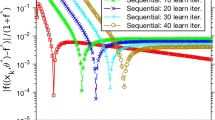
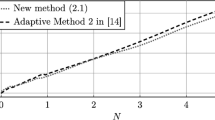
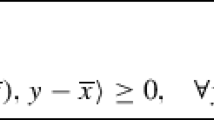Abstract
This paper settles an open and challenging question pertaining to the design of simple and optimal high-order methods for solving smooth and monotone variational inequalities (VIs). A VI involves finding \(x^\star \in {\mathcal {X}}\) such that \(\langle F(x), x - x^\star \rangle \ge 0\) for all \(x \in {\mathcal {X}}\). We consider the setting in which \(F: {\mathbb {R}}^d \rightarrow {\mathbb {R}}^d\) is smooth with up to \((p-1)^{\text {th}}\)-order derivatives. For \(p = 2\), the cubic regularization of Newton’s method has been extended to VIs with a global rate of \(O(\epsilon ^{-1})\) (Nesterov in Cubic regularization of Newton’s method for convex problems with constraints, Tech. rep., Université catholique de Louvain, Center for Operations Research and Econometrics (CORE), 2006). An improved rate of \(O(\epsilon ^{-2/3}\log \log (1/\epsilon ))\) can be obtained via an alternative second-order method, but this method requires a nontrivial line-search procedure as an inner loop. Similarly, the existing high-order methods based on line-search procedures have been shown to achieve a rate of \(O(\epsilon ^{-2/(p+1)}\log \log (1/\epsilon ))\) (Bullins and Lai in SIAM J Optim 32(3):2208–2229, 2022; Jiang and Mokhtari in Generalized optimistic methods for convex–concave saddle point problems, 2022; Lin and Jordan in Math Oper Res 48(4):2353–2382, 2023). As emphasized by Nesterov (Lectures on convex optimization, vol 137, Springer, Berlin, 2018), however, such procedures do not necessarily imply the practical applicability in large-scale applications, and it is desirable to complement these results with a simple high-order VI method that retains the optimality of the more complex methods. We propose a \(p^{\text {th}}\)-order method that does not require any line search procedure and provably converges to a weak solution at a rate of \(O(\epsilon ^{-2/(p+1)})\). We prove that our \(p^{\text {th}}\)-order method is optimal in the monotone setting by establishing a lower bound of \(\Omega (\epsilon ^{-2/(p+1)})\) under a generalized linear span assumption. A restarted version of our \(p^{\text {th}}\)-order method attains a linear rate for smooth and \(p^{\text {th}}\)-order uniformly monotone VIs and another restarted version of our \(p^{\text {th}}\)-order method attains a local superlinear rate for smooth and strongly monotone VIs. Further, the similar \(p^{\text {th}}\)-order method achieves a global rate of \(O(\epsilon ^{-2/p})\) for solving smooth and nonmonotone VIs satisfying the Minty condition. Two restarted versions attain a global linear rate under additional \(p^{\text {th}}\)-order uniform Minty condition and a local superlinear rate under additional strong Minty condition.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
For ease of presentation, we choose the factor of 5 here. It is worth noting that other large coefficients also suffice to achieve the same global convergence rate guarantee.
References
Adil, D., Bullins, B., Jambulapati, A., Sachdeva, S.: Optimal methods for higher-order smooth monotone variational inequalities. ArXiv Preprint: arXiv:2205.06167 (2022)
Antipin, A.S.: Method of convex programming using a symmetric modification of Lagrange function. Matekon 14(2), 23–38 (1978)
Arjevani, Y., Shamir, O., Shiff, R.: Oracle complexity of second-order methods for smooth convex optimization. Math. Program. 178(1), 327–360 (2019)
Baes, M.: Estimate Sequence Methods: Extensions and Approximations. Institute for Operations Research, ETH, Zürich (2009)
Bauschke, H.H., Combettes, P.L.: Convex Analysis and Monotone Operator Theory in Hilbert Spaces. Springer, Berlin (2017)
Birgin, E.G., Gardenghi, J.L., Martinez, J.M., Santos, S.A., Toint, P.L.: Evaluation complexity for nonlinear constrained optimization using unscaled KKT conditions and high-order models. SIAM J. Optim. 26(2), 951–967 (2016)
Birgin, E.G., Gardenghi, J.L., Martínez, J.M., Santos, S.A., Toint, P.L.: Worst-case evaluation complexity for unconstrained nonlinear optimization using high-order regularized models. Math. Program. 163(1–2), 359–368 (2017)
Brighi, L., John, R.: Characterizations of pseudomonotone maps and economic equilibrium. J. Stat. Manag. Syst. 5(1–3), 253–273 (2002)
Bullins, B.: Highly smooth minimization of nonsmooth problems. In: COLT, pp. 988–1030. PMLR (2020)
Bullins, B., Lai, K.A.: Higher-order methods for convex-concave min-max optimization and monotone variational inequalities. SIAM J. Optim. 32(3), 2208–2229 (2022)
Carmon, Y., Duchi, J.: Gradient descent finds the cubic-regularized nonconvex Newton step. SIAM J. Optim. 29(3), 2146–2178 (2019)
Carmon, Y., Duchi, J.C., Hinder, O., Sidford, A.: Lower bounds for finding stationary points I. Math. Program. 184(1–2), 71–120 (2020)
Carmon, Y., Hausler, D., Jambulapati, A., Jin, Y., Sidford, A.: Optimal and adaptive Monteiro-Svaiter acceleration. In: NeurIPS, pp. 20338–20350 (2022)
Cartis, C., Gould, N.I., Toint, P.L.: Universal regularization methods: varying the power, the smoothness and the accuracy. SIAM J. Optim. 29(1), 595–615 (2019)
Cartis, C., Gould, N.I.M., Toint, P.L.: On the complexity of steepest descent, Newton’s and regularized Newton’s methods for nonconvex unconstrained optimization problems. SIAM J. Optim. 20(6), 2833–2852 (2010)
Cartis, C., Gould, N.I.M., Toint, P.L.: Adaptive cubic regularisation methods for unconstrained optimization. Part I: motivation, convergence and numerical results. Math. Program. 127(2), 245–295 (2011)
Cartis, C., Gould, N.I.M., Toint, P.L.: Adaptive cubic regularisation methods for unconstrained optimization. Part II: worst-case function-and derivative-evaluation complexity. Math. Program. 130(2), 295–319 (2011)
Cartis, C., Gould, N.I.M., Toint, P.L.: Evaluation Complexity of Algorithms for Nonconvex Optimization: Theory, Computation and Perspectives. SIAM, Philadelphia (2022)
Cesa-Bianchi, N., Lugosi, G.: Prediction, Learning, and Games. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2006)
Chen, Y., Lan, G., Ouyang, Y.: Accelerated schemes for a class of variational inequalities. Math. Program. 165(1), 113–149 (2017)
Choi, S.C., DeSarbo, W.S., Harker, P.T.: Product positioning under price competition. Manag. Sci. 36(2), 175–199 (1990)
Cottle, R., Giannessi, F., Lions, J.L.: Variational Inequalities and Complementarity Problems: Theory and Applications. Wiley, New York (1980)
Dang, C.D., Lan, G.: On the convergence properties of non-Euclidean extragradient methods for variational inequalities with generalized monotone operators. Comput. Optim. Appl. 60(2), 277–310 (2015)
Daskalakis, C., Skoulakis, S., Zampetakis, M.: The complexity of constrained min-max optimization. In: STOC, pp. 1466–1478 (2021)
Diakonikolas, J.: Halpern iteration for near-optimal and parameter-free monotone inclusion and strong solutions to variational inequalities. In: COLT, pp. 1428–1451. PMLR (2020)
Diakonikolas, J., Daskalakis, C., Jordan, M.I.: Efficient methods for structured nonconvex-nonconcave min-max optimization. In: AISTATS, pp. 2746–2754. PMLR (2021)
Doikov, N., Nesterov, Y.: Local convergence of tensor methods. Math. Program. 193(1), 315–336 (2022)
Ewerhart, C.: Cournot games with biconcave demand. Games Econ. Behav. 85, 37–47 (2014)
Facchinei, F., Pang, J.S.: Finite-Dimensional Variational Inequalities and Complementarity Problems. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Fercoq, O., Qu, Z.: Adaptive restart of accelerated gradient methods under local quadratic growth condition. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 39(4), 2069–2095 (2019)
Freund, R.M., Lu, H.: New computational guarantees for solving convex optimization problems with first order methods, via a function growth condition measure. Math. Program. 170(2), 445–477 (2018)
Fukushima, M.: Equivalent differentiable optimization problems and descent methods for asymmetric variational inequality problems. Math. Program. 53, 99–110 (1992)
Gallego, G., Hu, M.: Dynamic pricing of perishable assets under competition. Manag. Sci. 60(5), 1241–1259 (2014)
Gasnikov, A., Dvurechensky, P., Gorbunov, E., Vorontsova, E., Selikhanovych, D., Uribe, C.A., Jiang, B., Wang, H., Zhang, S., Bubeck, S., Jiang, Q., Lee, Y.T., Li, Y., Sidford, A.: Near optimal methods for minimizing convex functions with Lipschitz \(p\)-th derivatives. In: COLT, pp. 1392–1393. PMLR (2019)
Ghadimi, S., Lan, G.: Optimal stochastic approximation algorithms for strongly convex stochastic composite optimization, II: shrinking procedures and optimal algorithms. SIAM J. Optim. 23(4), 2061–2089 (2013)
Giselsson, P., Boyd, S.: Monotonicity and restart in fast gradient methods. In: CDC, pp. 5058–5063. IEEE (2014)
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., Bengio, Y.: Generative adversarial nets. In: NIPS, pp. 2672–2680 (2014)
Gould, N.I.M., Lucidi, S., Roma, M., Toint, P.L.: Solving the trust-region subproblem using the Lanczos method. SIAM J. Optim. 9(2), 504–525 (1999)
Gould, N.I.M., Robinson, D.P., Thorne, H.S.: On solving trust-region and other regularised subproblems in optimization. Math. Program. Comput. 2(1), 21–57 (2010)
Grapiglia, G.N., Nesterov, Y.: Regularized Newton methods for minimizing functions with Hölder continuous Hessians. SIAM J. Optim. 27(1), 478–506 (2017)
Grapiglia, G.N., Nesterov, Y.: Accelerated regularized Newton methods for minimizing composite convex functions. SIAM J. Optim. 29(1), 77–99 (2019)
Grapiglia, G.N., Nesterov, Y.: Tensor methods for minimizing convex functions with Hölder continuous higher-order derivatives. SIAM J. Optim. 30(4), 2750–2779 (2020)
Grapiglia, G.N., Nesterov, Y.: On inexact solution of auxiliary problems in tensor methods for convex optimization. Optim. Methods Softw. 36(1), 145–170 (2021)
Grapiglia, G.N., Nesterov, Y.: Adaptive third-order methods for composite convex optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 33(3), 1855–1883 (2023)
Hammond, J.H., Magnanti, T.L.: Generalized descent methods for asymmetric systems of equations. Math. Oper. Res. 12(4), 678–699 (1987)
Harker, P.T., Pang, J.S.: Finite-dimensional variational inequality and nonlinear complementarity problems: a survey of theory, algorithms and applications. Math. Program. 48(1), 161–220 (1990)
Hartman, P., Stampacchia, G.: On some non-linear elliptic differential-functional equations. Acta Math. 115, 271–310 (1966)
Huang, K., Zhang, J., Zhang, S.: Cubic regularized Newton method for the saddle point models: a global and local convergence analysis. J. Sci. Comput. 91(2), 1–31 (2022)
Huang, K., Zhang, S.: An approximation-based regularized extra-gradient method for monotone variational inequalities. ArXiv Preprint: arXiv:2210.04440 (2022)
Huang, K., Zhang, S.: Beyond monotone variational inequalities: solution methods and iteration complexities. ArXiv Preprint: arXiv:2304.04153 (2023)
Iusem, A.N., Jofré, A., Oliveira, R.I., Thompson, P.: Extragradient method with variance reduction for stochastic variational inequalities. SIAM J. Optim. 27(2), 686–724 (2017)
Jiang, B., Lin, T., Zhang, S.: A unified adaptive tensor approximation scheme to accelerate composite convex optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 30(4), 2897–2926 (2020)
Jiang, R., Mokhtari, A.: Generalized optimistic methods for convex–concave saddle point problems. ArXiv Preprint: arXiv:2202.09674 (2022)
Kannan, A., Shanbhag, U.V.: Optimal stochastic extragradient schemes for pseudomonotone stochastic variational inequality problems and their variants. Comput. Optim. Appl. 74(3), 779–820 (2019)
Kinderlehrer, D., Stampacchia, G.: An Introduction to Variational Inequalities and Their Applications. SIAM, Philadelphia (2000)
Kleinberg, B., Li, Y., Yuan, Y.: An alternative view: when does SGD escape local minima? In: ICML, pp. 2698–2707. PMLR (2018)
Kornowski, G., Shamir, O.: High-order oracle complexity of smooth and strongly convex optimization. ArXiv Preprint: arXiv:2010.06642 (2020)
Korpelevich, G.M.: The extragradient method for finding saddle points and other problems. Matecon 12, 747–756 (1976)
Kotsalis, G., Lan, G., Li, T.: Simple and optimal methods for stochastic variational inequalities, I: operator extrapolation. SIAM J. Optim. 32(3), 2041–2073 (2022)
Kovalev, D., Gasnikov, A.: The first optimal acceleration of high-order methods in smooth convex optimization. In: NeurIPS, pp. 35339–35351 (2022)
Lan, G., Zhou, Y.: An optimal randomized incremental gradient method. Math. Program. 171(1), 167–215 (2018)
Lan, G., Zhou, Y.: Random gradient extrapolation for distributed and stochastic optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 28(4), 2753–2782 (2018)
Lemke, C.E., Howson, J.T.: Equilibrium points of bimatrix games. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 12(2), 413–423 (1964)
Li, Y., Yuan, Y.: Convergence analysis of two-layer neural networks with ReLU activation. In: NIPS, pp. 597–607 (2017)
Lin, T., Jordan, M.I.: A control-theoretic perspective on optimal high-order optimization. Math. Program. 195(1), 929–975 (2022)
Lin, T., Jordan, M.I.: Monotone inclusions, acceleration, and closed-loop control. Math. Oper. Res. 48(4), 2353–2382 (2023)
Lin, T., Mertikopoulos, P., Jordan, M.I.: Explicit second-order min-max optimization methods with optimal convergence guarantee. ArXiv Preprint: arXiv:2210.12860 (2022)
Liu, M., Rafique, H., Lin, Q., Yang, T.: First-order convergence theory for weakly-convex–weakly-concave min–max problems. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 22(169), 1–34 (2021)
Madry, A., Makelov, A., Schmidt, L., Tsipras, D., Vladu, A.: Towards deep learning models resistant to adversarial attacks. In: ICLR (2018). https://openreview.net/forum?id=rJzIBfZAb
Magnanti, T.L., Perakis, G.: A unifying geometric solution framework and complexity analysis for variational inequalities. Math. Program. 71(3), 327–351 (1995)
Magnanti, T.L., Perakis, G.: Averaging schemes for variational inequalities and systems of equations. Math. Oper. Res. 22(3), 568–587 (1997)
Magnanti, T.L., Perakis, G.: The orthogonality theorem and the strong-f-monotonicity condition for variational inequality algorithms. SIAM J. Optim. 7(1), 248–273 (1997)
Magnanti, T.L., Perakis, G.: Solving variational inequality and fixed point problems by line searches and potential optimization. Math. Program. 101(3), 435–461 (2004)
Marques Alves, M.: Variants of the A-HPE and large-step A-HPE algorithms for strongly convex problems with applications to accelerated high-order tensor methods. Optim. Methods Softw. 37(6), 2021–2051 (2022)
Martínez, J.: On high-order model regularization for constrained optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 27(4), 2447–2458 (2017)
Mertikopoulos, P., Zhou, Z.: Learning in games with continuous action sets and unknown payoff functions. Math. Program. 173(1), 465–507 (2019)
Minty, G.J.: Monotone (nonlinear) operators in Hilbert space. Duke Math. J. 29(3), 341–346 (1962)
Mokhtari, A., Ozdaglar, A.E., Pattathil, S.: Convergence rate of o(1/k) for optimistic gradient and extragradient methods in smooth convex-concave saddle point problems. SIAM J. Optim. 30(4), 3230–3251 (2020)
Monteiro, R.D.C., Svaiter, B.F.: On the complexity of the hybrid proximal extragradient method for the iterates and the ergodic mean. SIAM J. Optim. 20(6), 2755–2787 (2010)
Monteiro, R.D.C., Svaiter, B.F.: Complexity of variants of Tseng’s modified FB splitting and Korpelevich’s methods for hemivariational inequalities with applications to saddle-point and convex optimization problems. SIAM J. Optim. 21(4), 1688–1720 (2011)
Monteiro, R.D.C., Svaiter, B.F.: Iteration-complexity of a Newton proximal extragradient method for monotone variational inequalities and inclusion problems. SIAM J. Optim. 22(3), 914–935 (2012)
Monteiro, R.D.C., Svaiter, B.F.: An accelerated hybrid proximal extragradient method for convex optimization and its implications to second-order methods. SIAM J. Optim. 23(2), 1092–1125 (2013)
Necoara, I., Nesterov, Y., Glineur, F.: Linear convergence of first order methods for non-strongly convex optimization. Math. Program. 175(1), 69–107 (2019)
Nemirovski, A.: Prox-method with rate of convergence o(1/t) for variational inequalities with Lipschitz continuous monotone operators and smooth convex-concave saddle point problems. SIAM J. Optim. 15(1), 229–251 (2004)
Nemirovski, A.S., Nesterov, Y.E.: Optimal methods of smooth convex minimization. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 25(2), 21–30 (1985)
Nesterov, Y.: Cubic regularization of Newton’s method for convex problems with constraints. Tech. rep., Université catholique de Louvain, Center for Operations Research and Econometrics (CORE) (2006)
Nesterov, Y.: Dual extrapolation and its applications to solving variational inequalities and related problems. Math. Program. 109(2), 319–344 (2007)
Nesterov, Y.: Accelerating the cubic regularization of Newton’s method on convex problems. Math. Program. 112(1), 159–181 (2008)
Nesterov, Y.: Gradient methods for minimizing composite functions. Math. Program. 140(1), 125–161 (2013)
Nesterov, Y.: Lectures on Convex Optimization, vol. 137. Springer, Berlin (2018)
Nesterov, Y.: Implementable tensor methods in unconstrained convex optimization. Math. Program. 186(1), 157–183 (2021)
Nesterov, Y.: Inexact accelerated high-order proximal-point methods. Mathematical Programming, pp. 1–26 (2021)
Nesterov, Y.: Inexact high-order proximal-point methods with auxiliary search procedure. SIAM J. Optim. 31(4), 2807–2828 (2021)
Nesterov, Y.: Superfast second-order methods for unconstrained convex optimization. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 191(1), 1–30 (2021)
Nesterov, Y., Polyak, B.T.: Cubic regularization of Newton method and its global performance. Math. Program. 108(1), 177–205 (2006)
Nesterov, Y.E.: A method of solving a convex programming problem with convergence rate o(k\(^{2}\)). In: Doklady Akademii Nauk, vol. 269, pp. 543–547. Russian Academy of Sciences (1983)
Ostroukhov, P., Kamalov, R., Dvurechensky, P., Gasnikov, A.: Tensor methods for strongly convex strongly concave saddle point problems and strongly monotone variational inequalities. ArXiv Preprint: arXiv:2012.15595 (2020)
Ouyang, Y., Xu, Y.: Lower complexity bounds of first-order methods for convex–concave bilinear saddle-point problems. Math. Program. 185(1), 1–35 (2021)
O’donoghue, B., Candes, E.: Adaptive restart for accelerated gradient schemes. Found. Comput. Math. 15(3), 715–732 (2015)
Popov, L.D.: A modification of the Arrow–Hurwicz method for search of saddle points. Math. Notes Acad. Sci. USSR 28(5), 845–848 (1980)
Ralph, D., Wright, S.J.: Superlinear convergence of an interior-point method for monotone variational inequalities. Complementarity and Variational Problems: State of the Art pp. 345–385 (1997)
Renegar, J., Grimmer, B.: A simple nearly optimal restart scheme for speeding up first-order methods. Found. Comput. Math. 22(1), 211–256 (2022)
Rockafellar, R.T., Wets, R.J.B.: Variational Analysis, vol. 317. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Roulet, V., d’Aspremont, A.: Sharpness, restart and acceleration. In: NIPS, pp. 1119–1129 (2017)
Scarf, H.: The approximation of fixed points of a continuous mapping. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 15(5), 1328–1343 (1967)
Sinha, A., Namkoong, H., Duchi, J.: Certifiable distributional robustness with principled adversarial training. In: ICLR (2018). https://openreview.net/forum?id=Hk6kPgZA-
Solodov, M.V., Svaiter, B.F.: A new projection method for variational inequality problems. SIAM J. Control. Optim. 37(3), 765–776 (1999)
Song, C., Jiang, Y., Ma, Y.: Unified acceleration of high-order algorithms under general Hölder continuity. SIAM J. Optim. 31(3), 1797–1826 (2021)
Song, C., Zhou, Z., Zhou, Y., Jiang, Y., Ma, Y.: Optimistic dual extrapolation for coherent non-monotone variational inequalities. In: NeurIPS, pp. 14303–14314 (2020)
Titov, A.A., Ablaev, S.S., Alkousa, M.S., Stonyakin, F.S., Gasnikov, A.V.: Some adaptive first-order methods for variational inequalities with relatively strongly monotone operators and generalized smoothness. In: ICOPTA, pp. 135–150. Springer (2022)
Todd, M.J.: The Computation of Fixed Points and Applications. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Trémolières, R., Lions, J.L., Glowinski, R.: Numerical Analysis of Variational Inequalities. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2011)
Tseng, P.: A modified forward-backward splitting method for maximal monotone mappings. SIAM J. Control. Optim. 38(2), 431–446 (2000)
Wibisono, A., Wilson, A.C., Jordan, M.I.: A variational perspective on accelerated methods in optimization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 113(47), E7351–E7358 (2016)
Zhang, J., Hong, M., Zhang, S.: On lower iteration complexity bounds for the convex–concave saddle point problems. Math. Program. 194(1), 901–935 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Mathematical Data Science program of the Office of Naval Research under Grant Number N00014-18-1-2764 and by the Vannevar Bush Faculty Fellowship program under Grant Number N00014-21-1-2941.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, T., Jordan, M.I. Perseus: a simple and optimal high-order method for variational inequalities. Math. Program. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-024-02075-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-024-02075-2
Keywords
- Variational inequality
- Simple and optimal high-order method
- Acceleration
- Iteration complexity
- Local superlinear convergence