Abstract
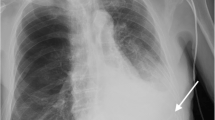
To evaluate embolotherapy for the emergency management of acute bleeding from intercostal arteries. Between October 2003 and August 2012, 19 consecutive patients with hemorrhage from intercostal arteries were scheduled for emergency embolization. The primary study endpoints were technical and clinical success, which were defined as angiographic cessation of bleeding, and cessation of clinical signs of hemorrhage. The secondary study endpoints were periprocedural complications and 30-day mortality rate. In most patients (74 %), hemorrhage was caused by iatrogenic procedures with subsequent intercostal artery laceration. One of the patients was treated twice for recurrent hemothorax caused by a new intercostal artery pseudoaneurysm 7.5 years after the initial procedure. Thus, 20 procedures were performed in these 19 patients. Overall technical success was 85 %. In six patients, no embolization of the “backdoor” was feasible, and in two of these patients additional embolization of other intercostal arteries was necessary to prevent hemorrhage via collateral vessels. Clinical signs of hemorrhage ceased after embolotherapy in 16 of 20 procedures (clinical success 80 %). The mean follow-up was 358.7 ± 637.1 days. One minor procedure-related complication occurred. The 30-day mortality rate was 21 %, however, this was unrelated to intercostal artery hemorrhage. Embolotherapy is an effective emergency therapy for patients with acute hemorrhage from intercostal arteries. Especially if embolization of the backdoor is not feasible, collateral supply via other intercostal arteries should be either ruled out or embolized to prevent ongoing hemorrhage. Despite successful embolotherapy, a majority of patients underwent surgery during follow-up to remove the symptomatic hematoma.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sommer CM, Stampfl U, Bellemann N, Ramsauer S, Loenard BM, Haferkamp A, Hallscheidt P, Richter GM, Kauczor HU, Radeleff BA (2010) Patients with life-threatening arterial renal hemorrhage: CT angiography and catheter angiography with subsequent superselective embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 33:498–508. doi:10.1007/s00270-009-9787-0
Sunga KL, Bellolio MF, Gilmore RM, Cabrera D (2012) Spontaneous retroperitoneal hematoma: etiology, characteristics, management, and outcome. J Emerg Med 43:157–161. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2011.06.006
Kos S, Gutzeit A, Hoppe H, Liu DM, Jacob AL (2013) Diagnosis and therapy of acute hemorrhage in patients with pelvic fractures. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 17:396–406. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1356469
Sofocleous CT, Hinrichs CR, Hubbi B, Doddakashi S, Bahramipour P, Schubert J (2005) Embolization of isolated lumbar artery injuries in trauma patients. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 28:730–735
Hagiwara A, Iwamoto S (2009) Usefulness of transcatheter arterial embolization for intercostal arterial bleeding in a patient with burst fractures of the thoracic vertebrae. Emerg Radiol 16:489–491. doi:10.1007/s10140-008-0780-8
Chemelli AP, Thauerer M, Wiedermann F, Strasak A, Klocker J, Chemelli-Steingruber IE (2009) Transcatheter arterial embolization for the management of iatrogenic and blunt traumatic intercostal artery injuries. J Vasc Surg 49:1505–1513. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2009.02.001
Saad WE, Davies MG, Darcy MD (2008) Management of bleeding after percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography or transhepatic biliary drain placement. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol 11:60–71. doi:10.1053/j.tvir.2008.05.007
Yoneyama H, Arahata M, Temaru R, Ishizaka S, Minami S (2010) Evaluation of the risk of intercostal artery laceration during thoracentesis in elderly patients by using 3D-CT angiography. Intern Med 49:289–292
Leoni CJ, Potter JE, Rosen MP, Brophy DP, Lang EV (2001) Classifying complications of interventional procedures: a survey of practicing radiologists. J Vasc Interv Radiol 12:55–59
Yacovone ML, Kartan R, Bautista M (2010) Intercostal artery laceration following thoracentesis. Respir Care 55:1495–1498
Hongsakul K, Rookkapan S, Tanutit P, Pakdeejit S, Songjamrat A, Sungsiri J (2013) Spontaneous massive hemothorax in a patient with neurofibromatosis type 1 with successful transarterial embolization. Korean J Radiol 14:86–90. doi:10.3348/kjr.2013
Shah RD, Nagar S, Shanley CJ, Janczyk RJ (2008) Factors affecting the severity of spontaneous retroperitoneal hemorrhage in anticoagulated patients. Am J Surg 195:410–413. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.12.003
Chan YC, Morales JP, Reidy JF, Taylor PR (2008) Management of spontaneous and iatrogenic retroperitoneal haemorrhage: conservative management, endovascular intervention or open surgery? Int J Clin Pract 62:1604–1613
Ivascu FA, Janczyk RJ, Bair HA, Bendick PJ, Howells GA (2005) Spontaneous retroperitoneal hemorrhage. Am J Surg 189:345–347
Miura H, Taira O, Uchida O, Usuda J, Hirai S, Kato H (1997) Spontaneous haemothorax associated with von Recklinghausen's disease: review of occurrence in Japan. Thorax 52:575–578
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stampfl, U., Sommer, CM., Bellemann, N. et al. Emergency embolization for the treatment of acute hemorrhage from intercostal arteries. Emerg Radiol 21, 565–570 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-014-1231-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-014-1231-3