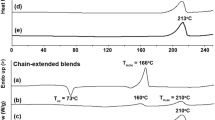
Abstract
Stereocomplex-type polylactide (SC-PLA) consisting of alternatively arranged poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) and poly(D-lactide) (PDLA) chains has gained a good reputation as a sustainable engineering plastic with outstanding heat resistance and durability, however its practical applications have been considerably hindered by the weak SC crystallizability. Current methods used to enhance the SC crystallizability are generally achieved at the expense of the precious bio-renewability and/or bio-degradability of PLAs. Herein, we demonstrate a feasible method to address these challenges by incorporating small amounts of poly(D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) into linear high-molecular-weight PLLA/PDLA blends. The results show that the incorporation of the atactic PDLLA leads to a significant enhancement in the SC crystallizability because its good miscibility with the isotactic PLAs makes it possible to greatly improve the chain mixing between PLLA and PDLA as an effective compatibilizer. Meanwhile, the melt stability (i.e., the stability of PLLA/PDLA chain assemblies upon melting) could also be improved substantially. Very intriguingly, SC crystallites are predominantly formed with increasing content and molecular weight of PDLLA. More notably, exclusive SC crystallization can be obtained in the racemic blends with 20 wt% PDLLA having weight-average molecular weight of above 1×105 g/mol, where the chain mixing level and intermolecular interactions between the PLA enantiomers could be strikingly enhanced. Overall, our work could not only open a promising horizon for the development of all SC-PLA-based engineering plastic with exceptional SC crystallizability but also give a fundamental insight into the crucial role of PDLLA in improving the SC crystallizability of PLLA/PDLA blends.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tschan, J. L.; Brulé, E.; Haquette, P.; Thomas, C. M. Synthesis of biodegradable polymers from renewable resources. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 836–851.
Reddy, M. M.; Vivekanandhan, S.; Misra, M.; Bhatia, S. K.; Mohanty, A. K. Biobased plastics and bionanocomposites: current status and future opportunities. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1653–1689.
Schneiderman, D. K.; Hillmyer, M. A. 50th Anniversary perspective: there is a great future in sustainable polymers. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 3733–3750.
Lim, L. T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M. Processing technologies for poly(lactic acid). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 820–852.
Saeidlou, S.; Huneault, M. A.; Li, H. B.; Park, C. B. Poly(lactic acid) crystallization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1657–1677.
Nagarajan, V.; Mohanty, A. K.; Misratt, M. Perspective on polylactic acid (PLA) based sustainable materials for durable applications: focus on toughness and heat resistance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2899–2916.
Farah, S.; Anderson, D. G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications—a comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392.
Inkinen, S.; Hakkarainen, M.; Albertsson, A. C.; Sodergard, A. From lactic acid to poly(lactic acid) (PLA): characterization and analysis of PLA and its precursors. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 523–532.
Harris, A. M.; Lee, E. C. Durability of polylactide-based polymer blends for injection-molded applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 2136–2144.
Andersson, S. R.; Hakkarainen, M.; Albertsson, A. C. Long-term properties and migration of low molecular mass compounds from modified PLLA materials during accelerated ageing. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2012, 97, 914–920.
Auras, R.; Harte, B.; Selke, S. An overview of polylactides as packaging materials. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 835–864.
Bai, H. W.; Huang, C. M.; Xiu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, H.; Wang, K.; Chen, F.; Fu, Q. Significantly improving oxygen barrier properties of polylactide via constructing parallel-aligned shish-kebab-like crystals with well-interlocked boundaries. Bimacromolecules 2014, 15, 1507–1514.
Ikada, Y.; Jamshidi, K.; Tsuji, H.; Hyon, S. H. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactides). Macromolecules 1987, 20, 904–906.
Tsuji, H.; Hyon, S. H.; Ikada, Y. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactic acid)s. 4. Differential scanning calorimetric studies on precipitates from mixed-solutions of poly(D-lactic acid) and poly(L-lactic acid). Macromolecules 1991, 24, 5657–5662.
Tsuji, H.; Ikada, Y. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactic acid)s. 9. Stereocomplexation from the melt. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 6918–6926.
Tsuji, H. Poly(lactic acid) stereocomplexes: a decade of progress. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 97–135.
Tashiro, K.; Wang, H. F.; Kouno, N.; Koshobu, J.; Watanabe, K. Confirmation of the X-ray-analyzed heterogeneous distribution of the PDLA and PLLA chain stems in the crystal lattice of poly(lactic acid) stereocomplex on the basis of the vibrational circular dichroism IR spectral measurement. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 8066–8071.
Tashiro, K.; Kouno, N.; Wang, H.; Tsuji, H. Crystal structure of poly(lactic acid) stereocomplex: Random packing model of PDLA and PLLA chains as studied by X-ray diffraction Analysis. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 8048–8065.
Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z. F.; Zhou, Z. P.; Nie, Y. J. Stereocomplex crystallization in asymmetric diblock copolymers studied by dynamic monte carlo simulations. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 39, 632–639.
Masutani, K.; Lee, C. W.; Kimura, Y. Synthesis and thermomechanical properties of stereo triblock polylactides with nonequivalent block compositions. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2012, 213, 695–704.
Wu, B. G.; Yang, W. J.; Niu, D. Y.; Dong, W. F.; Chen, M. Q.; Liu, T. X.; Du, M. L.; Ma, P. M. Stereocomplexed poly(lactide) composites toward engineering plastics with superior toughness, heat resistance and anti-hydrolysis. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 73–82.
Tsuji, H.; Fukui, I. Enhanced thermal stability of poly(lactide)s in the melt by enantiomeric polymer blending. Polymer 2003, 44, 2891–2896.
Han, L. L.; Xie, Q.; Bao, J. N.; Shan, G. R.; Bao, Y. Z.; Pan, P. J. Click chemistry synthesis, stereocomplex formation, and enhanced thermal properties of well-defined poly(L-lactic acid)-b-poly(D-lactic acid) stereo diblock copolymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 1006–1016.
Andersson, S. R.; Hakkarainen, M.; Inkinen, S.; Sodergard, A.; Albertsson, A. C. Polylactide stereocomplexation leads to higher hydrolytic stability but more acidic hydrolysis product pattern. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1067–1073.
Li, Y.; Yu, Y. C.; Han, C. Y.; Wang, X. H.; Huang, D. X. Sustainable blends of poly(propylene carbonate) and stereocomplex polylactide with enhanced rheological properties and heat resistance. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 1267–1275.
Lee, S.; Kimoto, M.; Tanaka, M.; Tsuji, H.; Nishino, T. Crystal modulus of poly(lactic acid)s, and their stereocomplex. Polymer 2018, 138, 124–131.
Zhang, X. W.; Nakagawa, R.; Chan, K. H. K.; Kotaki, M. Mechanical property enhancement of polylactide nanofibers through optimization of molecular weight, electrospinning conditions, and stereocomplexation. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 5494–5500.
Tsuji, H.; Ikada, Y. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactic acid)s. XI. Mechanical properties and morphology of solution-cast films. Polymer 1999, 40, 6699–6708.
Ma, P. M.; Shen, T. F.; Xu, P. W.; Dong, W. F.; Lemstra, P. J.; Chen, M. Q. Superior performance of fully biobased poly(lactide) via stereocomplexation-induced phase separation: structure versus property. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1470–1478.
Tsuji, H. Poly(lactide) stereocomplexes: formation, structure, properties, degradation, and applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 569–597.
Na, B.; Zhu, J.; Lv, R. H.; Ju, Y. H.; Tian, R. P.; Chen, B. B. Stereocomplex formation in enantiomeric polylactides by melting recrystallization of homocrystals: crystallization kinetics and crystal Morphology. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 347–352.
Bao, R. Y.; Yang, W.; Jiang, W. R.; Liu, Z. Y.; Xie, B. H.; Yang, M. B.; Fu, Q. Stereocomplex formation of high-molecular-weight polylactide: a low temperature approach. Polymer 2012, 53, 5449–5454.
Liu, Y. L.; Sun, J. R.; Bian, X. C.; Feng, L. D.; Xiang, S.; Sun, B.; Chen, Z. M.; Li, G.; Chen, X. S. Melt stereocomplexation from poly(L-lactic acid) and poly(D-lactic acid) with different optical purity. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2013, 98, 844–852.
Biela, T.; Duda, A.; Penczek, S. Enhanced melt stability of star-shaped stereocomplexes as compared with linear stereocomplexes. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 3710–3713.
Bai, H. W.; Liu, H. L.; Bai, D. Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, K.; Deng, H.; Chen, F.; Fu, Q. Enhancing the melt stability of polylactide stereocomplexes using a solid-state cross-linking strategy during a melt-blending process. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 5985–5993.
He, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wei, J.; Fan, Z. Y.; Li, S. M. Unique crystallization behavior of poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide) stereocomplex depending on initial melt states. Polymer 2008, 49, 5670–5675.
Bai, D. Y.; Wang, K.; Bai, H. W.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Polymer processing via learning from nature and metal metallurgy. Acta Polymerica Sinica (in Chinese) 2016, 843–849.
Bai, D. Y.; Diao, X. Y.; Ju, Y. L.; Liu, H. L.; Bai, H. W.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Low-temperature sintering of stereocomplex-type polylactide nascent powder: the role of optical purity in directing the chain interdiffusion and cocrystallization across the particle interfaces. Polymer 2018, 150, 169–176.
He, S. W.; Bai, H. W.; Bai, D. Y.; Ju, Y. L.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. A promising strategy for fabricating high-performance stereocomplex-type polylactide products via carbon nanotubes-assisted low-temperature sintering. Polymer 2019, 162, 50–57.
Li, X. L.; Yang, D. S.; Zhao, Y. B.; Diao, X. Y.; Bai, H. W.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Toward all stereocomplex-type polylactide with outstanding melt stability and crystallizability via solid-state transesterification between enantiomeric poly(L-lactide) and poly(D-lactide). Polymer 2020, 205, 122850.
Chen, Y.; Hua, W. Q.; Zhang, Z. C.; Xu, J. Z.; Bian, F. G.; Zhong, G. J.; Xu, L.; Li, Z. M. An efficient, food contact accelerator for stereocomplexation of high-molecular-weight poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide) blend under nonisothermal crystallization. Polymer 2019, 170, 54–64.
Xu, Y.; Wu, H. T.; Yang, J.; Liu, R. J.; Nie, Y. J. Molecular simulations of microscopic mechanism of the effects of chain length on stereocomplex formation in polymer blends. Comp. Mater. Sci. 2020, 172, 109297.
Zhang, Z. C.; Sang, Z. H.; Huang, Y. F.; Ru, J. F.; Zhong, G. J.; Ji, X.; Wang, R. Y.; Li, Z. M. Enhanced heat deflection resistance via shear flow-induced stereocomplex crystallization of polylactide systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1692–1703.
Nie, Y. J.; Liu, Y. D.; Liu, R. J.; Zhou, Z. P.; Hao, T. F. Dynamic Monte Carlo simulations of competition in crystallization of mixed polymers grafted on a substrate. J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys. 2019, 57, 89–97.
Hemmi, K.; Matsuba, G.; Tsuji, H.; Kawai, T.; Kanaya, T.; Toyohara, K.; Oda, A.; Endou, K. Precursors in stereo-complex crystals of poly(L-lactic acid)/poly(D-lactic acid) blends under shear flow. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2014, 47, 14–21.
Shao, J.; Liu, Y. L.; Xiang, S.; Bian, X. C.; Sun, J. R.; Li, G.; Chen, X. S.; Hou, H. Q. The stereocomplex formation and phase separation of PLLA/PDLA blends with different optical purities and molecular weights. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 33, 1713–1720.
Fukushima, K.; Chang, Y. H.; Kimura, Y. Enhanced stereocomplex formation of poly(L-lactic acid) and poly(D-lactic acid) in the presence of stereoblock poly(lactic acid). Macromol. Biosci. 2007, 7, 829–835.
Pan, P. J.; Han, L. L.; Bao, J. N.; Xie, Q.; Shan, G. R.; Bao, Y. Z. Competitive stereocomplexation, homocrystallization, and polymorphic crystalline transition in poly(L-lactic acid)/poly(D-lactic acid) racemic blends: molecular weight effects. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 6462–6470.
Liu, J. Q.; Qi, X. L.; Feng, Q. J.; Lan, Q. F. Suppression of phase separation for exclusive stereocomplex crystallization of a high-molecular-weight racemic poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide) blend from the glassy state. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 3493–3503.
Bao, J. N.; Xue, X. J.; Li, K.; Chang, X. H.; Xie, Q.; Yu, C. T.; Pan, P. J. Competing stereocomplexation and homocrystallization of poly(L-lactic acid)/poly(D-lactic acid) racemic mixture: effects of miscible blending with other polymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 6934–6943.
Kakuta, M.; Hirata, M.; Kimura, Y. Stereoblock polylactides as high-performance bio-based polymers. Polym. Rev. 2009, 49, 107–140.
Fukushima, K.; Kimura, Y. Stereocomplexed polylactides (Neo-PLA) as high-performance bio-based polymers: their formation, properties, and application. Polym. Int. 2006, 55, 626–642.
Li, W.; Chen, X. Y.; Ma, Y.; Fan, Z. Y. The accelerating effect of the star-shaped poly(D-lactide)-block-poly(L-lactide) stereoblock copolymer on PLLA melt crystallization. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 1242–1250.
Han, L. L.; Shan, G. R.; Bao, Y. Z.; Pan, P. J. Exclusive stereocomplex crystallization of linear and multiarm star-shaped high-molecular-weight stereo diblock poly(lactic acid)s. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 14270–14279.
Ma, P. M.; Jiang, L.; Xu, P. W.; Dong, W. F.; Chen, M. Q.; Lemstra, P. J. Rapid stereocomplexation between enantiomeric comb-shaped cellulose-g-poly(L-lactide) nanohybrids and poly(D-lactide) from the melt. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3723–3729.
Isono, T.; Kondo, Y.; Ozawa, S.; Chen, Y.; Sakai, R.; Sato, S.; Tajima, K.; Kakuchi, T.; Satoh, T. Stereoblock-like brush copolymers consisting of poly(L-lactide) and poly(D-lactide) side chains along poly(norbornene) backbone: synthesis, stereocomplex formation, and structure-property relationship. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 7118–7128.
Zhou, K. Y.; Li, J. B.; Wang, H. X.; Ren, J. Effect of star-shaped chain architectures on the polylactide stereocomplex crystallization behaviors. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 35, 974–991.
Pan, P. J.; Bao, J. N.; Han, L. L.; Xie, Q.; Shan, G. R.; Bao, Y. Z. Stereocomplexation of high-molecular-weight enantiomeric poly(lactic acid)s enhanced by miscible polymer blending with hydrogen bond interactions. Polymer 2016, 98, 80–87.
Xie, Q.; Han, L. L.; Shan, G. R.; Bao, Y. Z.; Pan, P. J. Polymorphic crystalline structure and crystal morphology of enantiomeric poly(lactic acid) blends tailored by a self-assemblable aryl amide nucleator. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2680–2688.
Han, L. L.; Pan, P. J.; Shan, G. R.; Bao, Y. Z. Stereocomplex crystallization of high-molecular-weight poly(L-lactic acid)/poly(D-lactic acid) racemic blends promoted by a selective nucleator. Polymer 2015, 63, 144–153.
Shen, S. Q.; Bao, R. Y.; Liu, Z. Y.; Yang, W.; Xie, B. H.; Yang, M. B. Supercooling-dependent morphology evolution of an organic nucleating agent in poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide) blends. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 1648–1657.
Yin, H. Y.; Wei, X. F.; Bao, R. Y.; Dong, Q. X.; Liu, Z. Y.; Yang, W.; Xie, B. H.; Yang, M. B. Enantiomeric poly(D-lactide) with a higher melting point served as a significant nucleating agent for poly(L-lactide). CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 4334–4342.
Zhu, J.; Na, B.; Lv, R. H.; Li, C. Enhanced stereocomplex formation of high-molecular-weight polylactides by gelation in an ionic liquid. Polym. Int. 2014, 63, 1101–1104.
Bao, R. Y.; Yang, W.; Wei, X. F.; Xie, B. H.; Yang, M. B. Enhanced formation of stereocomplex crystallites of high molecular weight poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide) blends from melt by using poly(ethylene glycol). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2301–2309.
Samuel, C.; Cayuela, J.; Barakat, I.; Müller, A.; Raquez, J. M.; Dubois, P. Stereocomplexation of polylactide enhanced by poly(methyl methacrylate): improved processability and thermomechanical properties of stereocomplexable polylactide-based materials. Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 11797–11807.
Pan, P. J.; Liang, Z. C.; Zhu, B.; Dong, T.; Inoue, Y. Blending effects on polymorphic crystallization of poly(L-lactide). Macromolecules 2009, 42, 3374–3380.
Tsuji, H.; Tajima, T. Crystallization behavior of stereo diblock poly(lactide)s with relatively short poly(D-lactide) segment from partially melted state. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2015, 299, 1089–1105.
Sakamoto, Y.; Tsuji, H. Stereocomplex crystallization behavior and physical properties of linear 1-arm, 2-arm, and branched 4-arm poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide) blends: effects of chain directional change and branching. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 776–786.
Hirata, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Kimura, Y. Synthesis and properties of high-molecular-weight stereo di-block polylactides with nonequivalent D/L ratios. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 794–801.
Fukushima, K.; Furuhashi, Y.; Sogo, K.; Miura, S.; Kimura, Y. Stereoblock poly(lactic acid): synthesis via solid-state polycondensation of a stereocomplexed mixture of poly(L-lactic acid) and poly(D-lactic acid). Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 21–29.
Zhang, P.; Tian, R. P.; Na, B.; Lv, R. H.; Liu, Q. X. Intermolecular ordering as the precursor for stereocomplex formation in the electrospun polylactide fibers. Polymer 2015, 60, 221–227.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51873129).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Information
10118_2021_2588_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Mixing of Racemic Poly(L-lactide)/Poly(D-lactide) Blend with Miscible Poly(D,L-lactide): Toward All Stereocomplex-type Polylactide with Strikingly Enhanced SC Crystallizability
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ju, YL., Li, XL., Diao, XY. et al. Mixing of Racemic Poly(L-lactide)/Poly(D-lactide) Blend with Miscible Poly(D,L-lactide): Toward All Stereocomplex-type Polylactide with Strikingly Enhanced SC Crystallizability. Chin J Polym Sci 39, 1470–1480 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-021-2588-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-021-2588-x