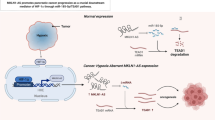
Abstract
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs) are crucially implicated in the cancer progression. The current study intends to excavate and clarify the mechanisms of the key IGF2BPs in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The expression of IGF2BPs and kinesin family member 2A (KIF2A) was examined using immunohistochemistry, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and western blot in NSCLC tissue samples or cell lines. NSCLC cell viability was examined using a cell counting kit-8 assay. Cell apoptotic rate was assessed using flow cytometry analysis. The migration and invasion of H1299 cells were subject to scratch test and Transwell assays, respectively. Starbase 2.0 was used to detect the downstream factors of the IGF2BP1 protein. The binding of IGF2BP with KIF2A was detected using RNA binding protein immunoprecipitation assays. Ki-67 immunohistochemistry assay and TUNEL assays were applied for the evaluation of proliferation and apoptosis in vivo, respectively. IGF2BP1 was upregulated in NSCLC tissue samples and cells. Functionally, IGF2BP1 overexpression promoted the proliferative ability, migration, and invasiveness of H1299 cells, while inhibiting cell apoptosis in vitro. In vivo studies revealed that overexpression of IGF2BP1 promoted tumor growth of NSCLC. Mechanistically, IGF2BP1 was involved in KIF2A mRNA stabilization. KIF2A exerted the same functions as IGF2BP1 via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. In conclusion, IGF2BP1 enhances NSCLC malignant progression by stabilizing KIF2A to modulate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
References
An Y, Duan H (2022) The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer metabolism. Mol Cancer 21:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-022-01500-4
Chen J, Wen J, Liu D, Xu X, Fan M, Zhang Z (2022) The molecular mechanism of kinesin family member 2A (KIF2A) underlying non-small cell lung cancer: the effect of its knockdown on malignant behaviors, stemness, chemosensitivity, and potential regulated signaling pathways. Am J Transl Res 14:68–85
Chen LJ, Liu HY, Xiao ZY, Qiu T, Zhang D, Zhang LJ, Han FY, Chen GJ, Xu XM, Zhu JH, Ding YQ, Wang SY, Ye YP, Jiao HL (2023a) IGF2BP3 promotes the progression of colorectal cancer and mediates cetuximab resistance by stabilizing EGFR mRNA in an m(6)A-dependent manner. Cell Death Dis 14:581. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-023-06099-y
Chen S, Xia H, Sheng L (2023b) WTAP-mediated m6A modification on circCMTM3 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma ferroptosis by recruiting IGF2BP1 to increase PARK7 stability. Dig Liver Dis 55:967–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2022.12.005
Du QY, Zhu ZM, Pei DS (2021) The biological function of IGF2BPs and their role in tumorigenesis. Investig New Drugs 39:1682–1693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-021-01148-9
Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, Akerley W, Bauman JR, Bharat A, Bruno DS, Chang JY, Chirieac LR, D’Amico TA, DeCamp M, Dilling TJ, Dowell J, Gettinger S, Grotz TE, Gubens MA, Hegde A, Lackner RP, Lanuti M et al (2022) Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 20:497–530. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2022.0025
Gouvinhas C, De Mello RA, Oliveira D, Castro-Lopes JM, Castelo-Branco P, Dos Santos RS, Hespanhol V, Pozza DH (2018) Lung cancer: a brief review of epidemiology and screening. Future Oncol 14:567–575. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2017-0486
Guan S, Chen X, Chen Y, Xie W, Liang H, Zhu X, Yang Y, Fang W, Huang Y, Zhao H, Zhuang W, Liu S, Huang M, Wang X, Zhang L (2022) FOXM1 variant contributes to gefitinib resistance via activating Wnt/beta-catenin signal pathway in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 28:3770–3784. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-0791
Guan XQ, Yuan XN, Feng KX, Shao YC, Liu Q, Yang ZL, Chen YY, Deng J, Hu MS, Li J, Tian YH, Chu MF, Zhang JW, Wei L (2023) IGF2BP2-modified UBE2D1 interacts with Smad2/3 to promote the progression of breast cancer. Am J Cancer Res 13:2948–2968
Harethardottir H, Jonsson S, Gunnarsson O, Hilmarsdottir B, Asmundsson J, Gudmundsdottir I, Saevarsdottir VY, Hansdottir S, Hannesson P, Gudbjartsson T (2022) Advances in lung cancer diagnosis and treatment - a review. Laeknabladid 108:17–29. https://doi.org/10.17992/lbl.2022.01.671
Hayat R, Manzoor M, Hussain A (2022) Wnt signaling pathway: a comprehensive review. Cell Biol Int 46:863–877. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11797
He PC, He C (2021) m(6) A RNA methylation: from mechanisms to therapeutic potential. EMBO J 40:e105977. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2020105977
Huang H, Weng H, Sun W, Qin X, Shi H, Wu H, Zhao BS, Mesquita A, Liu C, Yuan CL, Hu YC, Huttelmaier S, Skibbe JR, Su R, Deng X, Dong L, Sun M, Li C, Nachtergaele S et al (2018) Recognition of RNA N(6)-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat Cell Biol 20:285–295. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0045-z
Korn SM, Ulshofer CJ, Schneider T, Schlundt A (2021) Structures and target RNA preferences of the RNA-binding protein family of IGF2BPs: an overview. Structure 29:787–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2021.05.001
Li B, Zhu L, Lu C, Wang C, Wang H, Jin H, Ma X, Cheng Z, Yu C, Wang S, Zuo Q, Zhou Y, Wang J, Yang C, Lv Y, Jiang L, Qin W (2021) circNDUFB2 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression via destabilizing IGF2BPs and activating anti-tumor immunity. Nat Commun 12:295. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20527-z
Li S, Jiang F, Chen F, Deng Y, Huang H (2023) Silencing long noncoding RNA LINC01133 suppresses pancreatic cancer through regulation of microRNA-1299-dependent IGF2BP3. J Biochem Mol Toxicol:e23534. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.23534
Liang J, Guan X, Bao G, Yao Y, Zhong X (2022) Molecular subtyping of small cell lung cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 86:450–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.05.010
Liang X, Xia R (2022) Kinesin family member 2A acts as a potential prognostic marker and treatment target via interaction with PI3K/AKT and RhoA/ROCK pathways in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncol Rep 47. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2021.8229
Liu J, Li Z, Cheang I, Li J, Zhou C (2022a) RNA-binding protein IGF2BP1 associated with prognosis and immunotherapy response in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Genet 13:777399. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.777399
Liu L, Li H, Hu D, Wang Y, Shao W, Zhong J, Yang S, Liu J, Zhang J (2022b) Insights into N6-methyladenosine and programmed cell death in cancer. Mol Cancer 21:32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-022-01508-w
Liu TY, Hu CC, Han CY, Mao SY, Zhang WX, Xu YM, Sun YJ, Jiang DB, Zhang XY, Zhang JX, Wang J, Qiao XP, Pan JY, Yang SY, Yang K (2023) IGF2BP2 promotes colorectal cancer progression by upregulating the expression of TFRC and enhancing iron metabolism. Biol Direct 18:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13062-023-00373-x
Oliver AL (2022) Lung cancer: epidemiology and screening. Surg Clin North Am 102:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2021.12.001
Qu L, Tian Y, Wang F, Li Z (2022) NOVA1 promotes NSCLC proliferation and invasion by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. BMC Cancer 22:1091. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-022-10164-8
Rim EY, Clevers H, Nusse R (2022) The Wnt pathway: from signaling mechanisms to synthetic modulators. Annu Rev Biochem 91:571–598. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-040320-103615
Sharma G, Tran TM, Bansal I, Beg MS, Bhardwaj R, Bassi J, Tan Y, Jaiswal AK, Tso C, Jain A, Singh J, Chattopadhyay P, Singh A, Chopra A, Bakhshi S, Casero D, Rao DS, Palanichamy JK (2023) RNA binding protein IGF2BP1 synergizes with ETV6-RUNX1 to drive oncogenic signaling in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 42:231. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-023-02810-1
Tsuchiya K, Yoshimura K, Iwashita Y, Inoue Y, Ohta T, Watanabe H, Yamada H, Kawase A, Tanahashi M, Ogawa H, Funai K, Shinmura K, Suda T, Sugimura H (2022) m(6)A demethylase ALKBH5 promotes tumor cell proliferation by destabilizing IGF2BPs target genes and worsens the prognosis of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 29:1355–1372. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-022-00451-8
Wang F, Li J, Li L, Chen Z, Wang N, Zhu M, Mi H, Xiong Y, Guo G, Gu Y (2022a) Circular RNA circ_IRAK3 contributes to tumor growth through upregulating KIF2A via adsorbing miR-603 in breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int 22:81. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-022-02497-y
Wang JJ, Chen DX, Zhang Y, Xu X, Cai Y, Wei WQ, Hao JJ, Wang MR (2023) Elevated expression of the RNA-binding protein IGF2BP1 enhances the mRNA stability of INHBA to promote the invasion and migration of esophageal squamous cancer cells. Exp Hematol Oncol 12:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40164-023-00429-8
Wang Y, Wang J, Zhao A, Huang X, Zhang X (2022b) HPV16 E6E7 up-regulates KIF2A expression by activating JNK/c-Jun signal, is beneficial to migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells. Open Med (Wars) 17:1780–1787. https://doi.org/10.1515/med-2022-0578
Wu S, Chi C, Weng S, Zhou W, Liu Z (2023) IGF2BP2 promotes lncRNA DANCR stability mediated glycolysis and affects the progression of FLT3-ITD + acute myeloid leukemia. Apoptosis 28:1035–1047. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-023-01846-0
Xi Y, Wang Y (2022) IGF2BP1, a new target to overcome drug resistance in melanoma? Front Pharmacol 13:947363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.947363
Yang F, Ma Q, Huang B, Wang X, Pan X, Yu T, Ran L, Jiang S, Li H, Chen Y, Liu Y, Liang C, Ren J, Zhang Y, Wang S, Li W, Xiao B (2023) CircNFATC3 promotes the proliferation of gastric cancer through binding to IGF2BP3 and restricting its ubiquitination to enhance CCND1 mRNA stability. J Transl Med 21:402. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-023-04235-y
Zhao H, Wang Y, Liang C, Xie M (2023a) LncRNA FOXD3-AS1/miR-128-3p axis-mediated IGF2BP3 in glioma stimulates cancer angiogenesis and progression. Folia Neuropathol 61:168–184. https://doi.org/10.5114/fn.2023.126862
Zhao X, Chen J, Zhang C, Xie G, Othmane B, Kuang X, Liu B (2023b) LncRNA AGAP2-AS1 interacts with IGF2BP2 to promote bladder cancer progression via regulating LRG1 mRNA stability. Cell Signal 111:110839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110839
Zhao Y, Shi Y, Shen H, Xie W (2020) m(6)A-binding proteins: the emerging crucial performers in epigenetics. J Hematol Oncol 13:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00872-8
Zheng P, Jiang J, Li L, Wei L, Li J, Jin L (2022) Circ_SATB2 knockdown inhibits the tumorigenesis of non-small cell lung cancer via miR-760/KIF2A axis. Histol Histopathol:18530. https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-18-530
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RZ contributed to the study conception and design. MS, LW, and DX performed the assays. LG contributed to statistical analysis. LW contributed to data presentation. MS and RZ wrote the initial manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study involving human participants was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University. All patients signed written informed consent and all experimental protocols were implemented in accordance with relevant regulations. The animal experiments were approved by the animal Ethics Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, M., Wang, L., Ge, L. et al. IGF2BP1 facilitates non-small cell lung cancer progression by regulating the KIF2A-mediated Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Funct Integr Genomics 24, 4 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01275-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01275-x