Abstract
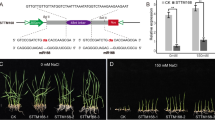
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are important molecules that regulate gene expression under salinity stress. Despite their evolutionary conservation, these regulatory elements have been shown to behave differently in different plant species under a particular environmental stress. In this study, we investigated the behavior of salt responsive osa-miR393a and its target gene (TIR1, LOC_Os05g05800) in salt-tolerant (FL478) and salt-sensitive (IR29) rice genotypes. It was found that the mature and precursor sequences of osa-miR393a as well as its cleavage site in TIR1 were conserved among salt tolerant and sensitive genotypes. Promoters of different salt-responsive miRNAs were also found to be less variable between salt-tolerant and salt-susceptible genotypes. Analysis of gene expression, promoter methylation, and cis-element abundance showed that osa-miR393a behaves differently in FL478 and IR29. Salt stress altered the expression pattern of osa-miR393a-TIR1 module in a time-dependent manner in the roots and shoots of two genotypes. Promoter methylation of this regulatory module was also altered at different time points under salt stress. Expression analysis in two genotypes indicated the overall down-regulation of osa-miR393a and up-regulation of TIR1 in FL478 and their reciprocal regulation in IR29. The expression results were complemented by the differential promoter methylation and cis-element abundance of this regulatory module. Together, the results of transcript abundance and promoter methylation of osa-miR393a-TIR1 module signified the association between these two processes which is reported for the first time in plants to the best of our knowledge.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bottino MC, Rosario S, Grativol C, Thiebaut F (2013) High-throughput sequencing of small RNA transcriptome reveals salt stress regulated microRNAs in sugarcane. PLoS ONE 8:59423–59435
Boyko A, Kovalchuk I (2011) Genome instability and epigenetic modification-heritable responses to environmental stress? Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:260–266
Chen H, Li Z, Xiong L (2012) A plant microRNA regulates the adaptation of roots to drought stress. FEBS Lett 586:1742–1747
Choi CS, Sano H (2007) Abiotic-stress induces demethylation and transcriptional activation of a gene encoding a glycerophosphodiesterase-like protein in tobacco plants. Mol Genet Genomics 277:589–600
Devi SJSR, Madhav MS, Kumar GR, Goel AK, Umakanth B, Jahnavi B, Viraktamath BC (2013) Identification of abiotic stress miRNA transcription factor binding motifs (TFBMs) in rice. Gene 531:15–22
Ding D, Zhang L, Wang H, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Zheng Y (2009) Differential expression of miRNAs in response to salt stress in maize roots. Ann Bot 103:29–38
Dupont JM, Tost J, Jammes H, Gut IG (2004) De novo quantitative bisulfite sequencing using the pyrosequencing technology. Anal Biochem 333:119–127
Egger G, Liang G, Aparicio A, Jones PA (2004) Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy. Nature 429:457–463
Ferreira JL, Azevedo V, Maroco J, Oliveira MM, Santos AP (2015) Salt tolerant and sensitive rice varieties display differential methylome flexibility under salt stress. PLoS ONE 10:e0124060
Gao P, Bai X, Yang L, Lv D, Pan X et al (2011) OsmiR393: a salinity-and alkaline stress-related microRNA gene. Mol Biol Rep 38:237–242
Garcia AAF, Benchimol LL, Barbosa AMM, Geraldi IO, Souza CL Jr, de Souza AP (2004) Comparison of RAPD, RFLP, AFLP and SSR marker for diversity studies in tropical maize inbred lines. Genet Mol Biol 27:579–588
Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Korenaga T (1999) Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database. Nucleic Acids Res 27:297–300
Islam MR, Gregorio GB, Salam MA, Collard BCY, Singh RK, Hassan L (2012) Validation of SalTol linked markers and haplotype diversity on chromosome 1 of rice. Mol Plant Breed 3:103–114
Jaiswal P, Ni J, Yap I (2006) Gramene: a bird’s eye view of cereal genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D717–D723
Karan R, DeLeon T, Biradar H, Subudhi PK (2012) Salt stress induced variation in DNA methylation pattern and its influence on gene expression in contrasting rice genotypes. PLoS ONE 7:e40203
Kou HP, Li Y, Song XX, Ou XF, Xing SC et al (2011) Heritable alteration in DNA methylation induced by nitrogen-deficiency stress accompanies enhanced tolerance by progenies to the stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Plant Physiol 168:1685–1693
Kumar RR, Pathak H, Sharma SK, Kala YK, Nirjal MK, Singh GP, Rai RD (2015) Novel and conserved heat-responsive microRNAs in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Funct Integr Genomics 15:323–348
Li Y, Zhu J, Tian G, Li N, Li Q, Ye M, Zheng H, Yu J, Wu H, Sun J et al (2010) The DNA methylome of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. PLoS Biol 8:e1000533
Lister R, Pelizzola M, Kida YS, Hawkins RD, Nery JR, Hon G et al (2011) Hotspots of aberrant epigenomic reprogramming in human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 471:68–73
Liu HH, Tian X, Li YJ, Wu CA, Zheng CC (2008) Microarray-based analysis of stress-regulated microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. RNA 14:836–843
Lu XY, Huang XL (2008) Plant miRNAs and abiotic stress responses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 368:458–462
Lu S, Sun YH, Chiang VL (2008) Stress-responsive microRNAs in Populus. Plant J 55:131–151
Megraw M, Baev V, Rusinov V, Jensen ST, Kalantidis K, Hatzigeorgiou AG (2006) MicroRNA promoter element discovery in Arabidopsis. RNA 12:1612–1619
Mirouze M, Paszkowski J (2011) Epigenetic contribution to stress adaptation in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:267–274
Molla KA, Debnath AB, Ganie SA, Mondal TK (2015) Identification and analysis of novel salt responsive candidate gene based SSRs (cgSSRs) from rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 15:122
Mondal TK, Ganie SA (2014) Identification and characterization of salt responsive miRNA-SSR markers in rice (Oryza sativa). Gene 535:204–209
Murrell A, Rakyan VK, Beck S (2005) From genome to epigenome. Hum Mol Genet 14:R3–R10
Mutum RD, Balyan SC, Kansal S, Agarwal P, Kumar S, Kumar M, Raghuvanshi S (2013) Evolution of variety-specific regulatory schema for expression of osa-miR408 in indica rice varieties under drought stress. doi:10.1111/febs.12186
Nageshbabu R, Jyothi MN, Sharadamma N, Sahu S, Rai DV, Devaraj VR (2013) Expression of miRNAs regulates growth and development of French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) under salt and drought stress conditions. Int Res J Biol Sci 2:52–56
Navarro L, Dunoyer P, Jay F, Arnold B, Dharmasiri N, Estelle M, Voinnet O, Jones JDG (2006) A Plant miRNA Contributes to Antibacterial Resistance by Repressing Auxin Signaling. Science 312:436
Pan Y, Wang W, Zhao, Zhu L, Fu B, Li Z (2011) DNA methylation alterations of rice in response to cold stress. POJ 4:364–369
Park HC, Kim ML, Kang YH et al (2004) Pathogen- and NaCl-induced expression of the SCaM-4 promoter is mediated in part by a GT-1 box that interacts with a GT-1-like transcription factor. Plant Physiol 135:2150–2161
Ren Y, Chen L, Zhang Y, Kang X, Zhang Z, Wang Y (2013) Identification and characterization of salt-responsive microRNAs in Populus tomentosa by high-throughput sequencing. Biochimie 95:743–750
Su Z, Xia J, Zhao Z (2011) Functional complementation between transcriptional methylation regulation and post-transcriptional microRNA regulation in the human genome. BMC Genomics 12(Suppl 5):S15
Sun J, Gong X, Purow B, Zhao Z (2012) Uncovering microRNA and transcription factor mediated regulatory networks in Glioblastoma. PLoS Comput Biol 8:e1002488
Sunkar R, Zhou X, Zheng Y, Zhang W, Zhu JK (2008) Identification of novel and candidate miRNAs in rice by high throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol 8:25
Taguchi Y (2013) Correlation between miRNA-targeted-gene promoter methylation and miRNA regulation of target genes. F1000Research 2: 21. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.2-21.v2
Tóth G, Gáspári Z, Jurka J (2000) Microsatellites in different eukaryotic genomes: survey and analysis. Genome Res 10:967–998
Tran LSP, Nakashima K, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi- Shinozaki K (2007) Plant gene networks in osmotic stress response: from genes to regulatory networks. Meth Enzymol 428:109–128
Wang WS, Pan JY, Zhao XQ, Dwivedi D, Zhu LH, Ali J, Fu BY, Li ZK (2011) Drought-induced site-specific DNA methylation and its association with drought tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Exp Bot 62:951–1960
Wang Z, Huang J, Sun Z, Zheng B (2015) Identification of microRNAs differentially expressed involved in male flower development. Funct Integr Genomics 15:225–232
Wankhade SD, Bahaji A, Mateu-Andres I, Cornejo MJ (2010) Phenotypic indicators of NaCl tolerance levels in rice seedlings: variations in development and leaf anatomy. Acta Physiol Plant 32:1161–1169
Xia K, Wang R, Ou X, Fang Z, Tian C et al (2012) OsTIR1 and OsAFB2 downregulation via OsmiR393 overexpression leads to more tillers, early flowering and less tolerance to salt and drought in rice. PLoS ONE 7:e30039. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030039
Xue GP (2002) Characterisation of the DNA-binding profile of barley HvCBF1 using an enzymatic method for rapid, quantitative and high-throughput analysis of the DNA-binding activity. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e77
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:781–803
Yin F, Gao J, Liu M, Qin C, Zhang W, Yang A, Pan G (2014) Genome-wide analysis of Water-stress-responsive microRNA expression profile in tobacco roots. Funct Integr Genomics 14:319–332
Zhang BH, Pan XP, Wang QL, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2005) Identification and characterization of new plant microRNA using EST analysis. Cell Res 15:336–360
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2006) Plant microRNA: a small regulatory molecule with big impact. Dev Biol 289:3–16
Zhang Z, Yu J, Li D et al (2010) PMRD: plant microRNA database. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D806–D813
Zhao X, Li L (2013) Comparative analysis of microRNA promoters in Arabidopsis and Rice. Genom Proteom Bioinform 11:56–60
Zhou X, Ruan J, Wang G, Zhang W (2007) Characterization and identification of microRNA core promoters in four model species. PLoS Comput Biol 3:e37
Zhu J, Li W, Yang W, Qi L, Han S (2013) Identification of microRNAs in Caragana intermedia by high throughput sequencing and expression analysis of 12 microRNAs and their targets under salt stress. Plant Cell Rep 32:1339–1349
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. K.V. Bhat, Head, Division of Genomic Resources, NBPGR, New Delhi for his support and advice to carry out this work. Mr. Showkat Ahmad Ganie is grateful to the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India for the award of Senior Research Fellow.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the reported research.
Funding
The authors are also grateful to Director, ICAR-NBPGR for funding the project through in-house grant (Project Code: IXX10476).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganie, S.A., Dey, N. & Mondal, T.K. Promoter methylation regulates the abundance of osa-miR393a in contrasting rice genotypes under salinity stress. Funct Integr Genomics 16, 1–11 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-015-0460-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-015-0460-1