Abstract
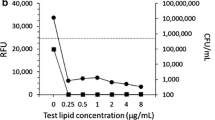
One mechanism of ciprofloxacin resistance is attributed to chromosomal DNA-encoded efflux pumps such as the MepA and NorB proteins. The goal of this research is to find a way to bypass Staphylococcus aureus’ efflux pumps. Because of its high membrane permeability and low association with NorB and MepA efflux proteins, a liposome-encapsulating antibiotic is one of the promising, cost-effective drug carriers and coating mechanisms for overcoming active transport of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) multidrug-resistant efflux protein . The calculated “Log Perm RRCK” membrane permeability values of 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphocholine (DSPC) ciprofloxacin liposome-encapsulated (CFL) showed a lower negative value of − 4,652 cm/s and greater membrane permeability than ciprofloxacin free (CPF). The results of RT-qPCR showed that cationic liposomes containing ciprofloxacin in liposome-encapsulated form (CFL) improved CPF antibacterial activity and affinity for negatively charged bacterial cell surface membrane in comparison to free drug and liposome, as it overcame several resistance mechanisms and reduced the expression of efflux pumps. Ciprofloxacin liposome-encapsulated (CFL) is therefore more effective than ciprofloxacin alone. Liposomes can be combined with a variety of drugs that interact with bacterial cell efflux pumps to maintain high sustained levels of antibiotics in bacterial cells.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data obtained from NCBI Protein and NCBI GenBank databases included in this research study presented accession code/numbers for research or reanalysis.
Change history
27 June 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-022-00260-x
Abbreviations
- CPF:
-
Ciprofloxacin
- DSC:
-
Differential scanning calorimetry
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared
- MRSA:
-
Methicillin-resistant S. aureus
- DSPC:
-
1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
- SA:
-
Stearyl amine
- EE:
-
Entrapment efficiency
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- TSB:
-
Trypticase soy broth
- CFL:
-
Ciprofloxacin doped in liposomes
- Ala:
-
Alanine
- Phe:
-
Phenylalanine
- CT:
-
Cycle threshold
References
Abbey TC, Deak E (2019) What’s New from the CLSI Subcommittee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing M100. Clin Microbiol Newsl 41:203–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinmicnews.2019.11.002
Akbarzadeh A, Rezaei-Sadabady R, Davaran S et al (2013) Liposome: classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res Lett. 8: 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-8-102
Alavi M, Karimi N, Safaei M (2017) Application of various types of liposomes in drug delivery systems. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 7 :3. https://doi.org/10.15171/apb.2017.002
Alonso MJ (2004) Nanomedicines for overcoming biological barriers. Biomed. Pharmacother.58(3): 168–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2004.01.007
Andersson DI, Hughes D (2010) Antibiotic resistance and its cost: is it possible to reverse resistance? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 8:260–271. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2319
Appiah T, Boakye YD, Agyare C (2017) Antimicrobial activities and time-kill kinetics of extracts of selected Ghanaian mushrooms. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med 2017: https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4534350
Aslam B, Wang W, Arshad MI, et al (2018) Antibiotic resistance: a rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 11: 1645. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S173867
Balouiri M, Sadiki M, Ibnsouda SK (2016) Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: a review. J Pharm Anal 6:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2015.11.005.
Bangham, A. D., Hill, M. W., & Miller, N. G. A. (1974). Preparation and use of liposomes as models of biological membranes. In Methods in membrane biology. Springer, Boston, MA, 1-68. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-7422-4_1
Benkert P, Biasini M, Schwede T (2011) Toward the estimation of the absolute quality of individual protein structure models. Bioinformatics. 27 : 343-350. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq662
Bertoni M, Kiefer F, Biasini M et al (2017) Modeling protein quaternary structure of homo- and hetero-oligomers beyond binary interactions by homology. Sci Rep. 7: 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09654-8
Bienert S, Waterhouse A, De Beer TAP et al (2017) The SWISS-MODEL repository-new features and functionality. Nucleic Acids Res. 45: D313-D319. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1132
Blair JMA, Webber MA, Baylay AJ, et al (2015) Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 13: 42-51. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3380
Blume A, Hiibner W, Messner G (1988) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy of13c=0-labeled phospholipids hydrogen bonding to carbonyl groups. Biochemistry. 27: 8239-8249. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00421a038
Chifiriuc MC, Holban AM, Curutiu C, et al (2016) Antibiotic drug delivery systems for the intracellular targeting of bacterial pathogens. In: Smart Drug Delivery System
Chithrani DB, Dunne M, Stewart J et al (2010) Cellular uptake and transport of gold nanoparticles incorporated in a liposomal carrier. Nanomedicine Nanotechnology, Biol Med. 6: 161-169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2009.04.009
Cipolla D, Wu H, Gonda I et al (2014) Modifying the release properties of liposomes toward personalized medicine. J Pharm Sci. 103: 1851-1862. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.23969
Collin F, Karkare S, Maxwell A (2011) Exploiting bacterial DNA gyrase as a drug target: current state and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 92: 479-497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3557-z
Cong W, Liu Q, Liang Q et al (2009) Investigation on the interactions between pirarubicin and phospholipids. Biophys Chem. 143: 154-160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpc.2009.05.005
Cordeiro C, Wiseman DJ, Lutwyche P et al (2000) Antibacterial efficacy of gentamicin encapsulated in pH-sensitive liposomes against an in vivo Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium intracellular infection model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 44: 533-539. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.44.3.533-539.2000
Costa S, Falcão C, Viveiros M et al (2011) Exploring the contribution of efflux on the resistance to fluoroquinolones in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Microbiol. 11: 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-11-241
Ding Y, Onodera Y, Lee JC, Hooper DC (2008) NorB, an efflux pump in Staphylococcus aureus strain MW2, contributes to bacterial fitness in abscesses. J Bacteriol. 190: 7123-7129. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00655-08
Drulis-Kawa Z, Dorotkiewicz-Jach A (2010) Liposomes as delivery systems for antibiotics. Int. J. Pharm. 387:187-198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.11.033
Du D, Wang-Kan X, Neuberger A, et al (2018) Multidrug efflux pumps: structure, function and regulation. 16: 523-539. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-018-0048-6
El-Nesr OH, Yahiya SA, El-Gazayerly ON (2010) Effect of formulation design and freeze-drying on properties of fluconazole multilamellar liposomes. Saudi Pharm J. 18: 217-224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2010.07.003
Fedorowicz J, Sączewski J (2018) Modifications of quinolones and fluoroquinolones: hybrid compounds and dual-action molecules. Monatshefte fur Chemie. 149: 1199-1245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-018-2215-x
Freitas PR, de Araújo ACJ, dos Santos Barbosa CR, et al (2021) Inhibition of the MepA efflux pump by limonene demonstrated by in vitro and in silico methods. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-021-00909-6
Friesner RA, Murphy RB, Repasky MP et al (2006) Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J Med Chem 49:6177–6196. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm051256o
Georgieva R, Chachaty C, Hazarosova R, et al (2015) Docosahexaenoic acid promotes micron scale liquid-ordered domains. A comparison study of docosahexaenoic versus oleic acid containing phosphatidylcholine in raft-like mixtures. Biochim Biophys Acta - Biomembr. 1848: 1424-1435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.02.027
Guex N, Peitsch MC, Schwede T (2009) Automated comparative protein structure modeling with SWISS‐MODEL and Swiss‐PdbViewer: a historical perspective. Electrophoresis 30: S162-S173. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200900140
Gupta AK, Katoch VM, Chauhan DS et al (2010) Microarray analysis of efflux pump genes in multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis during stress induced by common anti-tuberculous drugs. Microb Drug Resist. 16: 21-28. https://doi.org/10.1089/mdr.2009.0054
Handzlik J, Matys A, Kieć-Kononowicz K (2013) Recent advances in multi-drug resistance (MDR) efflux pump inhibitors of Gram-positive bacteria S. aureus. Antibiotics. 2: 28-45.https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics2010028
Harbarth S, Balkhy HH, Goossens H et al (2015) Antimicrobial resistance: one world, one fight! Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13756-015-0091-2
Hosny KM (2009) Preparation and evaluation of thermosensitive liposomal hydrogel for enhanced transcorneal permeation of ofloxacin. AAPS PharmSciTech. 10: 1336-1342. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-009-9335-x
Imbuluzqueta E (2010) Drug delivery systems for potential treatment of intracellular bacterial infections. Front Biosci. https://doi.org/10.2741/3627
Ishii H, Sugimura K, Nishio Y (2019) Thermotropic liquid crystalline properties of (hydroxypropyl) cellulose derivatives with butyryl and heptafluorobutyryl substituents. Cellulose. 26: 399-412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2176-6
Jorgensen WL, Maxwell DS, Tirado-Rives J (1996) Development and testing of the OPLS all-atom force field on conformational energetics and properties of organic liquids. J Am Chem Soc. 118:11225-11236. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja9621760
Kaatz GW, McAleese F, Seo SM (2005) Multidrug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus due to overexpression of a novel multidrug and toxin extrusion (MATE) transport protein. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 49: 1857-1864. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.49.5.1857-1864.2005
Kahlmeter G, Giske CG, Kirn TJ, Sharp SE (2019) Point-counterpoint: differences between the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute recommendations for reporting antimicrobial susceptibility results. J Clin Microbiol 57:e01129-e1219 https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01129-19 .
Kaminski GA, Friesner RA, Tirado-Rives J, Jorgensen WL (2001) Evaluation and reparametrization of the OPLS-AA force field for proteins via comparison with accurate quantum chemical calculations on peptides. 105: 6474-6487. J Phys Chem B. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp003919d
Köhler T, Pechère JC, Plésiat P (1999) Bacterial antibiotic efflux systems of medical importance. In: Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 56:771-778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050024
Koynova R, Caffrey M (1998) Phases and phase transitions of the phosphatidylcholines. 1376: 91-145.Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Rev. Biomembr. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4157(98)00006-9
Kumar K, Woo SM, Siu T et al (2018) Cation-π interactions in protein-ligand binding: theory and data-mining reveal different roles for lysine and arginine. Chem Sci. 9: 2655-2665. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7sc04905f
Lasic DD (1995) Applications of liposomes. Handb Biol Phys. 1: 491-519. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-8121(06)80027-8
Leung SSF, Mijalkovic J, Borrelli K, Jacobson MP (2012) Testing physical models of passive membrane permeation. J Chem Inf Model. 52: 1621-1636 https://doi.org/10.1021/ci200583t
Leung SSF, Sindhikara D, Jacobson MP (2016a) Simple predictive models of passive membrane permeability incorporating size-dependent membrane-water partition. J Chem Inf Model. 56: 924-929. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.6b00005
Leung SSFF, Mijalkovic J, Borrelli K et al (2016b) Supporting Information Testing physical models of passive membrane permeation table of contents. J Chem Inf Model. 52: 1621-1636. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.6b00005
Lewis RN, McElhaney RN, Pohle W, Mantsch HH (1994) Components of the carbonyl stretching band in the infrared spectra of hydrated 1,2-diacylglycerolipid bilayers: a reevaluation. Biophys J. 67: 2367-2375. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80723-4
Li G, Zhang J, Guo Q et al (2015) Efflux pump gene expression in multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates. PLoS ONE. 10: e0119013 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119013
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25: 402-408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Mady MM, Darwish MM, Khalil S, Khalil WM (2009) Biophysical studies on chitosan-coated liposomes. Eur Biophys J. 38: 1127-1133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-009-0524-z
Mady MM, Shafaa MW, Abbase ER, Fahium AH (2012) Interaction of doxorubicin and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine liposomes. Cell Biochem Biophys. 62: 481-486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-011-9334-x
Magallanes M, Dijkstra J, Fierer J (1993) Liposome-incorporated ciprofloxacin in treatment of murine salmonellosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 37:2293-2297. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.37.11.2293
Majumdar S, Flasher D, Friend DS, et al (1992) Efficacies of liposome-encapsulated streptomycin and ciprofloxacin against Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare complex infections in human peripheral blood monocyte/macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 36: 2808-2815. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.36.12.2808
McAleese F, Petersen P, Ruzin A et al (2005) A novel MATE family efflux pump contributes to the reduced susceptibility of laboratory-derived Staphylococcus aureus mutants to tigecycline. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 49:1865-1871. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.49.5.1865-1871.2005
Moreno-Sastre M, Pastor M, Esquisabel A, Pedraz JL (2016) The use of nanoparticles for antimicrobial delivery. In: Villa TG, Vinas M (eds) New Weapons to Control Bacterial Growth. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 453–487
Moyá ML, López-López M, Lebrón JA, et al (2019) Preparation and characterization of new liposomes. Bactericidal activity of cefepime encapsulated into cationic liposomes. Pharmaceutics 11:69. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020069
Nagarsenker MS, Londhe VY, Nadkarni GD (1999) Preparation and evaluation of liposomal formulations of tropicamide for ocular delivery. Int J Pharm.190: 63-71. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(99)00265-3
Ng VWL, Ke X, Lee ALZ et al (2013) Synergistic co-delivery of membrane-disrupting polymers with commercial antibiotics against highly opportunistic bacteria. Adv Mater 25:6730–6736. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201302952
Nguyen S, Hiorth M, Rykke M, Smistad G (2013) Polymer coated liposomes for dental drug delivery–interactions with parotid saliva and dental enamel. Eur J Pharm Sci 50:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2013.03.004.
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 29: e45-e45 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Piddock LJV, Williams KJ, Ricci V (2000) Accumulation of rifampicin by Mycobacterium aurum, Mycobacterium smegmatis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 45:159-165. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/45.2.159
Pignatello R, Leonardi A, Fuochi V et al (2018) A method for efficient loading of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride in cationic solid lipid nanoparticles: formulation and microbiological evaluation. Nanomaterials 8:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050304
Rahman T, Yarnall B, Doyle DA (2017) Efflux drug transporters at the forefront of antimicrobial resistance. Eur. Biophys. J. 46:647-653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-017-1238-2
Remmert M, Biegert A, Hauser A, Söding J (2012) HHblits: lightning-fast iterative protein sequence searching by HMM-HMM alignment. Nat Methods. 9:173-175. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1818
Rezai T, Yu B, Millhauser GL et al (2006) Testing the conformational hypothesis of passive membrane permeability using synthetic cyclic peptide diastereomers. J Am Chem Soc.128: 2510-2511. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0563455
Rukavina Z, Vanić Ž (2016) Current trends in development of liposomes for targeting bacterial biofilms. Pharmaceutics. 8: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics8020018
Russo G, Witos J, Rantamäki AH, Wiedmer SK (2017) Cholesterol affects the interaction between an ionic liquid and phospholipid vesicles. A study by differential scanning calorimetry and nanoplasmonic sensing. Biochim Biophys Acta - Biomembr. 12: 2361-2372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.09.011
Sabatini S, Gosetto F, Serritella S et al (2012) Pyrazolo [4, 3-c][1, 2] benzothiazines 5, 5-dioxide: a promising new class of Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump inhibitors. J Med Chem 55: 3568–3572. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm201446h
Salem HF, Ahmed SM, Omar MM (2016) Liposomal flucytosine capped with gold nanoparticle formulations for improved ocular delivery. Drug Des Devel Ther. 10: 277. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S91730
Salem II, Flasher DL, Düzgüneş N (2005) Liposome-encapsulated antibiotics. Methods Enzymol. 391: 261-291. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(05)91015-X
Schindler BD, Frempong-Manso E, DeMarco CE, et al (2015) Analyses of multidrug efflux pump-like proteins encoded on the Staphylococcus aureus chromosome. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59:747-748.https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.04678-14
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc. 3:1101-1108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Schrodinger LLC (2013) MacroModel, Version 10.2. New York
Schrödinger Release 2019–1 (2019) Prime. New York
Severcan F, Sahin I, Kazanci N (2005) Melatonin strongly interacts with zwitterionic model membranes-evidence from Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. Biochim Biophys Acta - Biomembr. 1668:215-222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.12.009
Shafaa, M. W. (2018). INTERACTION OF BISOPROLOL OR ENALAPRIL WITH DISTEAROYL PHOSPHATIDYLCHOLINE LIPOSOMES: FTIR AND DSC STUDIES. Romanian Journal of Biophysics, 28(3).
Shafaa MW, Elshazly AH, Dakrory AZ, Elsyed MR (2018) Interaction of Coenzyme Q10 with liposomes and its impact on suppression of selenite - induced experimental cataract. Adv Pharm Bull. 8: 1–9. https://doi.org/10.15171/apb.2018.001
Shafaa MW, Dayem SA, Elshemy WM (2008) In vitro antibacterial activity of liposomal cephalexin against Staphylococcus aureus. Rom J Biophys 18:293–300
Sofia Santos Costa, Miguel Viveiros LA and IC (2013) Multidrug efflux pumps in Staphylococcus aureus: an update. Open Microbiol J. 7:59. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874285801307010059
Tintino SR, de Souza VCA, Silva J et al (2020) Effect of vitamin K3 inhibiting the function of NorA efflux pump and its gene expression on Staphylococcus aureus. Membranes (basel) 10:130. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10060130
Toyran N, Severcan F (2007) Interaction between vitamin D2 and magnesium in liposomes: differential scanning calorimetry and FTIR spectroscopy studies. J Mol Struct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2006.11.005
Truong-Bolduc, Q.C., Dunman, P.M., Strahilevitz, J., Projan, S.J. and Hooper, D.C (2005) MgrA is a multiple regulator of two new efflux pumps in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 187(7), 2395-2405. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.7.2395-2405.2005
Tsuji, Brian T., Jenny C. Yang, Alan Forrest, Pamela A. Kelchlin, and Patrick F. Smith (2008) In vitro pharmacodynamics of novel rifamycin ABI-0043 against Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother 62:156–160
Wang Y (2021) Liposome as a delivery system for the treatment of biofilm-mediated infections. J Appl Microbiol 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.15053
Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, Studer G, Tauriello G, Gumienny R, Heer FT, de Beer TA, Rempfer C, Bordoli L, Lepore R (2018) SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2;46(W1):W296-303 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky427
Zhu, Qiang, Yilin Lu, Xibing He, Tao Liu, Hongwei Chen, Fang Wang, Dong Zheng, Hao Dong, and Jing Ma (2017) Entropy and polarity control the partition and transportation of drug-like molecules in biological membrane. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18012-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ahmed H. I. Faraag, Medhat W. Shafaa, Nourhan S. Elkholy, and Lina Jamil M. Abdel-Hafez have prepared the study; written the manuscript; designed and conducted the experiments; analyzed, reviewed, and interpreted the data; and supervised the research. Ahmed H. I. Faraag, Medhat W. Shafaa, and Lina Jamil M. Abdel-Hafez also read, revised, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies conducted by any of the authors with human or animal participants.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Multidrug resistance of many antibiotics is attributed to the bacterial efflux pump that reduces the antibiotic concentration to a sublethal level.
• Ciprofloxacin (CPF) is one of the most potent quinolones with the bactericidal mode of action against DNA gyrase that is responsible for double-stranded DNA supercoiling.
• Ciprofloxacin liposome-encapsulated (CFL) is one of the promising mechanisms for overcoming methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) efflux pumps due to its low antibiotic stress and reduced expression on the efflux pump.
The original online version of this article was revised: The authors regret that Figure 5c is missing from the original article.
It is now provided below.
The original article has been corrected.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faraag, A.H.I., Shafaa, M.W., Elkholy, N.S. et al. Stress impact of liposomes loaded with ciprofloxacin on the expression level of MepA and NorB efflux pumps of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int Microbiol 25, 427–446 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-021-00219-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-021-00219-4