Abstract
Background
Epithelium-specific ETS 3 (ESE3) is down-regulated frequently in several malignancies and involved in carcinogenesis and progression. However, ESE3 expression pattern and its relationship with clinical features and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are still largely unknown.
Methods
ESE3 expression was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR and western blotting in HCC cell lines, and then, it was analyzed by immunohistochemistry in HCC tissues and peritumoral normal tissues from total 94 HCC patients. The relationship between ESE3 expression and clinical features was investigated to illustrate the potential prognostic value in HCC. ESE3 roles on HCC progression were evaluated in vitro and vivo by MTT assay and mice tumor model, respectively.
Results
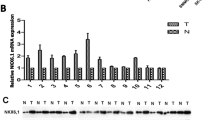
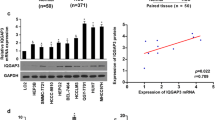
ESE3, mainly located in the cytoplasm, was remarkably down-regulated in HCC tissues and cell lines. Low ESE3 expression was positively associated with tumor progression and metastasis features. Kaplan–Meier analysis demonstrated that low ESE3 expression contributed to poor recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) (both p < 0.01) of patients, and maintained its prognostic value in predicting poor RFS and OS of “Early-stage” HCC patients regardless of clinical features being studied. Multivariate survival analysis was also identified ESE3 as an independent prognostic factor for RFS (p = 0.05 for marginal significance) and OS (p = 0.031). ESE3 expression restoration in cells led to a significant inhibition in HepG2 cell proliferation in vitro and vivo (both p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Down-regulated ESE3 expression in HCC tissues could serve as a potential therapeutic target against HCC and appears to be as a poor prognostic indicator for prognosis, especially in “Early-stage” HCC patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J (2018) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 391(10127):1301–1314
Kang KJ, Ahn KS (2017) Anatomical resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: a critical review of the procedure and its benefits on survival. World J Gastroenterol 23(7):1139–1146
Juarez-Hernandez E, Motola-Kuba D, Chavez-Tapia NC et al (2017) Biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma: an overview. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(6):549–558
Di Tommaso L, Roncalli M (2017) Tissue biomarkers in hepatocellular tumors: which, when, and how. Front Med (Lausanne) 4:10
Feldman RJ, Sementchenko VI, Watson DK (2003) The epithelial-specific Ets factors occupy a unique position in defining epithelial proliferation, differentiation and carcinogenesis. Anticancer Res 23(3A):2125–2131
Sharrocks AD (2001) The ETS-domain transcription factor family. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2(11):827–837
Oikawa T, Yamada T (2003) Molecular biology of the Ets family of transcription factors. Gene 303:11–34
Luk IY, Reehorst CM, Mariadason JM (2018) ELF3, ELF5, EHF and SPDEF transcription factors in tissue homeostasis and cancer. Molecules 23(9):2191
Seth A, Watson DK (2005) ETS transcription factors and their emerging roles in human cancer. Eur J Cancer 41(16):2462–2478
Kar A, Gutierrez-Hartmann A (2013) Molecular mechanisms of ETS transcription factor-mediated tumorigenesis. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 48(6):522–543
Albino D, Civenni G, Rossi S et al (2016) The ETS factor ESE3/EHF represses IL-6 preventing STAT3 activation and expansion of the prostate cancer stem-like compartment. Oncotarget 7(47):76756–76768
Zhao T, Jiang W, Wang X et al (2017) ESE3 Inhibits pancreatic cancer metastasis by upregulating E-cadherin. Cancer Res 77(4):874–885
Wang L, Xing J, Cheng R et al (2015) Abnormal localization and tumor suppressor function of epithelial tissue-specific transcription factor ese3 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 10(5):e0126319
Albino D, Longoni N, Curti L et al (2012) ESE3/EHF controls epithelial cell differentiation and its loss leads to prostate tumors with mesenchymal and stem-like features. Cancer Res 72(11):2889–2900
Albino D, Civenni G, Dallavalle C et al (2016) Activation of the Lin28/let-7 axis by Loss of ESE3/EHF promotes a tumorigenic and stem-like phenotype in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 76(12):3629–3643
Cangemi R, Mensah A, Albertini V et al (2008) Reduced expression and tumor suppressor function of the ETS transcription factor ESE-3 in prostate cancer. Oncogene 27(20):2877–2885
Li T, Zhu Y, Han L et al (2015) VEGFR-1 activation-induced MMP-9-dependent invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Future Oncol 11(23):3143–3157
Liu J, Han G, Liu H et al (2013) Suppression of cholangiocarcinoma cell growth by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: a possible role of Wnt and Akt signaling. PLoS ONE 8(4):e62844
Li T, Zhu Y, Ren W et al (2012) High co-expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 and Snail is associated with poor prognosis after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol 29(4):2750–2761
Bruix J, Llovet JM (2002) Prognostic prediction and treatment strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 35(3):519–524
Livraghi T (2003) Radiofrequency ablation, PEIT, and TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 10(1):67–76
Llover JMDBA, Bruix J (2008) Design and end-points of clinical trials in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 100:698–711
Longoni N, Kunderfranco P, Pellini S et al (2013) Aberrant expression of the neuronal-specific protein DCDC2 promotes malignant phenotypes and is associated with prostate cancer progression. Oncogene 32(18):2315–2324
Galang CK, Muller WJ, Foos G et al (2004) Changes in the expression of many Ets family transcription factors and of potential target genes in normal mammary tissue and tumors. J Biol Chem 279(12):11281–11292
Fujiwara N, Friedman SL, Goossens N et al (2018) Risk factors and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of precision medicine. J Hepatol 68:526–549
Choi SB, Lee JG, Kim KS et al (2008) The prognosis and survival analysis according to seven staging systems of hepatocellular carcinoma following curative resection. Hepatogastroenterology 55(88):2140–2145
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Prof. Bo Zhang (Shanghai Harmonious One Biotech Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China) for kindly providing HCC cell lines, technical assistance, and helpful discussion regarding this research area. This study was funded by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81602550 and No. 81871700), Science and Technology Development Project of Shandong Province (No. 2018GSF118072), and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2018BH003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and animal
Ethical approval for using human samples and animals was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Provincial Hospital affiliated to Shandong University.
Informed consent
Patients had to give written informed consent for the use of their tumor tissues for further investigations at time of the initial diagnosis.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Lyu, Z., Ma, M., Xu, Y. et al. Expression and prognostic significance of epithelial tissue-specific transcription factor ESE3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol 25, 1334–1345 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-020-01675-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-020-01675-0