Abstract
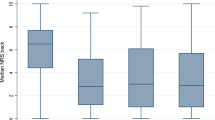
In order to evaluate the predictive effect of non-invasive preoperative imaging methods on surgical outcomes of lumbar fusion for patients with degenerative disc disease (DDD) and refractory chronic axial low back pain (LBP), the authors conducted a retrospective review of 45 patients with DDD and refractory LBP submitted to anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) at a single center from 2007 to 2010. Surgical outcomes - as measured by Visual Analog Scale (VAS/back pain) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) - were evaluated pre-operatively and at 6 weeks, 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year post-operatively. Linear mixed-effects models were generated in order to identify possible preoperative imaging characteristics (including bone scan/99mTc scintigraphy increased endplate uptake, Modic endplate changes, and disc degeneration graded according to Pfirrmann classification) which may be predictive of long-term surgical outcomes . After controlling for confounders, a combined score, the Lumbar Fusion Outcome Score (LUFOS), was developed. The LUFOS grading system was able to stratify patients in two general groups (Non-surgical: LUFOS 0 and 1; Surgical: LUFOS 2 and 3) that presented significantly different surgical outcomes in terms of estimated marginal means of VAS/back pain (p = 0.001) and ODI (p = 0.006) beginning at 3 months and continuing up to 1 year of follow-up. In conclusion, LUFOS has been devised as a new practical and surgically oriented grading system based on simple key parameters from non-invasive preoperative imaging exams (magnetic resonance imaging/MRI and bone scan/99mTc scintigraphy) which has been shown to be highly predictive of surgical outcomes of patients undergoing lumbar fusion for treatment for refractory chronic axial LBP.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert HB, Briggs AM, Kent P, Byrhagen A, Hansen C, Kjaergaard K (2011) The prevalence of MRI-defined spinal pathoanatomies and their association with modic changes in individuals seeking care for low back pain. Eur Spine J 20:1355–1362
Anderson T, Christensen FB, Laursen M, Hoy K, Hansen ES, Bunger C (2001) Smoking as a predictor of negative outcome in lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:2623–2628
Atlas SJ, Deyo RA, Keller RB, Chapin AM, Patrick DL, Long JM, Singer DE (1996) The Maine lumbar spine study, part III. 1-year outcomes of surgical and nonsurgical management of lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 21:1787–1794
Boden SD, Davis DO, Dina TS, Patronas NJ, Wiesel SW (1990) Abnormal magnetic-resonance scans of the lumbar spine in asymptomatic subjects. A prospective investigation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 72:403–408
Brown CW, Orme TJ, Richardson HD (1986) The rate of pseudarthrosis (surgical nonunion) in patients who are smokers and patients who are nonsmokers: a comparison study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 11:942–943
Buttermann GR, Garvey TA, Hunt AF, Transfeldt EE, Bradford DS, Boachie-Adjei O et al (1998) Lumbar fusion results related to diagnosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 23:116–127
Carragee EJ, Don AS, Hurwitz EL, Cuellar JM, Carrino JA, Herzog R (2009) 2009 ISSLS prize winner: does discography cause accelerated progression of degeneration changes in the lumbar disc: a ten-year matched cohort study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:2338–2345
Carragee EJ, Hannibal M (2004) Diagnostic evaluation of low back pain. Orthop Clin N Am 35:7–16
Carragee EJ, Tanner CM, Khurana S, Hayward C, Welsh J, Date E et al (2000) The rates of false-positive lumbar discography in select patients without low back symptoms. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 25:1373–1380
Carreon LY, Glassman SD, Kantamneni NR, Mugavin MO, Djurasovic M (2010) Clinical outcomes after posterolateral lumbar fusion in workers’ compensation patients: a case–control study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 25:1812–1817
Carreon LY, Glassman SD, Howard J (2008) Fusion and nonsurgical treatment for symptomatic lumbar degenerative disease: a systematic review of Oswestry Disability Index and MOS Short Form36 outcomes. Spine J 8:747–755
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2006) National Center for Health statistics with chartbook on trends in the health of Americans. Special feature: pain. Department of Health and Human Services, Hyattsville. (http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus06.pdf). Accessed 8 Dec 2013
Chou R, Baisden J, Carragee EJ, Resnick DK, Shaffer WO, Loeser JD (2009) Surgery for low back pain: a review of the evidence for an American Pain Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:1094–1109
ClinicalTrials.gov (US): Activ-L™ Artificial disc treatment of degenerative disc disease in the treatment of degenerative disc disease. U.S. National Institutes of Health, US. (http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00589797). Accessed 05 May 2014
Collier BD, Kir KM, Mills BJ, Patel NC, Pochis WT, Onsel C et al (1990) Bone scan: a useful test for evaluating patients with low back pain. Skelet Radiol 19:267–270
Cook GJ, Hannaford E, See M, Clarke SE, Fogelman I (2002) The value of bone scintigraphy in the evaluation of osteoporotic patients with back pain. Scand J Rheumatol 31:245–248
Djurasovic M, Bratcher KR, Glassman SD, Dimar JR, Carreon LY (2008) The effect of obesity on clinical outcomes after lumbar fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:1789–1792
Djurasovic M, Carreon LY, Crawford CH 3rd, Zook JD, Bratcher KR, Glassman SD (2012) The influence of preoperative MRI findings on lumbar fusion clinical outcomes. Eur Spine J 21:1616–1623
Errico TJ (2004) Why a mechanical disc? Spine J 4:151S–157S
Esposito P, Pinheiro-Franco JL, Froelich S, Matriot D (2006) Predictive value of MRI vertebral end-plate signal changes (Modic) on outcome of surgically treated degenerative disc disease. Results of a cohort study including 60 patients. Neurochirurgie 52:315–322
Eubanks JD, Thorpe SW, Cheruvu VK, Braley BA, Kang JD (2011) Does smoking influence fusion rates in posterior cervical arthrodesis with lateral mass instrumentation? Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:696–701
Fisher C, Kistler J, Davis J (1980) Relation of cerebral vasospasm to subarachnoid hemorrhage visualized by computerized tomographic scanning. Neurosurgery 6:1–9
Frelinghuysen P, Haung RC, Girardi FP, Cammisa FP Jr (2005) Lumbar total disc replacement part 1: rationale, biomechanics, and implant types. Orthop Clin N Am 36:293–299
Fritzell P, Hagg O, Wessberg P, Nordwall A (2001) Swedish Lumbar Spine Study Group: 2001 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies: lumbar fusion versus nonsurgical treatment for chronic low back pain: a multicenter randomized controlled trial from the Swedish Lumbar Spine Study Group. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:2521–2532
Gamie S, El-Maghraby T (2008) The role of PET/CT in evaluation of Facet and Disc abnormalities in patients with low back pain using (18)F-Fluoride. Nucl Med Rev Cent East Eur 11:17–21
Ghogawala Z, Benzel EC, Amin-Hanjani S, Barker FG 2nd, Harrington JF, Magge SN, Strugar J, Coumans JV, Borges LF (2004) Prospective outcomes evaluation after decompression with or without instrumented fusion for lumbar stenosis and degenerative grade I spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine 1:267–272
Glassman SD, Carreon LY, Djurasovic M, Dimar JR, Johnson JR, Puno RM et al (2009) Lumbar fusion outcomes stratified by specific diagnostic indication. Spine J 9:13–21
Glassman S, Gornet MF, Branch C, Polly D Jr, Peloza J, Schwender JD et al (2006) MOS short form 36 and Oswestry Disability Index outcomes in lumbar fusion: a multicenter experience. Spine J 6:21–26
Gum JL, Glassman SD, Carreon LY (2013) Is type of compensation a predictor of outcome after lumbar fusion? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 38:443–448
Hamilton MG, Spetzler RF (1994) The prospective application of a grading system for arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 34:2–6
Hochschuler SH, Ohnmeiss DD, Guyer RD, Blumenthal SL (2002) Artificial disc: preliminary results of a prospective study in the United States. Eur Spine J 11(Suppl 2):S106–S110
Jenkins LT, Jones AL, Harms JJ (1994) Prognostic factors in lumbar spinal fusion. Contemp Orthop 29:173–180
Jensen TS, Karppinen J, Sorensen JS, Niinimak J, Leboeuf-Yde C (2008) Vertebral endplate signal changes (Modic change): a systematic literature review of prevalence and association with non-specific low back pain. Eur Spine J 17:1407–1422
Jensen RK, Leboeuf-Yde C, Wedderkopp N, Sorensen JS, Jensen TS, Manniche C (2012) Is the development of Modic changes associated with clinical symptoms? Eur Spine J 21:2271–2291
Kalanithi PA, Arrigo R, Boakye M (2012) Morbid obesity increases cost and complication rates in spinal arthrodesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 37:982–988
Kalb S, Perez-Orribo L, Kalani MY, Snyder LA, Martirosyan NL, Burns K et al (2012) The influence of common medical conditions on the outcome of anterior interbody fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech
Kertulla L, Luoma K, Vehmas T, Gronblad M, Kaapa E (2012) Modic type I change may predict rapid progressive, deforming disc degeneration: a prospective 1-year follow-up study. Eur Spine J 21:1135–1142
Kjaer P, Korsholm L, Bendix T, Sorensen JS, Leboeuf-Yde C (2006) Modic changes and their associations with clinical findings. Eur Spine J 15:1312–1319
Klineberg E1, Gupta M, McCarthy I, Hostin R (2013) Detection of pseudarthrosis in adult spinal deformity: the use of health-related quality-of-life outcomes to predict pseudarthrosis. J Spinal Disord Tech
Knutsson B, Michaëlsson K, Sandén B (2013) Obesity is associated with inferior results after surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis: a study of 2633 patients from the Swedish spine register. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 38:435–441
Lee CF, Fong DY, Cheung KM, Cheng JC, Ng BK, Lam TP et al (2012) A new risk classification rule for curve progression in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine J 12:989–995
Luoma K, Vehmas T, Gronblad M, Kertulla L, Kaapa E (2009) Relationship of Modic type 1 change with disc degeneration: a prospective MRI study. Skelet Radiol 38:237–244
Makki D, Khazim R, Zaidan AA, Ravi K, Toma T (2010) Single photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT) scan-positive facet joints and other spinal structures in a hospital-wide population with spinal pain. Spine J 10:58–62
Martin BI, Devo RA, Mirza SK, Turner JA, Cornstock BA, Hollingworth W et al (2008) Expenditures and health status among adults with back and neck problems. JAMA 299:656–664
Maus TP, Aprill CN (2012) Lumbar diskogenic pain, provocation discography, and imaging correlates. Radiol Clin N Am 50:681–704
Mirza SK, Deyo RA, Heagerty PJ, Turner JA, Martin BI, Comstock BA (2013) One-year outcomes of surgical versus nonsurgical treatments for discogenic back pain: a community-based prospective cohort study. Spine J 13:1421–1433
Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Boos N (2001) Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:1873–1878
Quattrocchi CC, Alexandre AM, Della Pepa GM, Altavilla R, Zobel BB (2011) Modic changes: anatomy, pathophysiology and clinical correlation. Acta Neurochir Suppl 108:49–53
Rosen DS, Ferguson SD, Ogden AT, Huo D, Fessler RG (2008) Obesity and self-reported outcome after minimally invasive lumbar spinal fusion surgery. Neurosurgery 63:956–960
Schutte HE, Park WM (1983) The diagnostic value of bone scintigraphy in patients with low back pain. Skelet Radiol 10:1–4
Sköld C, Tropp H, Berg S (2013) Five-year follow-up of total disc replacement compared to fusion: a randomized controlled trial. Eur Spine J 22:2288–2295
Smith SE, Darden BV, Rhyne AL, Wood KE (1995) Outcome of unoperated discogram-positive low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 20:1997–2000
Spetzler RF, Martin NA (1986) A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 65:476–483
Vaidya R, Carp J, Bartol S, Ouellette N, Lee S, Sethi A (2009) Lumbar spine fusion in obese and morbidly obese patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:495–500
Wilkins P, Scheel IB, Grundnes O, Hellum C, Storheim K (2013) Prognostic factors of prolonged disability in patients with chronic low back pain and lumbar degeneration in primary care: a cohort study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 38:65–74
Willems PC, Staal JB, Walenkamp GH, de Bie RA (2013) Spinal fusion for chronic low back pain: systematic review on the accuracy of tests for patient selection. Spine J 13:99–109
Yu LP, Qian WW, Yin GY, Ren YX, Hu ZY (2012) MRI assessment of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration without lumbar degenerative disease using the Pfirrmann grading systems. PLoS One e48074
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattei, T.A., Rehman, A.A., Teles, A.R. et al. The ‘Lumbar Fusion Outcome Score’ (LUFOS): a new practical and surgically oriented grading system for preoperative prediction of surgical outcomes after lumbar spinal fusion in patients with degenerative disc disease and refractory chronic axial low back pain. Neurosurg Rev 40, 67–81 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-016-0751-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-016-0751-6