Abstract
Objective
Dysregulated circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been verified to function in the development of gastric cancer (GC). The current study was designed to investigate the role of circ_0000419 in GC progression, and the potential mechanistic pathway.
Methods
Relative expression of circ_0000419, microRNA-300 (miR-300) and Repulsive Guidance Molecule B (RGMB) was analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) assay. Cell metastasis, including migration and invasion, was assessed by wound healing and Transwell assays. Glucose consumption and lactate production were examined using kits. The association between miR-300 and circ_0000419 or RGMB was validated by dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays. Role of circ_0000419 in vivo was determined by xenograft experiment.
Results
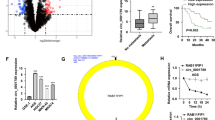
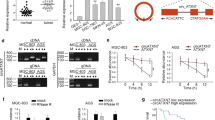
Circ_0000419 and RGMB were downregulated, while miR-300 was upregulated in GC tissues and cells. Gain of circ_0000419 inhibited migration, invasion and glycolysis in GC cells, which was attenuated by introduction of miR-300 or silencing of RGMB. Circ_0000419 sponged miR-300, and RGMB was direct target of miR-300. Circ_0000419 overexpression could block GC tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion
Circ_0000419 inhibited GC cell migration, invasion and glycolysis through regulation of miR-300/RGMB axis, at least in part, affording a molecular target for GC treatment.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Change history
13 September 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-023-02409-8
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I et al (2018) Global cancer statistics: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for cancers in countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 69(1):7–34. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21551
Zhang Z, Yu X, Zhou B et al (2020) Circular RNA circ_0026359 enhances cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer via targeting miR-1200/POLD4 pathway. Biomed Res Int 2020:5103272. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5103272
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K et al (2013) Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA (New York, NY) 19(2):141–157. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.035667.112
Guo JU, Agarwal V, Guo H et al (2014) Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular RNAs. Genome Biol 15(7):409. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0409-z
Zhou R, Wu Y, Wang W et al (2018) Circular RNAs (circRNAs) in cancer. Cancer Lett 425:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.03.035
Lin J, Zhang Y, Zeng X et al (2020) CircRNA CircRIMS acts as a MicroRNA sponge to promote gastric cancer metastasis. ACS Omega 5(36):23237–23246. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c02991
Wang D, Jiang X, Liu Y et al (2020) Circular RNA circ_HN1 facilitates gastric cancer progression through modulation of the miR-302b-3p/ROCK2 axis. Mol Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03897-2
Jin Y, Zhang S, Liu L (2020) Circular RNA circ_C16orf62 suppresses cell growth in gastric cancer by miR-421/Tubulin beta-2A Chain (TUBB2A) Axis. Med Sci Monitor 26:e924343. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.924343
Tao X, Shao Y, Lu R et al (2020) Clinical significance of hsa_circ_0000419 in gastric cancer screening and prognosis estimation. Pathol Res Pract 216(1):152763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2019.152763
Iorio MV, Croce CM (2012) MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med 4(3):143–159. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201100209
Kim D, Sung YM, Park J et al (2016) General rules for functional microRNA targeting. Nat Genet 48(12):1517–1526. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3694
Li H, Lian B, Liu Y et al (2020) MicroRNA-1297 downregulation inhibits breast cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition and proliferation in a FA2H-dependent manner. Oncol Lett 20(6):277. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.12140
Liu J, Li SM (2020) MiR-484 suppressed proliferation, migration, invasion and induced apoptosis of gastric cancer via targeting CCL-18. Int J Exp Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1111/iep.12366
Wang XY, Zhou YC, Wang Y et al (2020) miR-149 contributes to resistance of 5-FU in gastric cancer via targeting TREM2 and regulating β-catenin pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.05.135
Shen Z, Li C, Zhang K et al (2015) The up-regulation of miR-300 in gastric cancer and its effects on cells malignancy. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(5):6773–6783
Corradini E, Babitt JL, Lin HY (2009) The RGM/DRAGON family of BMP co-receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 20(5–6):389–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.10.008
Liu W, Chen B, Wang Y et al (2018) RGMb protects against acute kidney injury by inhibiting tubular cell necroptosis via an MLKL-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(7):E1475-e1484. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1716959115
Li J, Ye L, Sanders AJ et al (2012) Repulsive guidance molecule B (RGMB) plays negative roles in breast cancer by coordinating BMP signaling. J Cell Biochem 113(7):2523–2531. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24128
Shi Y, Chen GB, Huang XX et al (2015) Dragon (repulsive guidance molecule b, RGMb) is a novel gene that promotes colorectal cancer growth. Oncotarget 6(24):20540–20554. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4110
Xing C, Cai Z, Gong J et al (2018) Identification of potential biomarkers involved in gastric cancer through integrated analysis of non-coding RNA associated competing endogenous RNAs Network. Clin Lab 64(10):1661–1669. https://doi.org/10.7754/Clin.Lab.2018.180419
Yuan LW, Yamashita H, Seto Y (2016) Glucose metabolism in gastric cancer: the cutting-edge. World J Gastroenterol 22(6):2046–2059. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.2046
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods (San Diego, Calif) 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Khanipouyani F, Akrami H, Fattahi MR (2020) Circular RNAs as important players in human gastric cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-020-02419-2
Tian Y, Xing Y, Zhang Z et al (2020) Bioinformatics analysis of key genes and circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in gastric cancer. Biomed Res Int 2020:2862701. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2862701
Zhang JQ, Chen S, Gu JN et al (2018) MicroRNA-300 promotes apoptosis and inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by targeting CUL4B in pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 119(1):1027–1040. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26270
Bai J, Gao Y, Du Y et al (2019) MicroRNA-300 inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by downregulating CREPT/Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncol Lett 18(4):3743–3753. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10712
Kang Y, Zhang Y, Sun Y et al (2018) MicroRNA-300 suppresses metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Onco Targets Ther 11:5657–5666. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s173236
Ge W, Han C, Wang J et al (2016) MiR-300 suppresses laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and metastasis by targeting ROS1. Am J Transl Res 8(9):3903–3911
Wang L, Yu P (2016) miR-300 promotes proliferation and EMT-mediated colorectal cancer migration and invasion by targeting p53. Oncol Rep 36(6):3225–3232. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2016.5193
Xue Z, Zhao J, Niu L et al (2015) Up-regulation of MiR-300 promotes proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma by targeting BRD7. PLoS One 10(5):e0127682. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127682
Hwang J, Min BH, Jang J et al (2018) MicroRNA expression profiles in gastric carcinogenesis. Sci Rep 8(1):14393. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32782-8
Liu J, Wang W, Liu M et al (2016) Repulsive guidance molecule b inhibits renal cyst development through the bone morphogenetic protein signaling pathway. Cell Signal 28(12):1842–1851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.08.015
Li J, Ye L, Shi X et al (2016) Repulsive guidance molecule B inhibits metastasis and is associated with decreased mortality in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 7(13):15678–15689. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7463
Zhang S, He Y, Liu C et al (2020) miR-93-5p enhances migration and invasion by targeting RGMB in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Cancer 11(13):3871–3881. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.43854
Funding
Jiaxing City Science and Technology Plan Project (No.2019AD32262). 2019 Jiaxing Key Discipline of Medicine–Oncology (Supporting Subject) 2019-zc-11. 2023 Jiaxing city and provinces to build medical key disciplines-Oncology (2023-SSGJ-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL designed and performed the research; YZ and ZC analyzed the data; HJ, JL and GD wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Written informed consents were obtained from all participants and this study was permitted by the Ethics Committee of The First Hospital of Jiaxing, The Affiliated Hospital of Jiaxing University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original article has been revised for update in text under Materials and Methods section.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, J., Zhou, Y., Chen, Z. et al. Circ_0000419 acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer development via regulating miR-300/RGMB axis. Int J Clin Oncol 28, 1475–1485 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-023-02379-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-023-02379-x