Abstract
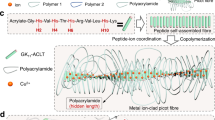
Recently, numerous mechanically robust synthetic hydrogels have been created. However, unlike natural loading-bearing materials such as cartilages and muscles, most hydrogels have inherently contradictory requirements, obstructing the design of hydrogels with characteristics of robustness and rapid self-recoverability. Herein, we present a facile strategy for constructing mechanically robust and rapidly self-recoverable hydrogels. The linear poly(acrylamide-co-itaconic acid) chains crosslink via coordination bonds and minimal chemical crosslinkers to form the hydrogel network. Such design endows the coordination interactions to be asymmetrically distributed. Under deformation, the coordination interactions exhibit a reversible dissociation-and-reorganization property, demonstrating a new mechanism for energy dissipation and stress redistribution. Thus, the hydrogels possess tensile strength up to 12.5 MPa and toughness up to 28.2 MJ/m3. Moreover, the inherent dynamic nature of the coordination bonds imparts these hydrogels with stretch rate- and temperature-dependent mechanical behavior as well as excellent self-recovery performance. The method employed in this study is universal and is applicable to other polymers with load-bearing yet rapid recovery conditions. This study will facilitate diverse applications of most metallosupramolecular hydrogels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gjorevski, N.; Nikolaev, M.; Brown, T. E.; Mitrofanova, O.; Brandenberg, N.; DelRio, F. W.; Yavitt, F. M.; Liberali, P.; Anseth, K. S.; Lutolf, M. P. Tissue geometry drives deterministic organoid patterning. Science 2022, 375, eaaw9021.
Miao, S.; Castro, N.; Nowicki, M.; Xia, L.; Cui, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, W.; Lee, S. Jun; Sarkar, K.; Vozzi, G.; Tabata, Y.; Fisher, J.; Zhang, L. G. 4D printing of polymeric materials for tissue and organ regeneration. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 577–591.
Zhu, J.; Yang, S.; Qi, Y.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liang, K.; Shen, P.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, W.; Yue, L.; Fan, S.; Shen, S.; Mikos, A. G.; Wang, X.; Fang, X. Stem cell-homing hydrogel-based miR-29b-5p delivery promotes cartilage regeneration by suppressing senescence in an osteoarthritis rat model. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabk0011.
Liang, Q.; Xia, X.; Sun, X.; Yu, D.; Huang, X.; Han, G.; Mugo, S. M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Q. Highly stretchable hydrogels as wearable and implantable sensors for recording physiological and brain neural signals. Adv. Sci. 2022, 2201059.
Zhang, C.; Wang, M.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, P.; Sun, B.; Gao, Q.; Gao, C.; Liu, R. Highly adhesive and self-healing γ-PGA/PEDOT:PSS conductive hydrogels enabled by multiple hydrogen bonding for wearable electronics. Nano Energy 2022, 95, 106991.
Zhuo, S.; Song, C.; Rong, Q.; Zhao, T.; Liu, M. Shape and stiffness memory ionogels with programmable pressure-resistance response. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1743.
Li, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Huang, G. Stability, seepage and displacement characteristics of heterogeneous branched-preformed particle gels for enhanced oil recovery. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4881–4889.
Yin, H.; Yin, X.; Cao, R.; Zeng, P.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Luo, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Y. In situ crosslinked weak gels with ultralong and tunable gelation times for improving oil recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 432, 134350.
Kim, J.; Zhang, G.; Shi, M.; Suo, Z. Fracture, fatigue, and friction of polymers in which entanglements greatly outnumber cross-links. Science 2021, 374, 212–216.
Cao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, C.; Li, H.; Zheng, J.; Wu, J.; Huang, G. Tough, ultrastretchable and tear-resistant hydrogels enabled by linear macro-cross-linker. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 3503–3513.
Hua, M.; Wu, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Frenkel, I.; Strzalka, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, X.; He, X. Strong tough hydrogels via the synergy of freeze-casting and salting out. Nature 2021, 590, 594–599.
Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Qiao, K.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z.; Lu, T.; Suo, Z.; Hu, J. Topoarchitected polymer networks expand the space of material properties. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1622.
Gong, J. P.; Katsuyama, Y.; Kurokawa, T.; Osada, Y. Doublenetwork hydrogels with extremely high mechanical strength. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1155–1158.
Gong, J. P. Why are double network hydrogels so tough. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 2583–2590.
Liu, C.; Morimoto, N.; Jiang, L.; Kawahara, S.; Noritomi, T.; Yokoyama, H.; Mayumi, K.; Ito, K. Tough hydrogels with rapid self-reinforcement. Science 2021, 372, 1078–1081.
Liu, R.; Wang, H.; Lu, W.; Cui, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Highly tough, stretchable and resilient hydrogels strengthened with molecular springs and their application as a wearable, flexible sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 128839.
Hu, J.; Hiwatashi, K.; Kurokawa, T.; Liang, S. M.; Wu, Z. L.; Gong, J. P. Microgel-reinforced hydrogel films with high mechanical strength and their visible mesoscale fracture structure. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 7775–7781.
Xia, L. W.; Xie, R.; Ju, X. J.; Wang, W.; Chen, Q.; Chu, L. Y. Nano-structured smart hydrogels with rapid response and high elasticity. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–11.
Nan, W.; Wang, W.; Gao, H.; Liu, W. Fabrication of a shape memory hydrogel based on imidazole-zinc ion coordination for potential cell-encapsulating tubular scaffold application. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 132–137.
Sun, T. L.; Kurokawa, T.; Kuroda, S.; Ihsan, A. Bin; Akasaki, T.; Sato, K.; Haque, M. A.; Nakajima, T.; Gong, J. P. Physical hydrogels composed of polyampholytes demonstrate high toughness and viscoelasticity. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 932–937.
Lin, P.; Ma, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F. Molecularly engineered dual-crosslinked hydrogel with ultrahigh mechanical strength, toughness, and good self-recovery. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2054–2059.
Hu, Y.; Du, Z.; Deng, X.; Wang, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C. Dual physically cross-linked hydrogels with high stretchability, toughness, and good self-recoverability. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 5660–5668.
Zheng, S. Y.; Ding, H.; Qian, J.; Yin, J.; Wu, Z. L.; Song, Y.; Zheng, Q. Metal-coordination complexes mediated physical hydrogels with high toughness, stick-slip tearing behavior, and good processability. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 9637–9646.
Cao, J.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J. Dual physical crosslinking strategy to construct moldable hydrogels with ultrahigh strength and toughness. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800739.
Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, Z.; Yu, H.; Huang, G.; Wu, Q.; Ling, F.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zheng, J.; Wu, J. Wide-range linear viscoelastic hydrogels with high mechanical properties and their applications in quantifiable stress-strain sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125697.
Yu, H. C.; Zheng, S. Y.; Fang, L.; Ying, Z.; Du, M.; Wang, J.; Ren, K. F.; Wu, Z. L.; Zheng, Q. Reversibly transforming a highly swollen polyelectrolyte hydrogel to an extremely tough one and its application as a tubular grasper. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2005171.
Jiao, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, T.; Peng, X.; Wang, H. Mechanically strong, tough, and shape deformable poly(acrylamide-co-vinylimidazole) hydrogels based on Cu2+ complexation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 44205–44214.
Yu, H. C.; Hao, X. P.; Zhang, C. W.; Zheng, S. Y.; Du, M.; Liang, S.; Wu, Z. L.; Zheng, Q. Engineering tough metallosupramolecular hydrogel films with kirigami structures for compliant soft electronics. Small 2021, 17, 2103836.
Sun, J. Y.; Zhao, X.; Illeperuma, W. R. K.; Chaudhuri, O.; Oh, K. H.; Mooney, D. J.; Vlassak, J. J.; Suo, Z. Highly stretchable and tough hydrogels. Nature 2012, 489, 133–136.
Shao, C.; Chang, H.; Wang, M.; Xu, F.; Yang, J. High-srrength, tough, and self-healing nanocomposite physical hydrogels based on the synergistic effects of dynamic hydrogen bond and dual coordination bonds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28305–28318.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51873110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Notes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Electronic Supplementary Information
10118_2022_2818_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Ultra-robust Metallosupramolecular Hydrogels with Unprecedented Self-recoverability using Asymmetrically Distributed Carboxyl-Fe3+ Coordination Interactions
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, ZY., Cao, ZX., Wu, R. et al. Ultra-robust Metallosupramolecular Hydrogels with Unprecedented Self-recoverability using Asymmetrically Distributed Carboxyl-Fe3+ Coordination Interactions. Chin J Polym Sci 41, 250–257 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-022-2818-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-022-2818-x