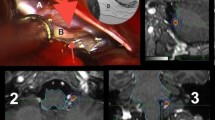
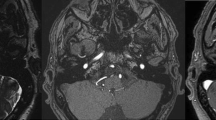
Abstract
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia (GPN) is a neurological condition characterized by paroxysmal, stabbing-like pain along the distribution of the glossopharyngeal nerve that lasts from a couple of seconds to minutes. Pharmacological treatment with anticonvulsants is the first line of treatment; however, about 25% of patients remain symptomatic and require surgical intervention, which is usually done via microvascular decompression (MVD) with or without rhizotomy. More recently, the use of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) has been utilized as an alternative treatment method to relieve patient symptoms by causing nerve ablation. We conducted a systematic review to analyze whether MVD without rhizotomy is an equally effective treatment for GPN as MVD with the use of concurrent rhizotomy. Moreover, we sought to explore if SRS, a minimally invasive alternative surgical option, achieves comparable outcomes. We included retrospective studies and case reports in our search. We consulted PubMed and Medline, including articles from the year 2000 onwards. A total of 36 articles were included for review. Of all included patients with glossopharyngeal neuralgia, the most common offending artery compressing the glossopharyngeal nerve was the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA). MVD alone was successful achieving pain relief immediately postoperatively in about 85% of patients, and also long term in 65–90% of patients. The most common complication found on MVD surgery was found to be transient hoarseness and transient dysphagia. Rhizotomy alone shows an instant pain relief in 85–100% of the patients, but rate of long-term pain relief was lower compared to MVD. The most common adverse effects observed after a rhizotomy were dysphagia and dysesthesia along the distribution of the glossopharyngeal nerve. SRS had promising results in pain reduction when using 75 Gy radiation or higher; however, long-term rates of pain relief were lower. MVD, rhizotomy, and SRS are effective methods to treat GPN as they help achieve instant pain relief and the decrease use of medication. Patients with MVD alone presented with less adverse effects than the group that underwent MVD plus rhizotomy. Although SRS may be a viable alternative treatment for GPN, further studies must be done to evaluate long-term treatment efficacy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pearce J (2006) Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia. Eur Neurol 55:49-52 Available at: (https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/91429#)
Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) (2018) The International Classification of Headache Disorders. Cephalalgia 38(1):1–211 (Available at: https://journals-sagepub-com.ezproxy.universidadeuropea.es/doi/10.1177/0333102417738202?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%20%200pubmed)
Singh P, Kaur M, Trikha A (2013) An uncommonly common: glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 16(1):1–8 (Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3644765/)
Wang J, Yu R, Qu C, Jiang J, Wang C, Meng Q, Wei S (2018) Does glossopharyngeal neuralgia need rhizotomy in neurovascular decompression surgery? J Craniofac Surg. 29(8):2192–2194 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30320682/)
Sindou M, Keravel Y (2009) Traitement neurochirurgical de la névralgie vago-glossopharyngienne [Neurosurgical treatment of vago-glossopharyngeal neuralgia]. Neurochirurgie 55(2):231–5 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19298981/ )
Kawashima M, Matsushima T, Inoue T, Mineta T, Masuoka J, Hirakawa N (2010) Microvascular decompression for glossopharyngeal neuralgia through the transcondylar fossa (supracondylar transjugular tubercle) approach. Neurosurgery 66(6 Suppl Operative):275–80 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20489516/)
Sampson JH, Grossi PM, Asaoka K, Fukushima T (2004) Microvascular decompression for glossopharyngeal neuralgia: long-term effectiveness and complication avoidance. Neurosurgery 54(4):884–889 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15046654/)
Kandan SR, Khan S, Jeyaretna DS, Lhatoo S, Patel NK, Coakham HB (2010) Neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal and vagal nerves: long-term outcome following surgical treatment and literature review. Br J Neurosurg 24(4):441–6 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20726751/)
Gaul C, Hastreiter P, Duncker A, Naraghi R (2011) Diagnosis and neurosurgical treatment of glossopharyngeal neuralgia: clinical findings and 3-D visualization of neurovascular compression in 19 consecutive patients. J Headache Pain 12(5):527–34 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21567138/)
Kim MK, Park JS, Ahn YH (2017) Microvascular decompression for glossopharyngeal neuralgia: clinical analyses of 30 cases. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60(6):738–748 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29142635/)
Xia L, Li YS, Liu MX, Zhong J, Dou NN, Li B, Li ST (2018) Microvascular decompression for glossopharyngeal neuralgia: a retrospective analysis of 228 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 160(1):117–123 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29103137/)
Zheng X, Wei XY, Zhu J, Yuan Y, Ying TT, Li ST (2020) Microvascular decompression alone without rhizotomy is an effective way of treating glossopharyngeal neuralgia: clinical analysis of 46 cases. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 98(2):129–135 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32101860/)
Wang X, Meng D, Wang L, Chen G (2021) The clinical characteristics and surgical treatment of glossopharyngeal neuralgia with pain radiating to the innervated area of the trigeminal nerve. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 79(4):786.e1-786.e8 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33387474/)
Zheng W, Zhao P, Song H, Liu B, Zhou J, Fan C, Wang D, Liu R (2021) Prognostic factors for long-term outcomes of microvascular decompression in the treatment of glossopharyngeal neuralgia: a retrospective analysis of 97 patients. J Neurosurg 17:1–8 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34920419/)
Roser F, Ebner FH, Schuhmann MU, Tatagiba M (2013) Glossopharyngeal neuralgia treated with an endoscopic assisted midline suboccipital subtonsillar approach: technical note. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg 74(5):318–20 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23042141/)
Alafaci C, Granata F, Cutugno M, Marino D, Conti A, Tomasello F (2015) Glossopharyngeal neuralgia caused by a complex neurovascular conflict: case report and review of the literature. Surg Neurol Int 6(1):19 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25709856/)
Ma Y, Li Y, Wang Q, Wang B, Huang H (2016) Neurosurgical treatment of glossopharyngeal neuralgia: analysis of 103 cases. J Neurosurg 124(4):1088–1092 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26339847/)
Motoyama Y, Nakagawa I, Takatani T, Park H, Kotani Y, Tanaka Y et al (2016) Microvascular decompression for glossopharyngeal neuralgia using intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring: technical case report. Surg Neurol Int 7(3):28 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26862458/)
Bishnoi I, Singh D, Bishnoi S, Mewada T, Sachdeva D et al (2018) Ring graft technique for microvascular decompression. Neurol Ind 66(6):1687–1691 (Available at: https://www.neurologyindia.com/article.asp?issn=0028-3886;year=2018;volume=66;issue=6;spage=1687;epage=1691;aulast=Bishnoi)
Patel A, Kassam A, Horowitz M, Chang YF (2002) Microvascular decompression in the management of glossopharyngeal neuralgia: analysis of 217 cases. Neurosurgery 50(4):705–10 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11904019/)
Ferroli P, Fioravanti A, Schiariti M et al (2009) Microvascular decompression for glossopharyngeal neuralgia: a long-term retrospectic review of the Milan-Bologna experience in 31 consecutive cases. Acta Neurochir 151:1245–1250 (Available at: https://link-springer-com.ezproxy.universidadeuropea.es/article/10.1007/s00701-009-0330-5)
Xiong N, Zhao H, Zhang F, Liu R (2012) Vagoglossopharyngeal neuralgia treated by microvascular decompression and glossopharyngeal rhizotomy: clinical results of 21 cases. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 90(1):45–50 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22249175/)
Wang X, Tang Y, Zeng Y, Ni J (2016) Long-term outcomes of percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation for glossopharyngeal neuralgia: a retrospective observational study. Medicine (Baltimore). 95(48):e5530 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27902620/)
Song L, He L, Pei Q, Peng K, Wang N, Guo Z, Ni J (2019) CT-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation for glossopharyngeal neuralgia: a retrospective clinical study of 117 cases. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 178:42–45 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30708339/)
Ozenci M, Karaoguz R, Conkbayir C, Altin T, Kanpolat Y (2003) Glossopharyngeal neuralgia with cardiac syncope treated by glossopharyngeal rhizotomy and microvascular decompression. EP Europace. 5(2):149–152 (Available at: https://academic.oup.com/europace/article/5/2/149/2344620?login=false)
Zhang W, Chen M, Zhang W, Chai Y (2014) Use of electrophysiological monitoring in selective rhizotomy treating glossopharyngeal neuralgia. J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg 42(5):e182–e185 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24095216/)
Yomo S, Arkha Y, Donnet A, Régis J (2009) Gamma Knife surgery for glossopharyngeal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 110(3):559–63 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19025360/)
Williams BJ, Schlesinger D, Sheehan J (2010) Glossopharyngeal neuralgia treated with gamma knife radiosurgery. World Neurosurg 73(4):413–7 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20849803/)
Stanic S, Franklin S, Pappas C, Stern R (2012) Gamma knife radiosurgery for recurrent glossopharyngeal neuralgia after microvascular decompression. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 90(3):188–191
Lévêque M, Park M, Melhaoui A, Yomo S, Donnet A, Régis J (2011) Gamma knife radiosurgery for glossopharyngeal neuralgia: Marseille experience*. J Radiosurg SBRT 1(1):41–46 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29296296/)
Stieber VW, Bourland JD, Ellis TL (2005) Glossopharyngeal neuralgia treated with gamma knife surgery: treatment outcome and failure analysis. Case report. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):155–7 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15662801/)
O’Connor J, Bidiwala S (2013) Effectiveness and safety of gamma knife radiosurgery for glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Baylor Univ Med Center Proc 26(3):262–264 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23814384/)
Martínez-Álvarez R, Martínez-Moreno N, Kusak M, Rey-Portolés G (2014) Glossopharyngeal neuralgia and radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 121(Suppl_2):222–225 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25434956/)
Héroux F, Mathieu D (2015) Treatment of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by gamma knife radiosurgery. Can J Neurol Sci / Journal Canadien des Sciences Neurologiques. 42(5):350–352 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26348903/)
Xiong N, Tan D, Fu P, Zhao H (2015) Gamma knife radiosurgery for glossopharyngeal neuralgia by targeting the medial cisternal segment of the glossopharyngeal nerve: report of 3 cases. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 93(4):292–296 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26183516/)
Borius PY, Tuleasca C, Muraciole X, Negretti L, Schiappacasse L, Dorenlot A, Marguet M, Zeverino M, Donnet A, Levivier M, Regis J (2018) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for glossopharyngeal neuralgia: a study of 21 patients with long-term follow-up. Cephalalgia. 38(3):543–550 ( Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28952337/)
Fu P, Xiong NX, Abdelmaksoud A, Huang YZ, Song GB, Zhao HY (2018) Gamma knife radiosurgery of the superior laryngeal neuralgia: a report of 3 cases. World Neurosurg. 116:144–148 (Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29787878/)
Lara-Almunia M, Moreno NEM, Sarraga JG et al (2022) Gamma Knife radiosurgery and refractory glossopharyngeal neuralgia: a single-center series with long-term follow-up. Neurosurg Rev 45:525–531 (Available at: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10143-021-01557-7#citeas)
Chai S, Xu H, Xiao D, Wang J, Wang Y, Li J, Fu P, Pool H, Xiong N (2021) Salvage gamma knife surgery for recurrent glossopharyngeal neuralgia following microvascular decompression: a retrospective case series. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 163(4):1021–1026 (Available at: https://link-springer-com.ezproxy.universidadeuropea.es/content/pdf/10.1007/s00701-020-04654-6.pdf)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Berckemeyer, M.A., Suarez-Meade, P., Carcelen, M.F.V. et al. Current advances in the surgical treatment of glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Neurosurg Rev 46, 47 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-023-01948-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-023-01948-y