Abstract
Background
Radical cystectomy (RC) is the primary treatment strategy for muscle invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). However, it carries a high risk of urethral recurrence (UR) in male patients. The risk factors and oncological outcomes of UR remain unclear. We aimed to identify the risk factors and oncological outcomes of UR in male patients with MIBC after RC combined with urinary diversion.
Methods
After propensity score matching, we evaluated 137 male patients with MIBC who underwent RC combined with urinary diversion at our center between January 1, 2007 and December 31, 2015. Patient demographics, comorbidity, and perioperative data were recorded. Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression were used to estimate the hazard ratio and 95% confidence intervals. Cancer-specific survival (CSS) and overall survival (OS) were measured using the Kaplan–Meier curve with log-rank test. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
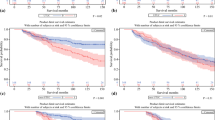
Of the 310 patients, 30 (9.7%) patients underwent UR. In the matched group, the independent risk factors of UR were history of TURB (HR = 3.069, P = 0.018), tumor stage (T3 vs. T2, HR = 3.997, P = 0.014; T4 vs. T2, HR = 2.962, P = 0.015), and tumor multifocality (HR = 2.854, P = 0.011). The CSS and OS of patients with UR were equivalent to the patients without UR (P = 0.295, P = 0.616).
Conclusion
This propensity score-matched case–control study showed that UR is not rare in male patients with MIBC after RC combined with urinary diversion. We identified three independent risk factors of UR: history of TURB, tumor stage, and tumor mutifocality. The oncological outcomes were equivalent between patients with and without UR. These findings could help improve treatment strategies and follow-up schedules.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E, Lortet-Tieulent J et al (2013) Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer 49(6):1374–1403
Rogers CG, Palapattu GS, Shariat SF et al (2006) Clinical outcomes following radical cystectomy for primary nontransitional cell carcinoma of the bladder compared to transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol. 175(6):2048–2053 (discussion 2053)
Mitra AP, Quinn DI, Dorff TB et al (2012) Factors influencing post-recurrence survival in bladder cancer following radical cystectomy. BJU Int 109(6):846–854
Boorjian SA, Kim SP, Weight CJ et al (2011) Risk factors and outcomes of urethral recurrence following radical cystectomy. Eur Urol 60(6):1266–1272
Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R et al (2001) Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: long-term results in 1054 patients. J Clin Oncol 19(3):666–675
Stein JP, Quek ML, Skinner DG (2006) Lymphadenectomy for invasive bladder cancer: I. historical perspective and contemporary rationale. BJU Int. 97(2):227–231
Ghoneim MA, El-Mekresh MM, El-Baz MA et al (1997) Radical cystectomy for carcinoma of the bladder: critical evaluation of the results in 1026 cases. J Urol 158(2):393–399
Ide H, Kikuchi E, Miyajima A et al (2008) The predictors of local recurrence after radical cystectomy in patients with invasive bladder cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 38(5):360–364
Fahmy O, Khairul-Asri MG, Schubert T et al (2018) Urethral recurrence after radical cystectomy for urothelial carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Urol Oncol 36(2):54–59
Word Health Organization (1997) Guidelines for controlling and monitoring the tobacco epidemic[M]. Tobacco or Health Programme, WHO, Geneva
Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI et al (2004) Pathology and genetics of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. IARCC Press, Lyon
Clark PE, Stein JP, Groshen SG et al (2004) The management of urethral transitional cell carcinoma after radical cystectomy for invasive bladder cancer. J Urol 172(4 Pt 1):1342–1347
Van Poppel H, Sorgeloose T (2003) Radical cystectomy with or without urethrectomy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 47(2):141–145
Beahrs JR, Fleming TR, Zincke H (1984) Risk of local urethral recurrence after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. J Urol 131(2):264–266
Lopez-Almansa M, Molina R, Huben RP (1988) Transitional cell carcinoma of the urethra in men after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Is prophylactic urethrectomy indicated. Br J Urol. 61(6):507–509
Tongaonkar HB, Dalal AV, Kulkarni JN et al (1993) Urethral recurrences following radical cystectomy for invasive transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Br J Urol 72(6):910–914
Miller MI, Benson MC (1996) Management of urethral recurrence after radical cystectomy and neobladder creation by urethroscopic resection and fulguration. J Urol 156(5):1768
Ali-el-Dein B, Abdel-Latif M, Ashamallah A et al (2004) Local urethral recurrence after radical cystectomy and orthotopic bladder substitution in women: a prospective study. J Urol 171(1):275–278
Cho KS, Seo JW, Park SJ et al (2009) The risk factor for urethral recurrence after radical cystectomy in patients with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urol Int 82(3):306–311
Balcı U, Dogantekin E, Özer K et al (2015) Patterns, risks and outcomes of urethral recurrence after radical cystectomy for urothelial cancer; over 20 year single center experience. Int J Surg 13:148–151
Freeman JA, Esrig D, Stein JP et al (1994) Management of the patient with bladder cancer. Urethral recurrence. Urol Clin North Am 21(4):645–651
Hafner C, Knuechel R, Stoehr R et al (2002) Clonality of multifocal urothelial carcinomas: 10 years of molecular genetic studies. Int J Cancer 101(1):1–6
Kakizoe T (2006) Development and progression of urothelial carcinoma. Cancer Sci 97(9):821–828
Stein JP, Clark P, Miranda G et al (2005) Urethral tumor recurrence following cystectomy and urinary diversion: clinical and pathological characteristics in 768 male patients. J Urol 173(4):1163–1168
Huguet J, Monllau V, Sabaté S et al (2008) Diagnosis, risk factors, and outcome of urethral recurrences following radical cystectomy for bladder cancer in 729 male patients. Eur Urol. 53(4):785–792 (discussion 792–3)
Perlis N, Turker P, Bostrom PJ et al (2013) Upper urinary tract and urethral recurrences following radical cystectomy: review of risk factors and outcomes between centres with different follow-up protocols. World J Urol 31(1):161–167
Gakis G, Black PC, Bochner BH et al (2017) Systematic review on the fate of the remnant urothelium after radical cystectomy. Eur Urol 71(4):545–557
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported (MC05) by the Shengjing Hospital Science and Technology Program. We give special thanks to all the teachers at the Department of Urology of Shengjing Hospital for their help and support.
Funding
Song Bai certifies that all conflicts of interest, including specific financial interests, relationships, and affiliations relevant to the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript (eg, employment/affiliation, grants or funding, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, royalties, or patents filed, received, or pending) are none.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SB had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. SB project development, data collection, and data analysis. YJ, BW and XZ data collection. ZY data collection, data analysis, and manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
The study involved human participants.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all eligible patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Z., Jiang, Y., Zhu, X. et al. Risk factors and oncological outcomes of urethral recurrence in male patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer after radical cystectomy combined with urinary diversion: a propensity score-matched case control study. Int J Clin Oncol 25, 1377–1384 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-020-01679-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-020-01679-w