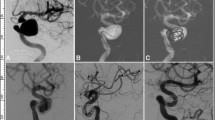
Abstract
The flow diverter (FD) device has become a feasible and effective option for treating intracranial aneurysms. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Tubridge FD (TFD) in treating intracranial aneurysms and provide evidence for further research and clinical application. Electronic databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and the Cochrane Library from inception to July 31, 2022, were searched. The eligible studies should include TFD investigations in treating intracranial aneurysms. Pooled technical success rate, complete occlusion rate, improvement rate, stable rate, symptom elimination rate, and adverse events rate were calculated with either the fixed-effects model or the random-effects model, depending on the results of tests for heterogeneity. Egger’s tests were performed to assess the potential publication bias. A total of 7 studies (145 patients) were included in this study. The pooled technical success rate was 0.98, the complete occlusion rate was 0.79, the improvement rate was 0.21, and the stable rate was 0.05. One included study reported that the surgery-related mortality rate in the Tubridge group was higher than that in the control group (3.66% vs. 1.61%), while the surgery-related morbidity rate in the Tubridge group was 2.4% and that in the control group was 0. Findings of this meta-analysis indicate that TFD manifests promising and effective performance with acceptable adverse events in the treatment of intracranial aneurysms.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article/as supplementary information files.
References
Vlak MH, Algra A, Brandenburg R, Rinkel GJ (2011) Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms, with emphasis on sex, age, comorbidity, country, and time period: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 10:626–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(11)70109-0
Adamou A, Alexandrou M, Roth C, Chatziioannou A, Papanagiotou P (2021) Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Life (Basel) 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11040335
Hackenberg KAM, Hänggi D, Etminan N (2018) Unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Stroke 49:2268–2275. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.118.021030
Ten Brinck MFM, Shimanskaya VE, Aquarius R, Bartels R, Meijer FJA, Koopmans PC, de Jong G, Wakhloo AK, de Vries J, Boogaarts HD (2022) Outcomes after flow diverter treatment in subarachnoid hemorrhage: a meta-analysis and development of a clinical prediction model (OUTFLOW). Brain Sci 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12030394
Broderick JP, Brott T, Tomsick T, Huster G, Miller R (1992) The risk of subarachnoid and intracerebral hemorrhages in Blacks as compared with Whites. N Engl J Med 326:733–736. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199203123261103
Korja M, Lehto H, Juvela S (2014) Lifelong rupture risk of intracranial aneurysms depends on risk factors: a prospective Finnish cohort study. Stroke 45:1958–1963. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.114.005318
Lee IT, Kao YS, Lai YJ, Yen HH (2022) Flow diverter retreatment for intracranial aneurysms: a meta-analysis of efficacy and feasibility. Interv Neuroradiol:15910199221095972. https://doi.org/10.1177/15910199221095972
Ichinose T, Misaki K, Uchiyama N, Kamide T, Nambu I, Yoshikawa A, Tsuchiya S, Nakada M (2022) Late complications of visual impairment and hydrocephalus after flow diverter-assisted coil embolisation for intracranial large aneurysm: a case report and literature review. Br J Neurosurg:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1080/02688697.2021.2024502
Xia JL, Li GL, Liu HE, Feng-Fei X, Gu XD (2021) Flow-diverting device versus coil embolization for unruptured intracranial aneurysm A meta-analysis. Medicine 100. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000026351
Pontes FGB, da Silva EM, Baptista-Silva JC, Vasconcelos V (2021) Treatments for unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5:Cd013312. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD013312.pub2
Jing L, Zhong J, Liu J, Yang X, Paliwal N, Meng H, Wang S, Zhang Y (2016) Hemodynamic effect of flow diverter and coils in treatment of large and giant intracranial aneurysms. World Neurosurg 89:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.01.079
Oliver AA, Carlson KD, Bilgin C, Arturo Larco JL, Kadirvel R, Guillory Ii RJ, Dragomir Daescu D, Kallmes DF (2022) Bioresorbable flow diverters for the treatment of intracranial aneurysms: review of current literature and future directions. J Neurointerv Surg. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2022-018941
Dabhi N, Sarathy D, Snyder MH, Kellogg RT, Park MS (2022) Flow diverter devices for treatment of intracranial aneurysms in small parent vessels—a systematic review of literature. World Neurosur 162:183–194.e187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2022.02.034
Ravindran K, Casabella AM, Cebral J, Brinjikji W, Kallmes DF, Kadirvel R (2020) Mechanism of action and biology of flow diverters in the treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 86:S13–s19. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyz324
Liu JM, Zhou Y, Li Y, Li T, Leng B, Zhang P, Liang G, Huang Q, Yang PF, Shi H et al (2018) Parent Artery reconstruction for large or giant cerebral aneurysms using the Tubridge flow diverter: a multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial (PARAT). AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 39:807–816. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A5619
Li S, Zeng C, Tao W, Huang Z, Yan L, Tian X, Chen F (2022) The safety and efficacy of flow diversion versus conventional endovascular treatment for intracranial aneurysms: a meta-analysis of real-world cohort studies from the past 10 years. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 43:1004–1011. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A7539
Fang YB, Wen WL, Yang PF, Zhou Y, Wu YN, Hong B, Xu Y, Zhao WY, Liu JM, Huang QH (2017) Long-term outcome of tubridge flow diverter(s) in treating large vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms-a pilot study. Clin Neuroradiol 27:345–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-015-0494-8
Jia L, Wang J, Zhang L, Zhang Y, You W, Yang X, Lv M (2020) Evaluating the Tubridge™ flow diverter for large cavernous carotid artery aneurysms. Chin Neurosurg J 6:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-020-00215-z
Zhou Y, Yang PF, Fang YB, Xu Y, Hong B, Zhao WY, Li Q, Zhao R, Huang QH, Liu JM (2014) A novel flow-diverting device (Tubridge) for the treatment of 28 large or giant intracranial aneurysms: a single-center experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:2326–2333. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3925
Zhang Y, Huang QH, Fang Y, Yang P, Xu Y, Hong B, Liu J (2017) A novel flow diverter (Tubridge) for the treatment of recurrent aneurysms: a single-center experience. Korean J Radiol 18:852–859. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2017.18.5.852
Liang F, Yang Y, Luo L, Liao B, Zhang G, Ou S, Xiao W, Guo N, Qi T (2020) Endovascular treatment of complex middle cerebral artery aneurysms using TuBridge flow diverters. Interv Neuroradiol 26:539–546. https://doi.org/10.1177/1591019920946216
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2010) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg 8:336–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.02.007
Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, Panis Y, Chipponi J (2003) Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg 73:712–716. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1445-2197.2003.02748.x
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA (2011) The cochrane collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj 343:d5928. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d5928
Sadasivan C, Cesar L, Seong J, Wakhloo AK, Lieber BB (2009) Treatment of rabbit elastase-induced aneurysm models by flow diverters: development of quantifiable indexes of device performance using digital subtraction angiography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28:1117–1125. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2008.2012162
Turfe ZA, Brinjikji W, Murad MH, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF (2015) Endovascular coiling versus parent artery occlusion for treatment of cavernous carotid aneurysms: a meta-analysis. J Neurointerv Surg 7:250–255. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2014-011102
Kan P, Siddiqui AH, Veznedaroglu E, Liebman KM, Binning MJ, Dumont TM, Ogilvy CS, Gaughen JR Jr, Mocco J, Velat GJ et al (2012) Early postmarket results after treatment of intracranial aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device: a U.S. multicenter experience. Neurosurgery 71:1080–1087. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e31827060d9
Kallmes DF, Hanel R, Lopes D, Boccardi E, Bonafé A, Cekirge S, Fiorella D, Jabbour P, Levy E, McDougall C et al (2015) International retrospective study of the pipeline embolization device: a multicenter aneurysm treatment study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 36:108–115. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4111
Lylyk P, Miranda C, Ceratto R, Ferrario A, Scrivano E, Luna HR, Berez AL, Tran Q, Nelson PK, Fiorella D (2009) Curative endovascular reconstruction of cerebral aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device: the Buenos Aires experience. Neurosurgery 64:632–642. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.Neu.0000339109.98070.65
Saatci I, Yavuz K, Ozer C, Geyik S, Cekirge HS (2012) Treatment of intracranial aneurysms using the pipeline flow-diverter embolization device: a single-center experience with long-term follow-up results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:1436–1446. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3246
Arrese I, Sarabia R, Pintado R, Delgado-Rodriguez M (2013) Flow-diverter devices for intracranial aneurysms: systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurgery 73:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000430297.17961.f1
Briganti F, Leone G, Marseglia M, Mariniello G, Caranci F, Brunetti A, Maiuri F (2015) Endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysms using flow-diverter devices: a systematic review. Neuroradiol J 28:365–375. https://doi.org/10.1177/1971400915602803
Lv X, Yang H, Liu P, Li Y (2016) Flow-diverter devices in the treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Neuroradiol J 29:66–71. https://doi.org/10.1177/1971400915621321
Kim CH, Lee CH, Kim YH, Sung SK, Son DW, Lee SW, Song GS (2021) Flow diverter devices for the treatment of unruptured vertebral artery dissecting aneurysm. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 64:891–900. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2021.0181
Brinjikji W, Murad MH, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF (2013) Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with flow diverters: a meta-analysis. Stroke 44:442–447. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.112.678151
Yu SC, Kwok CK, Cheng PW, Chan KY, Lau SS, Lui WM, Leung KM, Lee R, Cheng HK, Cheung YL et al (2012) Intracranial aneurysms: midterm outcome of pipeline embolization device--a prospective study in 143 patients with 178 aneurysms. Radiology 265:893–901. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12120422
Raymond J, Gentric JC, Darsaut TE, Iancu D, Chagnon M, Weill A, Roy D (2017) Flow diversion in the treatment of aneurysms: a randomized care trial and registry. J Neurosurg 127:454–462. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.4.Jns152662
McAuliffe W, Wycoco V, Rice H, Phatouros C, Singh TJ, Wenderoth J (2012) Immediate and midterm results following treatment of unruptured intracranial aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:164–170. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A2727
Rouchaud A, Brinjikji W, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Kadirvel R, Kallmes DF (2016) Delayed hemorrhagic complications after flow diversion for intracranial aneurysms: a literature overview. Neuroradiology 58:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1615-4
Byrne JV, Beltechi R, Yarnold JA, Birks J, Kamran M (2010) Early experience in the treatment of intra-cranial aneurysms by endovascular flow diversion: a multicentre prospective study. PLoS One 5. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0012492
Becske T, Potts MB, Shapiro M, Kallmes DF, Brinjikji W, Saatci I, McDougall CG, Szikora I, Lanzino G, Moran CJ et al (2017) Pipeline for uncoilable or failed aneurysms: 3-year follow-up results. J Neurosurg 127:81–88. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.6.Jns15311
Topcuoglu OM, Akgul E, Daglioglu E, Topcuoglu ED, Peker A, Akmangit I, Belen D, Arat A (2016) Flow Diversion in middle cerebral artery aneurysms: is it really an all-purpose treatment? World Neurosurg 87:317–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2015.11.073
Zhou G, Su M, Yin YL, Li MH (2017) Complications associated with the use of flow-diverting devices for cerebral aneurysms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Focus 42:E17. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.3.Focus16450
Giorgianni A, Agosti E, Molinaro S, Terrana AV, Vizzari FA, Nativo L, Garg K, Craparo G, Conti V, Locatelli D et al (2022) Flow diversion for acutely ruptured intracranial aneurysms treatment: a retrospective study and literature review. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 31:106284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.106284
Chalouhi N, Jabbour P, Singhal S, Drueding R, Starke RM, Dalyai RT, Tjoumakaris S, Gonzalez LF, Dumont AS, Rosenwasser R et al (2013) Stent-assisted coiling of intracranial aneurysms: predictors of complications, recanalization, and outcome in 508 cases. Stroke 44:1348–1353. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.111.000641
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: YF, YL, J LEI. Administrative support: YL. Provision of study materials or patients: YL, FF, J LIU. Collection and assembly of data: YF, J LEI, J LIU, FF. Data analysis and interpretation: YF, J LEI, J LIU, FF. Manuscript writing: All authors. Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article is a systematic review and does not require ethical approval.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
Supplementary Figure S1. Pooled results of sensitivity analysis on technical success rates in studies included. (JPG 49 kb)
ESM 2
Supplementary Figure S2. Pooled results of sensitivity analysis on complete occlusion rates in studies included. (JPG 75 kb)
ESM 3
Supplementary Figure S3. Pooled results of sensitivity analysis on improvement rates in studies included. (JPG 56 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Y., Lei, J., Fei, F. et al. A novel flow diverter device (Tubridge) for the treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev 46, 198 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-023-02100-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-023-02100-6