Abstract
Background
To evaluate the relationship between sarcopenia and myelosuppression or between sarcopenia and survival outcomes in patients with urothelial carcinoma (UC) undergoing chemotherapy with gemcitabine plus cisplatin (GC) or carboplatin (GCa).
Methods
We evaluated 80 patients with UC who underwent chemotherapy between 2013 and 2017 at our institution. In total, 53 patients had metastatic UC and were ultimately included in the study. Predictive factors for myelosuppression (neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia) in all patients and overall survival (OS) in metastatic UC patients were analyzed. Sarcopenia was assessed on computed tomography before chemotherapy. Each patient’s total psoas area was measured at the lumbar vertebrae (L3) and sarcopenia was defined as median values or lower. Predictive factors for myelosuppression were assessed using logistic regression analysis and survival was evaluated using Cox regression analysis.
Results
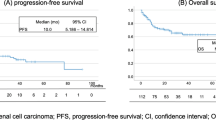
The patients’ mean age was 71.6 years (range 44.4–89.2 years). Of the initial 80 patients, 39 were diagnosed with sarcopenia and 26 of 53 patients with metastatic UC were diagnosed with sarcopenia. Sarcopenia was an independent predictive factor (P = 0.030; odds ratio, 3.526; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.128–11.01) for neutropenia on multivariate analysis. Patients without sarcopenia had a significantly longer OS compared to those with sarcopenia (P = 0.013). Sarcopenia and albumin (P = 0.045, 0.023; hazard ratio (HR), 2.309, 2.652; 95% CI 1.021–5.225, 1.141–6.165, respectively) were independent predictors of OS in multivariate analysis.
Conclusions
Sarcopenia was predictive for neutropenia associated with GC or GCa in UC patients and OS in metastatic UC.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenberg IH (1997) Sarcopenia: origins and clinical relevance. J Nutr 127:990S–991S
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM et al (2010) Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: report of the European working group on sarcopenia in older people. Age Ageing 39:412–423
Sabel MS, Lee J, Cai S et al (2011) Sarcopenia as a prognostic factor among patients with stage III melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol 18:3579–3585
Del Fabbro E, Parsons H, Warneke CL et al (2012) The relationship between body composition and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in women with operable breast cancer. Oncologist 17:1240–1245
Mir O, Coriat R, Blanchet B et al (2012) Sarcopenia predicts early dose-limiting toxicities and pharmacokinetics of sorafenib in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 7:e37563
Zhuang CL, Huang DD, Pang WY et al (2016) Sarcopenia is an independent predictor of severe postoperative complications and long-term survival after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer: analysis from a large-scale cohort. Medicine (Baltimore) 95:e3164
Onesti JK, Wright GP, Kenning SE et al (2016) Sarcopenia and survival in patients undergoing pancreatic resection. Pancreatology 16:284–289
Wan F, Zhu Y, Gu C et al (2014) Lower skeletal muscle index and early complications in patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. World J Surg Oncol 12:14
Smith AB, Deal AM, Yu H et al (2014) Sarcopenia as a predictor of complications and survival following radical cystectomy. J Urol 191:1714–1720
Psutka SP, Carrasco A, Schmit GD et al (2014) Sarcopenia in patients with bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy: impact on cancer-specific and all-cause mortality. Cancer 120:2910–2918
Kasahara R, Kawahara T, Ohtake S et al (2017) A low psoas muscle index before treatment can predict a poorer prognosis in advanced bladder cancer patients who receive gemcitabine and nedaplatin therapy. Biomed Res Int 2017:7981549
Abe H, Takei K, Uematsu T et al (2018) Significance of sarcopenia as a prognostic factor for metastatic urothelial carcinoma patients treated with systemic chemotherapy. Int J Clin Oncol 23:338–346
Hori M, Matsuda T, Shibata A et al (2015) Cancer incidence and incidence rates in Japan in 2009: a study of 32 population-based cancer registries for the Monitoring of Cancer Incidence in Japan (MCIJ) project. Jpn J Clin Oncol 45:884–891
von der Maase H, Sengelov L, Roberts JT et al (2005) Long-term survival results of a randomized trial comparing gemcitabine plus cisplatin, with methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, plus cisplatin in patients with bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:4602–4608
Allard P, Bernard P, Fradet Y et al (1988) The early clinical course of primary Ta and T1 bladder cancer: a proposed prognostic index. Br J Urol 81:692–698
Kim TN, Choi KM (2013) Definition, epidemiology, and pathophysiology. J Bone Metab 20:1–10
Taguchi S, Akamatsu N, Nakagawa T et al (2016) Sarcopenia evaluated using the skeletal muscle index is a significant prognostic factor for metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer 14:237–243
Tan BH, Brammer K, Randhawa N et al (2015) Sarcopenia is associated with toxicity in patients undergoing neo-adjuvant chemotherapy for oesophago-gastric cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 41:333–338
Prado CM, Lieffers JR, McCargar LJ et al (2008) Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol 9:629–635
Sato S, Kunisaki C, Suematsu H et al (2018) Impact of sarcopenia in patients with unresectable locally advanced esophageal cancer receiving chemoradiotherapy. Vivo 32:603–610
Hirasawa Y, Nakashima J, Yunaiyama D et al (2016) Sarcopenia as a novel preoperative prognostic predictor for survival in patients with bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy. Ann Surg Oncol 23:1048–1054
Mayr R, Gierth M, Zeman F et al (2018) Sarcopenia as a comorbidity-independent predictor of survival following radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 9:505–513
Fukushima H, Nakanishi Y, Kataoka M et al (2016) Prognostic significance of sarcopenia in upper tract urothelial carcinoma patients treated with radical nephroureterectomy. Cancer Med 5:2213–2220
Ishihara H, Kondo T, Omae K et al (2017) Sarcopenia predicts survival outcomes among patients with urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract undergoing radical nephroureterectomy: a retrospective multi-institution study. Int J Clin Oncol 22:136–144
Anno T, Kikuchi E, Fukumoto K et al (2018) Preoperative sarcopenia status is associated with lymphovascular invasion in upper tract urothelial carcinoma patients treated with radical nephroureterectomy. Can Urol Assoc J 12:E132–E136
Fukushima H, Yokoyama M, Nakanishi Y et al (2015) Sarcopenia as a prognostic biomarker of advanced urothelial carcinoma. PLoS ONE 10:e0115895
Martin L, Birdsell L, Macdonald N et al (2013) Cancer cachexia in the age of obesity: skeletal muscle depletion is a powerful prognostic factor, independent of body mass index. J Clin Oncol 31:1539–1547
Tsutsumi S, Kawahara T, Teranishi JI et al (2018) A low psoas muscle volume predicts longer hospitalization and cancer recurrence in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Mol Clin Oncol 8:320–322
Mathijssen RH, de Jong FA, Loos WJ et al (2007) Flat-fixed dosing versus body surface area based dosing of anticancer drugs in adults: does it make a difference? Oncologist 12:913–923
Galsky MD, Hahn NM, Rosenberg J et al (2011) Treatment of patients with metastatic urothelial cancer “unfit” for cisplatin-based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 29:2432–2438
Dogliotti L, Cartenì G, Siena S et al (2007) Gemcitabine plus cisplatin versus gemcitabine plus carboplatin as first-line chemotherapy in advanced transitional cell carcinoma of the urothelium: results of a randomized phase 2 trial. Eur Urol 52:134–141
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
The need for informed consent was waived because of the retrospective nature of the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Yumioka, T., Honda, M., Nishikawa, R. et al. Sarcopenia as a significant predictive factor of neutropenia and overall survival in urothelial carcinoma patients underwent gemcitabine and cisplatin or carboplatin. Int J Clin Oncol 25, 158–164 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-019-01544-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-019-01544-5