Abstract
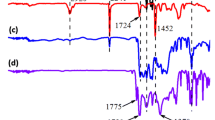
High-performance carbon nanofibers are highly dependent on the performance of their precursors, especially polyacrylonitrile (PAN). In this work, the copolymer of PAN (coPAN) was synthesized for electrospinning. A self-assembling set-up was used for the stretching of single coPAN nanofibers. FTIR and Raman spectroscopies were used to characterize the chemical structure of coPAN nanofibers. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) were used to monitor the morphology of single coPAN nanofibers under different drawing times. Micro-tensile test was used to determine the mechanical properties of single coPAN nanofibers. The results indicated that the drawing led to an increase in degree of molecular orientation along the fiber axis from 0.656 to 0.808, tensile strength from 304 MPa to 595 MPa, and modulus from 3.1 GPa to 12.4 GPa. This research would provide fundamental information of high-performance electrospun coPAN nanofibers and offer opportunities for the preparation of high-performance carbon nanofibers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chand, S. Carbon fibers for composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 1303–1313.
Yusof, N.; Ismail, A. F. Post spinning and pyrolysis processes of polyacrylonitrile (PAN)-based carbon fiber and activated carbon fiber: a review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 93, 1–13.
Liu, Y.; Kumar, S. Recent progress in fabrication, structure, and properties of carbon fibers. Polym. Rev. 2012, 52, 234–258.
Hou, H.; Xu, W.; Ding, Y. The recent progress on high-performance polymer nanofibers by electrospinning. Journal of Jiangxi Normal University (Natural Science) (in Chinese) 2018, 42, 551–564.
Wei, J.; Liao, M.; Ma, A.; Chen, Y.; Duan, Z.; Hou, X.; Li, M.; Jiang, N.; Yu, J. Enhanced thermal conductivity of polydimethylsiloxane composites with carbon fiber. Compos. Commun. 2020, 17, 141–146.
Kobets, L.; Deev, I. Carbon fibres: structure and mechanical properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1998, 57, 1571–1580.
Paris, O.; Loidl, D.; Peterlik, H. Texture of PAN-and pitch-based carbon fibers. Carbon 2002, 40, 551–555.
Zeng, H. The development of carbon fibre and its composites in china. In Proceedings of carbon fibres and their composites, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1985, pp. 288–293.
Duan, G.; Fang, H.; Huang, C.; Jiang, S.; Hou, H. Microstructures and mechanical properties of aligned electrospun carbon nanofibers from binary composites of polyacrylonitrile and polyamic acid. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 15096–15106.
Zhang, M. Y.; Niu, H. Q.; Qi, S. L.; Tian, G. F.; Wang, X. D.; Wu, D. Z. Structure evolutions involved in the carbonization of polyimide fibers with different chemical constitution. Mater. Today Commun. 2014, 1, 1–8.
Jiang, S.; Cheong, J. Y.; Nam, J. S.; Kim, I. D.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. High-density fibrous polyimide sponges with superior mechanical and thermal properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 19006–19014.
Jiang, S.; Uch, B.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. Ultralight, thermally insulating, compressible polyimide fiber assembled sponges. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 32308–32315.
Bermudez, V.; Ogale, A. A. Adverse effect of mesophase pitch draw-down ratio on carbon fiber strength. Carbon 2020, 168, 328–336.
Li, W. W.; Kang, H. L.; Xu, J.; Liu, R. G. Effects of ultra-high temperature treatment on the microstructure of carbon fibers. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 35, 764–772.
Deng, L.; Young, R. J.; Kinloch, I. A.; Zhu, Y.; Eichhorn, S. J. Carbon nanofibres produced from electrospun cellulose nanofibres. Carbon 2013, 58, 66–75.
Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Modified treatment for carbonized cellulose nanofiber application in composites. Compos. Part A 2016, 90, 786–793.
Tian, J.; Shi, Y.; Fan, W.; Liu, T. Ditungsten carbide nanoparticles embedded in electrospun carbon nanofiber membranes as flexible and high-performance supercapacitor electrodes. Compos. Commun. 2019, 12, 21–25.
Weng, W.; Kurihara, R.; Wang, J.; Shiratori, S. Electrospun carbon nanofiber-based composites for lithium-ion batteries: structure optimization towards high performance. Compos. Commun. 2019, 15, 135–148.
Wu, Q. Y.; Liang, H. Q.; Li, M.; Liu, B. T.; Xu, Z. K. Hierarchically porous carbon membranes derived from PAN and their selective adsorption of organic dyes. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 34, 23–33.
Santos de Oliveira Junior, M.; Manzolli Rodrigues, B. V.; Marcuzzo, J. S.; Guerrini, L. M.; Baldan, M. R.; Rezende, M. C. A statistical approach to evaluate the oxidative process of electrospun polyacrylonitrile ultrathin fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45458.
Hou, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Waclawik, E.; Wu, S. Stretching-induced crystallinity and orientation to improve the mechanical properties of electrospun PAN nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1726–1730.
Baseri, S. Preparation and characterization of conductive and antibacterial polyacrylonitrile terpolymer yarns produced by one-step organic coating. J. Text. Instit. 2017, 108, 20–29.
Yao, K.; Chen, J.; Li, P.; Duan, G.; Hou, H. Robust strong electrospun polyimide composite nanofibers from a ternary polyamic acid blend. Compos. Commun. 2019, 15, 92–95.
Zhou, Z.; Liu, K.; Lai, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Hou, H.; Reneker, D. H.; Fong, H. Graphitic carbon nanofibers developed from bundles of aligned electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers containing phosphoric acid. Polymer 2010, 51, 2360–2367.
Kaur, N.; Kumar, V.; Dhakate, S. R. Synthesis and characterization of multiwalled CNT-PAN based composite carbon nanofibers via electrospinning. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 483.
Papkov, D.; Zou, Y.; Andalib, M. N.; Goponenko, A.; Cheng, S. Z. D.; Dzenis, Y. A. Simultaneously strong and tough ultrafine continuous nanofibers. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3324–3331.
Jiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Duan, G.; Mei, C.; Greiner, A.; Agarwal, S. Electrospun nanofiber reinforced composites: a review. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2685–2720.
Liu, L.; Bakhshi, H.; Jiang, S.; Schmalz, H.; Agarwal, S. Composite polymeric membranes with directionally embedded fibers for controlled dual actuation. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, 1800082.
Sun, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Song, W. High performance, flexible and renewable nano-biocomposite artificial muscle based on mesoporous cellulose/ionic liquid electrolyte membrane. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2019, 283, 579–589.
Jiang, S.; Helfricht, N.; Papastavrou, G.; Greiner, A.; Agarwal, S. Low-density self-assembled poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) sponges with ultrahigh and extremely fast water uptake and release. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, 1700838.
Jian, S.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, S.; Chen, S.; Fang, H.; Song, Y.; Duan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, H. Nanofibers with diameter below one nanometer from electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4794–4802.
Jiang, S.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. Low-density open cellular sponges as functional materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15520–15538.
Agarwal, S.; Jiang, S.; Chen, Y. Progress in the field of water-and/or temperature-triggered polymer actuators. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1800548.
Molnar, K.; Jedlovszky-Hajdu, A.; Zrinyi, M.; Jiang, S.; Agarwal, S. Poly(amino acid)-based gel fibers with pH responsivity by coaxial reactive electrospinning. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2017, 38, 1700147.
Li, Y.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Electrospun nanofibers for highperformance air filtration. Compos. Commun. 2019, 15, 6–19.
Duan, G.; Liu, S.; Hou, H. Synthesis of polyacrylonitrile and mechanical properties of its electrospun nanofibers. e-Polymer 2018, 18, 569–573.
Liao, X.; Dulle, M.; de Souza e Silva, J. M.; Wehrspohn, R. B.; Agarwal, S.; Förster, S.; Hou, H.; Smith, P.; Greiner, A. High strength in combination with high toughness in robust and sustainable polymeric materials. Science 2019, 366, 1376–1379.
Zeng, Z. P.; Shao, Z. C.; Xiao, R.; Lu, Y. G. Structure evolution mechanism of poly(acrylonitrile/itaconic acid/acrylamide) during thermal oxidative stabilization process. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 35, 1020–1034.
Duan, G.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, S.; Xie, M.; Peng, X.; Chen, S.; Hanif, M.; Hou, H. Modification of precursor polymer using copolymerization: a good way to high performance electrospun carbon nanofiber bundles. Mater. Lett. 2014, 122, 178–181.
Kim, C.; Park, S. H.; Cho, J. I.; Lee, D. Y.; Park, T. J.; Lee, W. J.; Yang, K. S. Raman spectroscopic evaluation of polyacrylonitrile-based carbon nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2004, 35, 928–933.
Huang, Y. S.; Koenig, J. L. Raman spectra of polyacrylonitrile. Appl. Spectrosc. 1971, 25, 620–622.
Wang, D.; Yu, J.; Duan, G.; Liu, K.; Hou, H. Electrospun polyimide nonwovens with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties by addition of trace plasticizer. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 5667–5679.
Xu, H.; Jiang, S.; Ding, C.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Hou, H. High strength and high breaking load of single electrospun polyimide microfiber from water soluble precursor. Mater. Lett. 2017, 201, 82–84.
Yang, H.; Jiang, S.; Fang, H.; Hu, X.; Duan, G.; Hou, H. Molecular orientation in aligned electrospun polyimide nanofibers by polarized FTIR spectroscopy. Spectrochimica Acta Part A 2018, 200, 339–344.
Jiang, S.; Han, D.; Huang, C.; Duan, G.; Hou, H. Temperature-induced molecular orientation and mechanical properties of single electrospun polyimide nanofiber. Mater. Lett. 2018, 216, 81–83.
Fennessey, S. F.; Farris, R. J. Fabrication of aligned and molecularly oriented electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers and the mechanical behavior of their twisted yarns. Polymer 2004, 45, 4217–4225.
Yan, H.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z. Continually fabricating staple yarns with aligned electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 2419–2421.
Naraghi, M.; Chasiotis, I.; Kahn, H.; Wen, Y.; Dzenis, Y. Mechanical deformation and failure of electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers as a function of strain rate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 151901.
Lai, C.; Zhong, G.; Yue, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, L.; Vakili, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, J.; Fong, H. Investigation of post-spinning stretching process on morphological, structural, and mechanical properties of electrospun polyacrylonitrile copolymer nanofibers. Polymer 2011, 52, 519–528.
Hou, H.; Ge, J. J.; Zeng, J.; Li, Q.; Reneker, D. H.; Greiner, A.; Cheng, S. Z. D. Electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers containing a high concentration of well-aligned multiwall carbon nanotubes. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 967–973.
Cai, J.; Chawla, S.; Naraghi, M. Microstructural evolution and mechanics of hot-drawn CNT-reinforced polymeric nanofibers. Carbon 2016, 109, 813–822.
Li, Y.; Góra, A.; Anariba, F.; Baji, A. Enhanced tensile strength and electrical conductivity of electrospun polyacrylonitrile yarns via post-treatment. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 1702–1707.
Bazbouz, M. B.; Stylios, G. K. The tensile properties of electrospun nylon 6 single nanofibers. J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 1719–1731.
Zussman, E.; Burman, M.; Yarin, A. L.; Khalfin, R.; Cohen, Y. Tensile deformation of electrospun nylon-6,6 nanofibers. J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 1482–1489.
Tan, E. P. S.; Ng, S. Y.; Lim, C. T. Tensile testing of a single ultrafine polymeric fiber. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1453–1456.
Jiang, S.; Duan, G.; Zussman, E.; Greiner, A.; Agarwal, S. Highly flexible and tough concentric triaxial polystyrene fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5918–5923.
Chen, L.; Jiang, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, F.; He, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, H. Single electrospun nanofiber and aligned nanofiber belts from copolyimide containing pyrimidine units. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 8956–8963.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21774053, 21975111, and 51903123), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20190760), Major Special Projects of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology (No. 20114ABF05100), and Technology Plan Landing Project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education (No. GCJ2011-24).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, TC., Han, DH., Zhu, YM. et al. High Strength Electrospun Single Copolyacrylonitrile (coPAN) Nanofibers with Improved Molecular Orientation by Drawing. Chin J Polym Sci 39, 174–180 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-021-2516-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-021-2516-0