Abstract
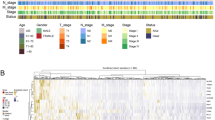
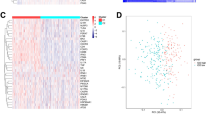
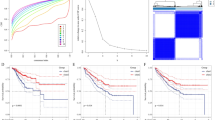
Immunogenic cell death (ICD), a type of cell death that activates the tumor-specific immune response and thus exerts anti-tumor effects, is an emerging target in tumor therapy, but research on ICD-related genes (ICDGs) in colorectal cancer (CRC) remains limited. This study aimed to identify the CRC-specific ICDGs and explore their potential roles. Through RNA sequencing for tissue samples from CRC patients and integration with The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data, we identified 33 differentially expressed ICDGs in CRC. We defined the ICD score based on these genes in single-cell data, where a high score indicated an immune-active microenvironment. Additionally, molecular subtypes identified in bulk RNA data showed distinct immune landscapes. The ICD-related signature constructed with machine learning effectively distinguished patients’ prognosis. The summary data–based Mendelian randomization (SMR) and colocalization analysis prioritized CFLAR for its positive association with CRC risk. Molecular docking revealed its stable binding with chemotherapeutic drugs like irinotecan. Furthermore, experimental validation confirmed CFLAR overexpression in CRC samples, and its knockdown inhibited tumor cell proliferation. Overall, this study expands the understanding of the potential roles and mechanisms of ICDGs in CRC and highlights CFLAR as a promising target for CRC.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Raw RNA-sequencing data of the tissues from CRC patients in this study have been deposited in the Genome Sequence Archive in National Genomics Data Center, China National Center for Bioinformation/Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (GSA: HRA005244) that are accessible at https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gsa. The SMR software is available at https://yanglab.westlake.edu.cn/software/smr. The summary-level data of the GWAS are available at https://www.finngen.fi/en, and the eQTL dataset is available at https://www.eqtlgen.org/ and https://gtexportal.org/. The public CRC transcriptome datasets were obtained from the UCSC Xena platform (http://xena.ucsc.edu) and the GEO database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/). Other data used and/or analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmed A, Tait SWG (2020) Targeting immunogenic cell death in cancer. Mol Oncol 14:2994–3006. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12851
Anderson KG, Stromnes IM, Greenberg PD (2017) Obstacles posed by the tumor microenvironment to T cell activity: a case for synergistic therapies. Cancer Cell 31:311–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2017.02.008
Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Tesniere A, Obeid M et al (2007) Toll-like receptor 4-dependent contribution of the immune system to anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Nat Med 13:1050–1059. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1622
Becht E, Giraldo NA, Lacroix L, Buttard B et al (2016) Estimating the population abundance of tissue-infiltrating immune and stromal cell populations using gene expression. Genome Biol 17:218. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-1070-5
Binnewies M, Roberts EW, Kersten K, Chan V et al (2018) Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat Med 24:541–550. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0014-x
Casares N, Pequignot MO, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F et al (2005) Caspase-dependent immunogenicity of doxorubicin-induced tumor cell death. J Exp Med 202:1691–1701. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20050915
Chen B, Khodadoust MS, Liu CL, Newman AM et al (2018) Profiling tumor infiltrating immune cells with CIBERSORT. Methods Mol Biol 1711:243–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7493-1_12
Chen L, Liu P, Evans TC Jr, Ettwiller LM (2017) DNA damage is a pervasive cause of sequencing errors, directly confounding variant identification. Science 355:752–756. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aai8690
Consortium GT (2020) The GTEx Consortium atlas of genetic regulatory effects across human tissues. Science 369:1318–1330. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaz1776
Dagogo-Jack I, Shaw AT (2018) Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 15:81–94. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.166
Eberhardt J, Santos-Martins D, Tillack AF, Forli S (2021) AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: new docking methods, expanded force field, and python bindings. J Chem Inf Model 61:3891–3898. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00203
Faiz A, Heijink IH, Vermeulen CJ, Guryev V et al (2018) Cigarette smoke exposure decreases CFLAR expression in the bronchial epithelium, augmenting susceptibility for lung epithelial cell death and DAMP release. Sci Rep 8:12426. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30602-7
Farh KK, Marson A, Zhu J, Kleinewietfeld M et al (2015) Genetic and epigenetic fine mapping of causal autoimmune disease variants. Nature 518:337–343. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13835
Fearon ER, Vogelstein B (1990) A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 61:759–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S, Kuhn M et al (2013) STRING v9.1: protein-protein interaction networks, with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D808–D815. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1094
Fucikova J, Kepp O, Kasikova L, Petroni G et al (2020) Detection of immunogenic cell death and its relevance for cancer therapy. Cell Death Dis 11:1013. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03221-2
Fuertes MB, Kacha AK, Kline J, Woo SR et al (2011) Host type I IFN signals are required for antitumor CD8+ T cell responses through CD8{alpha}+ dendritic cells. J Exp Med 208:2005–2016. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20101159
Gallagher MD, Chen-Plotkin AS (2018) The post-GWAS era: from association to function. Am J Hum Genet 102:717–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.04.002
Galluzzi L, Buque A, Kepp O, Zitvogel L et al (2015) Immunological effects of conventional chemotherapy and targeted anticancer agents. Cancer Cell 28:690–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2015.10.012
Galluzzi L, Buque A, Kepp O, Zitvogel L et al (2017) Immunogenic cell death in cancer and infectious disease. Nat Rev Immunol 17:97–111. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.107
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams JM et al (2018) Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ 25:486–541. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Warren S, Adjemian S et al (2020) Consensus guidelines for the definition, detection and interpretation of immunogenic cell death. J Immunother Cancer 8. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2019-000337
Giambartolomei C, Vukcevic D, Schadt EE, Franke L et al (2014) Bayesian test for colocalisation between pairs of genetic association studies using summary statistics. PLoS Genet 10:e1004383. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004383
Goldman MJ, Craft B, Hastie M, Repecka K et al (2020) Visualizing and interpreting cancer genomics data via the Xena platform. Nat Biotechnol 38:675–678. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-020-0546-8
Goodsell DS, Jenkinson J (2018) Molecular illustration in research and education: past, present, and future. J Mol Biol 430:3969–3981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2018.04.043
Green DR, Ferguson T, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G (2009) Immunogenic and tolerogenic cell death. Nat Rev Immunol 9:353–363. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2545
Hanahan D, Coussens LM (2012) Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 21:309–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.022
Hopfner KP, Hornung V (2020) Molecular mechanisms and cellular functions of cGAS-STING signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21:501–521. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-0244-x
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P et al (1997) Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP. Nature 388:190–195. https://doi.org/10.1038/40657
Ishwaran H, Kogalur UB, Blackstone EH, Lauer MS (2008) Random survival forests. Ann Appl Stat 2:841–860. https://doi.org/10.1214/08-AOAS169
Jiang P, Gu S, Pan D, Fu J et al (2018) Signatures of T cell dysfunction and exclusion predict cancer immunotherapy response. Nat Med 24:1550–1558. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0136-1
Kabakchiev B, Silverberg MS (2013) Expression quantitative trait loci analysis identifies associations between genotype and gene expression in human intestine. Gastroenterology 144:1488–1496. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2013.03.001
Kataoka T, Budd RC, Holler N, Thome M et al (2000) The caspase-8 inhibitor FLIP promotes activation of NF-kappaB and Erk signaling pathways. Curr Biol 10:640–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00512-1
Kepp O, Bezu L, Yamazaki T, Di Virgilio F et al (2021) ATP and cancer immunosurveillance. EMBO J 40:e108130. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2021108130
Kepp O, Sauvat A, Leduc M, Forveille S et al (2019) A fluorescent biosensor-based platform for the discovery of immunogenic cancer cell death inducers. Oncoimmunology 8:1606665. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2019.1606665
Kim S, Chen J, Cheng T, Gindulyte A et al (2023) PubChem 2023 update. Nucleic Acids Res 51:D1373–D1380. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac956
Korkolopoulou P, Saetta AA, Levidou G, Gigelou F et al (2007) c-FLIP expression in colorectal carcinomas: association with Fas/FasL expression and prognostic implications. Histopathology 51:150–156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02723.x
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Zitvogel L (2013) Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Immunol 31:51–72. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-100008
Kurki MI, Karjalainen J, Palta P, Sipila TP et al (2023) FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature 613:508–518. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05473-8
Lee HO, Hong Y, Etlioglu HE, Cho YB et al (2020) Lineage-dependent gene expression programs influence the immune landscape of colorectal cancer. Nat Genet 52:594–603. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-020-0636-z
Li B, Ritchie MD (2021) From GWAS to gene: transcriptome-wide association studies and other methods to functionally understand GWAS discoveries. Front Genet 12:713230. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.713230
Liberzon A, Subramanian A, Pinchback R, Thorvaldsdottir H et al (2011) Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 27:1739–1740. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr260
Meacham F, Boffelli D, Dhahbi J, Martin DI et al (2011) Identification and correction of systematic error in high-throughput sequence data. BMC Bioinformatics 12:451. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-451
Micheau O, Thome M, Schneider P, Holler N et al (2002) The long form of FLIP is an activator of caspase-8 at the Fas death-inducing signaling complex. J Biol Chem 277:45162–45171. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M206882200
Morris GM, Huey R, Olson AJ (2008) Using AutoDock for ligand-receptor docking. Curr Protoc Bioinform 8:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471250953.bi0814s24
Qiu X, Mao Q, Tang Y, Wang L et al (2017) Reversed graph embedding resolves complex single-cell trajectories. Nat Methods 14:979–982. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4402
Quail DF, Joyce JA (2013) Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med 19:1423–1437. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3394
Ryu BK, Lee MG, Chi SG, Kim YW et al (2001) Increased expression of cFLIP(L) in colonic adenocarcinoma. J Pathol 194:15–19. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.835
Schoning-Stierand K, Diedrich K, Ehrt C, Flachsenberg F et al (2022) ProteinsPlus: a comprehensive collection of web-based molecular modeling tools. Nucleic Acids Res 50:W611–W615. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac305
Shirley S, Micheau O (2013) Targeting c-FLIP in cancer. Cancer Lett 332:141–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2010.10.009
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A (2023) Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 73:17–48. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21763
Smith JJ, Deane NG, Wu F, Merchant NB et al (2010) Experimentally derived metastasis gene expression profile predicts recurrence and death in patients with colon cancer. Gastroenterology 138:958–968. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2009.11.005
Tesniere A, Schlemmer F, Boige V, Kepp O et al (2010) Immunogenic death of colon cancer cells treated with oxaliplatin. Oncogene 29:482–491. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.356
Tirosh I, Izar B, Prakadan SM, Wadsworth MH 2nd et al (2016) Dissecting the multicellular ecosystem of metastatic melanoma by single-cell RNA-seq. Science 352:189–196. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad0501
Vacchelli E, Ma Y, Baracco EE, Sistigu A et al (2015) Chemotherapy-induced antitumor immunity requires formyl peptide receptor 1. Science 350:972–978. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad0779
Vosa U, Claringbould A, Westra HJ, Bonder MJ et al (2021) Large-scale cis- and trans-eQTL analyses identify thousands of genetic loci and polygenic scores that regulate blood gene expression. Nat Genet 53:1300–1310. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-021-00913-z
Wu Y, Zeng J, Zhang F, Zhu Z et al (2018) Integrative analysis of omics summary data reveals putative mechanisms underlying complex traits. Nat Commun 9:918. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03371-0
Yang XT, Yan J, Xue Y, Sun Q et al (2023) Single-cell profiling reveals distinct immune response landscapes in tuberculous pleural effusion and non-TPE. Front Immunol 14:1191357. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1191357
Yuan Y, Bao J, Chen Z, Villanueva AD et al (2021) Multi-omics analysis to identify susceptibility genes for colorectal cancer. Hum Mol Genet 30:321–330. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddab021
Zhu C, Fang Z, Peng L, Gao F et al (2022) Curcumin suppresses the progression of colorectal cancer by improving immunogenic cell death caused by irinotecan. Chemotherapy 67:211–222. https://doi.org/10.1159/000518121
Zhu Q, Liu JY, Xu HW, Yang CM et al (2005) Mechanism of counterattack of colorectal cancer cell by Fas/Fas ligand system. World J Gastroenterol 11:6125–6129. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i39.6125
Zhu Z, Zhang F, Hu H, Bakshi A et al (2016) Integration of summary data from GWAS and eQTL studies predicts complex trait gene targets. Nat Genet 48:481–487. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3538
Acknowledgements
We are incredibly grateful to the TCGA, GEO, FinnGen, eQTLGen, GTEx and all public databases for their data support.
Funding
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82172956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yu Shao and Zhenling Wang contributed equally to this study. Conception and design were carried out by Zan Fu, Yu Shao, Zhenling Wang, and Jingyu Wu. Yu Shao, Yang Chen, and Yunfei Lu performed the analysis. Hongqiang Zhang, Changzhi Huang, Hengyang Shen, and Lei Xu collected and processed the data and samples. Yu Shao and Zhenling Wang wrote the main manuscript text and Jingyu Wu prepared figures. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University (No.2023-SR-206). All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and the Declaration of Helsinki. The age of all participants is greater than 16 years old, and written informed consent to participate in this study was provided by the participants.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Y., Wang, Z., Wu, J. et al. Unveiling immunogenic cell death–related genes in colorectal cancer: an integrated study incorporating transcriptome and Mendelian randomization analyses. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 316 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01238-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01238-2