tympanometric estimates of ear canal volume. J Speech Hear Res 24:557
Stepp CE, Voss SE (2005) Acoustics of the human middle-ear air space. J Acoust Soc Am 118:861–871
Stinson MR (1985a) The spatial distribution of sound pressure within scaled replicas of the human ear canal. J Acoust Soc Am 78:1596–1602
Stinson MR (1985b) Spatial variation of phase in ducts and the measurement of acoustic energy reflection coefficients. J Acoust Soc Am 77:386–393
Stinson MR, Khanna SM (1989) Sound propagation in the ear canal and coupling to the eardrum, with measurements on model systems. J Acoust Soc Am 85:2481–2491
Stinson MR, Shaw EAG, Lawton BW (1982) Estimation of acoustical energy reflectance at the eardrum from measurements of pressure distribution in the human ear canal. J Acoust Soc Am 72:766–773
Volandri G, Carmignani C, Di Puccio F, Forte P (2014) Finite element formulations applied to outer ear modeling. Stroj Vestn-J Mech Eng 60:363–372
Voss SE, Allen JB (1994) Measurement of acoustic impedance and reflectance in the human ear canal. J Acoust Soc Am 95:372–384
Wang X, Keefe DH, Gan RZ (2016) Predictions of middle-ear and passive cochlear mechanics using a finite element model of the pediatric ear. J Acoust Soc Am 139:1735–1746
Willi UB, Ferrazzini MA, Huber AM (2002) The incudo-malleolar joint and sound transmission losses. Hear Res 174:32–44
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Fonds de recherche en santé du Québec, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (Canada), the Montreal Children’s Hospital Research Institute and the McGill University Health Centre Research Institute. Computations were made on the supercomputer Guillimin of McGill University, managed by Calcul Québec and Compute Canada; the operation of this supercomputer is funded by the Canada Foundation for Innovation, NanoQuébec, the Réseau de Médecine Génétique Appliquée and the Fonds de recherche du Québec – Nature et technologies. The authors thank C. Northrop (Temporal Bone Foundation, Boston) for the histological images used to supplement and help interpret our CT scan. The authors would also like to thank the three anonymous reviewers who helped us to improve this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motallebzadeh, H., Maftoon, N., Pitaro, J. et al. Fluid-Structure Finite-Element Modelling and Clinical Measurement of the Wideband Acoustic Input Admittance of the Newborn Ear Canal and Middle Ear. JARO 18, 671–686 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10162-017-0630-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10162-017-0630-z