Abstract
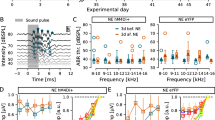
Some forms of tinnitus are believed to arise from abnormal central nervous system activity following a single or repeated noise exposure, for which there are no widely accepted pharmacological treatments. One central site that could be related to tinnitus awareness or modulation is the locus coeruleus, a brainstem structure associated with stress, arousal, and attention. In the present study, we evaluated the effects of cyclobenzaprine, a drug known to act on the rat locus coeruleus, on noise-induced tinnitus using Gap Prepulse Inhibition of the Acoustic Startle (GPIAS). In untreated rats, brief silent gaps presented prior to a 5–10-kHz bandpass startling stimulus produced robust GPIAS. Treatment with cyclobenzaprine alone had no effect on the ability of gaps to suppress the startle response. When animals were exposed to intense narrow-band (126 dB SPL, 16 kHz, 100 Hz BW) unilateral noise, GPIAS was significantly reduced, suggesting the presence of tinnitus. Following the noise exposure, a subset of rats that maintained a robust startle response continued to show GPIAS impairment at 6–20 kHz, 40 days post-noise, suggesting chronic tinnitus. When this subset of animals was treated with cyclobenzaprine, at a dose that had no significant effects on the startle response (0.5 mg/kg), GPIAS recovered partially or to near baseline levels at the affected frequencies. These results were consistent with the absence of tinnitus. By 48 h post-treatment, evidence of tinnitus re-emerged. Our results suggest that cyclobenzaprine was effective in transiently suppressing noise-induced tinnitus in rats.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aston-Jones G, Chiang C, Alexinsky T (1991) Discharge of noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons in behaving rats and monkeys suggests a role in vigilance. Prog Brain Res 88:501–520
Basmajian JV (1978) Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride effect on skeletal muscle spasm in the lumbar region and neck: two double-blind controlled clinical and laboratory studies. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 59:58–63
Bauer CA, Brozoski TJ (2001) Assessing tinnitus and prospective tinnitus therapeutics using a psychophysical animal model. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 2:54–64
Bauer CA, Brozoski TJ (2006) Effect of gabapentin on the sensation and impact of tinnitus. Laryngoscope 116:675–681
Bauer CA, Brozoski TJ, Rojas R, Boley J, Wyder M (1999) Behavioral model of chronic tinnitus in rats. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 121:457–462
Bauer CA, Turner JG, Caspary DM, Myers KS, Brozoski TJ (2008) Tinnitus and inferior colliculus activity in chinchillas related to three distinct patterns of cochlear trauma. J Neurosci Res 86:2564–2578
Brozoski TJ, Bauer CA, Caspary DM (2002) Elevated fusiform cell activity in the dorsal cochlear nucleus of chinchillas with psychophysical evidence of tinnitus. J Neurosci 22:2383–2390
Brozoski TJ, Spires TJ, Bauer CA (2007a) Vigabatrin, a GABA transaminase inhibitor, reversibly eliminates tinnitus in an animal model. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 8:105–118
Brozoski TJ, Ciobanu L, Bauer CA (2007b) Central neural activity in rats with tinnitus evaluated with manganese-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MEMRI). Hear Res 228:168–179
Cave KM, Cornish EM, Chandler DW (2007) Blast injury of the ear: clinical update from the global war on terror. Mil Med 172:726–730
Coelho C, Figueiredo R, Frank E, Burger J, Schecklmann M, Landgrebe M, Langguth B, Elgoyhen AB (2012) Reduction of tinnitus severity by the centrally acting muscle relaxant cyclobenzaprine: an open-label pilot study. Audiol Neuro-otol 17:179–188
Commissiong JW, Karoum F, Reiffenstein RJ, Neff NH (1981) Cyclobenzaprine: a possible mechanism of action for its muscle relaxant effect. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 59:37–44
Connor DE Jr, Nixon M, Nanda A, Guthikonda B (2012) Vagal nerve stimulation for the treatment of medically refractory epilepsy: a review of the current literature. Neurosurg Focus 32:E12
Davis H, Morgan CT, Hawkins JE Jr, Galambos R, Smith FW (1950) Temporary deafness following exposure to loud tones and noise. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 88:1–56
Dobie RA (1999) A review of randomized clinical trials in tinnitus. Laryngoscope 109:1202–1211
VA DoVA (2011) Annual Benefits Report. In: http://www.vba.va.gov/reports/abr/2011_abr.pdf
Edeline JM, Manunta Y, Hennevin E (2011) Induction of selective plasticity in the frequency tuning of auditory cortex and auditory thalamus neurons by locus coeruleus stimulation. Hear Res 274:75–84
Engineer ND, Riley JR, Seale JD, Vrana WA, Shetake JA, Sudanagunta SP, Borland MS, Kilgard MP (2011) Reversing pathological neural activity using targeted plasticity. Nature 470:101–104
Engineer ND, Moller AR, Kilgard MP (2013) Directing neural plasticity to understand and treat tinnitus. Hear Res 295:58–66
Giorgi FS, Mauceli G, Blandini F, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A, Murri L, Fornai F (2006) Locus coeruleus and neuronal plasticity in a model of focal limbic epilepsy. Epilepsia 47(Suppl 5):21–25
Guitton MJ, Caston J, Ruel J, Johnson RM, Pujol R, Puel JL (2003) Salicylate induces tinnitus through activation of cochlear NMDA receptors. J Neurosci 23:3944–3952
Hansen N, Manahan-Vaughan D (2014) Locus coeruleus stimulation facilitates long-term depression in the dentate gyrus that requires activation of beta-adrenergic receptors. Cereb Cortex. doi:10.1093/cercor/bht429
Hazell JW, Jastreboff PJ (1990) Tinnitus. I: auditory mechanisms: a model for tinnitus and hearing impairment. J Otolaryngol 19:1–5
Heffner HE (2011) A two-choice sound localization procedure for detecting lateralized tinnitus in animals. Behav Res Methods 43:577–589
Heffner HE, Harrington IA (2002) Tinnitus in hamsters following exposure to intense sound. Hear Res 170:83–95
Heffner HE, Koay G (2005) Tinnitus and hearing loss in hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus) exposed to loud sound. Behav Neurosci 119:734–742
Heffner HE, Koay G, Heffner RS (2008) Comparison of behavioral and auditory brainstem response measures of threshold shift in rats exposed to loud sound. J Acoust Soc Am 124:1093–1104
Hucker HB, Stauffer SC, Balletto AJ, White SD, Zacchei AG, Arison BH (1978) Physiological disposition and metabolism of cyclobenzaprine in the rat, dog, rhesus monkey, and man. Drug Metab Dispos: Biol Fate Chem 6:659–672
Ison JR (1982) Temporal acuity in auditory function in the rat: reflex inhibition by brief gaps in noise. J Comp Physiol Psychol 96:945–954
Ison JR, O’Connor K, Bowen GP, Bocirnea A (1991) Temporal resolution of gaps in noise by the rat is lost with functional decortication. Behav Neurosci 105:33–40
Jastreboff PJ (1990) Phantom auditory perception (tinnitus): mechanisms of generation and perception. Neurosci Res 8:221–254
Jastreboff PJ, Brennan JF, Sasaki CT (1988a) An animal model for tinnitus. Laryngoscope 98:280–286
Jastreboff PJ, Brennan JF, Coleman JK, Sasaki CT (1988b) Phantom auditory sensation in rats: an animal model for tinnitus. Behav Neurosci 102:811–822
Justice A, Feldman SM, Brown LL (1989) The nucleus locus coeruleus modulates local cerebral glucose utilization during noise stress in rats. Brain Res 490:73–84
Katz WA, Dube J (1988) Cyclobenzaprine in the treatment of acute muscle spasm: review of a decade of clinical experience. Clin Ther 10:216–228
Kim DK, Park SN, Kim HM, Son HR, Kim NG, Park KH, Yeo SW (2011) Prevalence and significance of high-frequency hearing loss in subjectively normal-hearing patients with tinnitus. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 120:523–528
Kraus KS, Mitra S, Jimenez Z, Hinduja S, Ding D, Jiang H, Gray L, Lobarinas E, Sun W, Salvi RJ (2010) Noise trauma impairs neurogenesis in the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 167:1216–1226
Lang IM, Barnes CD (1983) Cyclobenzaprine effects on locus coeruleus cells in tissue slice. Neuropharmacology 22:249–252
Le Prell CG, Dell S, Hensley B, Hall JW 3rd, Campbell KC, Antonelli PJ, Green GE, Miller JM, Guire K (2012) Digital music exposure reliably induces temporary threshold shift in normal-hearing human subjects. Ear Hear 33:e44–e58
Lobarinas E, Sun W, Cushing R, Salvi R (2004) A novel behavioral paradigm for assessing tinnitus using schedule-induced polydipsia avoidance conditioning (SIP-AC). Hear Res 190:109–114
Lobarinas E, Yang G, Sun W, Ding D, Mirza N, Dalby-Brown W, Hilczmayer E, Fitzgerald S, Zhang L, Salvi R (2006) Salicylate- and quinine-induced tinnitus and effects of memantine. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 13–19
Lobarinas E, Dalby-Brown W, Stolzberg D, Mirza NR, Allman BL, Salvi R (2011) Effects of the potassium ion channel modulators BMS-204352 Maxipost and its R-enantiomer on salicylate-induced tinnitus in rats. Physiol Behav 104:873–879
Lobarinas E, Hayes SH, Allman BL (2013) The gap-startle paradigm for tinnitus screening in animal models: limitations and optimization. Hear Res 295:150–160
Lockwood AH, Salvi RJ, Burkard RF, Galantowicz PJ, Coad ML, Wack DS (1999) Neuroanatomy of tinnitus. Scand Audiol Suppl 51:47–52
Lofland JH, Szarlej D, Buttaro T, Shermock S, Jalali S (2001) Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride is a commonly prescribed centrally acting muscle relaxant, which is structurally similar to tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and differs from amitriptyline by only one double bond. Clin J Pain 17:103–104
Maurin Y, Enz A, Le Saux F, Besson MJ (1986) Supernumerary locus coeruleus neurons as a determinant of inherited epilepsy in the convulsive mutant mouse quaking. Brain Res 366:379–384
McCombe A, Baguley D, Coles R, McKenna L, McKinney C, Windle-Taylor P (2001) Guidelines for the grading of tinnitus severity: the results of a working group commissioned by the British Association of Otolaryngologists, Head and Neck Surgeons, 1999. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 26:388–393
Middleton JW, Tzounopoulos T (2012) Imaging the neural correlates of tinnitus: a comparison between animal models and human studies. Front Syst Neurosci 6:35
Moller AR, Moller MB, Yokota M (1992) Some forms of tinnitus may involve the extralemniscal auditory pathway. Laryngoscope 102:1165–1171
Muhlnickel W, Elbert T, Taub E, Flor H (1998) Reorganization of auditory cortex in tinnitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:10340–10343
NCT01962558 (2014) A blinded randomized pilot study assessing vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) paired with tones for tinnitus vs. VNS with unpaired tones. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01962558
Norena AJ (2011) An integrative model of tinnitus based on a central gain controlling neural sensitivity. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35:1089–1109
Puel JL (2007) Cochlear NMDA receptor blockade prevents salicylate-induced tinnitus. B-Ent 3(Suppl 7):19–22
Roberts LE, Husain FT, Eggermont JJ (2013) Role of attention in the generation and modulation of tinnitus. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:1754–1773
Ruttiger L, Ciuffani J, Zenner HP, Knipper M (2003) A behavioral paradigm to judge acute sodium salicylate-induced sound experience in rats: a new approach for an animal model on tinnitus. Hear Res 180:39–50
Sahley TL, Hammonds MD, Musiek FE (2013) Endogenous dynorphins, glutamate and N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors may participate in a stress-mediated Type-I auditory neural exacerbation of tinnitus. Brain Res 1499:80–108
Salvi R, Lobarinas E, Sun W (2009) Pharmacological treatments for tinnitus: new and old. Drugs Future 34:381–400
Shargorodsky J, Curhan GC, Farwell WR (2010) Prevalence and characteristics of tinnitus among US adults. Am J Med 123:711–718
Spankovich C, Griffiths SK, Lobarinas E, Morgenstein KE, De la Calle S, Ledon V, Guersio D, Le Prell CG (2013) Temporary threshold shift after impulse-noise during video game play: laboratory data. International J Audiol Accepted
Turner JG, Parrish J (2008) Gap detection methods for assessing salicylate-induced tinnitus and hyperacusis in rats. Am J Audiol 17:S185–S192
Turner JG, Brozoski TJ, Bauer CA, Parrish JL, Myers K, Hughes LF, Caspary DM (2006) Gap detection deficits in rats with tinnitus: a potential novel screening tool. Behav Neurosci 120:188–195
Van Hoey NM (2005) Effect of cyclobenzaprine on tricyclic antidepressant assays. Ann Pharmacother 39:1314–1317
Vanneste S, Figueiredo R, De Ridder D (2012) Treatment of tinnitus with cyclobenzaprine: an open-label study. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 50:338–344
Yang S, Weiner BD, Zhang LS, Cho SJ, Bao S (2011) Homeostatic plasticity drives tinnitus perception in an animal model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:14974–14979
Zhang J (2013) Auditory cortex stimulation to suppress tinnitus: mechanisms and strategies. Hear Res 295:38–57
Zheng Y, Hooton K, Smith PF, Darlington CL (2008) Carbamazepine reduces the behavioural manifestations of tinnitus following salicylate treatment in rats. Acta Otolaryngol 128:48–52
Zheng Y, McNamara E, Stiles L, Darlington CL, Smith PF (2012) Evidence that memantine reduces chronic tinnitus caused by acoustic trauma in rats. Front Neurol 3:127
Conflict of Interest
The authors report no conflict of interest with the research presented in the manuscript.
All work was supported by the Tinnitus Research Initiative (TRI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
EL designed the experiments, EL and CB performed data collection and analysis, and all authors contributed to writing the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lobarinas, E., Blair, C., Spankovich, C. et al. Partial to Complete Suppression of Unilateral Noise-Induced Tinnitus in Rats after Cyclobenzaprine Treatment. JARO 16, 263–272 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10162-014-0500-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10162-014-0500-x