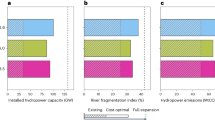
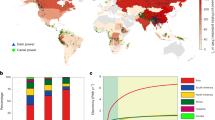
Abstract
Hydropower is the most economically developed renewable energy source in China. In the twenty-first century, the era of clean and low-carbon development, hydropower can meet the continuous growth of energy consumption and help China achieve its goal of carbon neutrality by 2060. In 2019, China’s installed hydropower capacity was 358.04 GW, and hydropower consumption was 1.132 × 1016 kJ, with a growth rate of 5.5%, well above the global average of 0.8%. Although China's hydropower achievements are renowned worldwide, hydropower development in China still faces challenges in relation to environmental, technological, economic and social issues. In this paper, we first review the history, achievements and current situation of China’s hydropower development and summarize the specific challenges mentioned above. Then, we take the Dadu River Hydropower Base as a case study. This project ranks fifth among China’s 13 largest hydropower bases, and the construction of 14 cascade hydropower stations was completed in December 2020, accounting for 61.3% of the total planned installed capacity of 28 cascades, with 3 more still under construction (accounting for another 16.3%). We comprehensively describe the background, tasks and exploitation of hydropower development in the Dadu River basin and highlight current practices, including exploration of environmental protection and ecological restoration, technical innovation, supporting facility construction, economic promotion and resettlement. Finally, based on the identified practices and lessons, we propose feasible suggestions for China's future hydropower development.
Graphic abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abas N, Kalair A, Khan N (2015) Review of fossil fuels and future energy technologies. Futures 69:31–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.futures.2015.03.003
Baleta J, Mikulcic H, Klemes JJ, Urbaniec K, Duic N (2019) Integration of energy, water and environmental systems for a sustainable development. J Clean Prod 215:1424–1436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.035
Cao N, Mao Z (2017) Countermeasures and suggestions on fish protection during hydropower development mainstream of Daduhe River. Water Res Hydropower Eng 48:116–121 (in Chinese)
Chen W, Li H, Wu Z (2011) Western China energy development and west to east energy transfer: application of the western China sustainable energy development model. Energy Policy 38:7106–7120
Chen G, Cao X, Wang Y (2018) Practice and exploration of multi- energy complementary in Dadu river basin. Water Power 044:83–86 (in Chinese)
Chen J, Wu Y, Xu C, Song M, Liu X (2019) Global non-fossil fuel consumption: driving factors, disparities, and trends. Manag Decis 57:791–810. https://doi.org/10.1108/md-04-2018-0409
Cheng C, Chen F, Li G, Ristic B, Mirchi A, Tu Q, Madani K (2018) Reform and renewables in China: The architecture of Yunnan’s hydropower dominated electricity market. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 94:682–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.06.033
Chu S, Majumdar A (2012) Opportunities and challenges for a sustainable energy future. Nature 488:294–303. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11475
Cui Q, He L, Han G, Chen H, Cao J (2020) Review on climate and water resource implications of reducing renewable power curtailment in China: A nexus perspective. Appl Energy 267:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115114
Dhar A, Naeth MA, Jennings PD, El-Din MG (2020) Perspectives on environmental impacts and a land reclamation strategy for solar and wind energy systems. Sci Total Environ 718:17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134602
Diduck AP, Pratap D, Sinclair AJ, Deane S (2013) Perceptions of impacts, public participation, and learning in the planning, assessment and mitigation of two hydroelectric projects in Uttarakhand, India. Land Use Policy 33:170–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2013.01.001
Duan B, Chen G, Zou Z, Deng L, Ma F, Guo J, Peng X (2020) Research and practice of key technology for efficient development and utilization of water power in large basins. Water Resour Power (china) 38:58–61 (in Chinese)
Dudgeon D et al (2006) Freshwater biodiversity: importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol Rev 81:163–182. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1464793105006950
Fang W, Huang Q, Huang S, Yang J, Meng E, Li Y (2017) Optimal sizing of utility-scale photovoltaic power generation complementarily operating with hydropower: A case study of the world’s largest hydro-photovoltaic plant. Energy Convers Manage 136:161–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.01.012
Feng K (2019) Analysis on the environmental problems of soil erosion in the development of Dadu River Hydropower Station. Water Res Hydropower Eng 50:232–234
Fu X (2007) Practice and thinking of developing Dadu River scientifically to build harmonic hydropower. Electric Power 40:11–14 (in Chinese)
Fu B, Wang YK, Xu P, Yan K, Li M (2014) Value of ecosystem hydropower service and its impact on the payment for ecosystem services. Sci Total Environ 472:338–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.015
Gao J, Zhao P, Zhang H, Mao G, Wang Y (2018) Operational water withdrawal and consumption factors for electricity generation technology in China-a literature review. Sustainability 10:15. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10041181
Hauer C et al (2018) State of the art, shortcomings and future challenges for a sustainable sediment management in hydropower: A review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 98:40–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.08.031
He Y, Xu Y, Zhang J (2020) Analysis of flood control effect of Pubugou Reservoir during “20·8” flood of Minjiang River. Yangtze River 51:149–154 (in Chinese)
Hennig T, Wang W, Feng Y, Ou X, He D (2013) Review of Yunnan’s hydropower development. Comparing small and large hydropower projects regarding their environmental implications and socio-economic consequences. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 27:585–595
Huang Y, Zhang R, Wan D, Cai H, Hu D (2020) Coupling analysis of river-system connectivity and cascade-hydropower development in the Dadu river basin. South Architecture 02:19–27 (in Chinese)
Humborg C, Ittekkot V, Cociasu A, VonBodungen B (1997) Effect of Danube River dam on Black Sea biogeochemistry and ecosystem structure. Nature 386:385–388. https://doi.org/10.1038/386385a0
Jenkins K, McCauley D, Heffron R, Stephan H, Rehner R (2016) Energy justice: A conceptual review. Energy Res Soc Sci 11:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2015.10.004
Jiang X, Chen J, Sun S (2009) Research on physical model test for high arch dam of Jinping I Hydropower Station. Yangtze River 40:76–78 (in Chinese)
Lee R (2011) The Outlook for population growth. Science 333:569–573. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1208859
Li S, Duan B (2016) The highest dam in the world under construction: the Shuangjiangkou core-wall Rockfill dam. Engineering 2:262–386
Li X-z, Chen Z-j, Fan X-c, Cheng Z-j (2018) Hydropower development situation and prospects in China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 82:232–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.08.090
Li Z et al (2019) The carbon footprint of large- and mid-scale hydropower in China: Synthesis from five China’s largest hydro-project. J Environ Manage 250:109363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109363
Liu XC, Tang QH, Voisin N, Cui HJ (2016) Projected impacts of climate change on hydropower potential in China. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 20:3343–3359. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-20-3343-2016
Liu S, Yang Q, Cai H, Yan M, Zhang M, Wu D, Xie M (2019) Market reform of Yunnan electricity in southwestern China: Practice, challenges and implications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 113:109265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109265
Liu L (2015) Study on the right transfer and willingness of residents and immigrants to share land in the resettlement area of hydropower projects: Taking the immigrant resettlement area of Pubugou Hydropower Station in Huangtu Town as an example. China Rural Studies:189–211(in Chinese)
Lu X, Wang S (2017) A GIS-based assessment of Tibet’s potential for pumped hydropower energy storage. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 69:1045–1054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.09.089
Luo L (2019) Impact of Dadu River hydropower development on regional economy. Yangtze River 50:9–15 (in Chinese)
Musa SD, Tang Z, Ibrahim AO, Habib M (2018) China’s energy status: A critical look at fossils and renewable options. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81:2281–2290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.06.036
Pascual U et al (2017) Valuing nature’s contributions to people: the IPBES approach. Curr Op Environ Sustain 26–27:7–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2016.12.006
Poff NL et al (1997) The natural flow regime. Bioscience 47:769–784. https://doi.org/10.2307/1313099
Sayan RC (2019) Exploring place-based approaches and energy justice: Ecology, social movements, and hydropower in Turkey. Energy Res Soc Sci 57:101234–101234
Sayan RC, Kibaroglu A (2016) Understanding water-society nexus: insights from Turkey’s small-scale hydropower policy. Water Policy 18:1286–1301. https://doi.org/10.2166/wp.2016.235
Sovacool BK, Dworkin MH (2015) Energy justice: Conceptual insights and practical applications. Appl Energy 142:435–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.01.002
Sun Y (2020) The achievement, significance and future prospect of China’s renewable energy initiative. Int J Energy Res 44:12209–12244. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.5243
Sun L, Niu D, Wang K, Xu X (2021) Sustainable development pathways of hydropower in China: Interdisciplinary qualitative analysis and scenario-based system dynamics quantitative modeling. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125528
Tahseen S, Karney BW (2017) Reviewing and critiquing published approaches to the sustainability assessment of hydropower. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 67:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.09.031
Wang C, Yan J, Cheng L (2010) Immigrant resettlement and management of pubugou hydropower station project. Water Power 36:20–22 (in Chinese)
Wang P, Lassoie JP, Dong S, Morreale SJ (2013) A framework for social impact analysis of large dams: A case study of cascading dams on the Upper-Mekong River, China. J Environ Manage 117C:131–140
Wang F, Lang Y, Liu C-Q, Qin Y, Yu N, Wang B (2019) Flux of organic carbon burial and carbon emission from a large reservoir: implications for the cleanliness assessment of hydropower. Science Bulletin 64:603–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2019.03.034
Wang P, Dong S, Lassoie JP (2014) The large dam dilemma: An exploration of the impacts of hydro projects on people and the environment in China.
Xiong C, Qu T (2019) Analysis of runoff variation in Dadu River Basin. Gansu Water Res Hydropower Technol 55:12–15 (in Chinese)
Yan J (2020) Study on flood control and water storage of main stream reservoirs on Dadu River. Sichuan Water Power 39:147–150 (in Chinese)
Yan Z, Qian G (2011) Sketch of mid-long term (2030,2050) development strategy study of hydropower in China. Eng Sci 13:108–112 (in Chinese)
Yaseen ZM, Sulaiman SO, Deo RC, Chau KW (2019) An enhanced extreme learning machine model for river flow forecasting: State-of-the-art, practical applications in water resource engineering area and future research direction. J Hydrol 569:387–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.11.069
Zhang G (2018) Blaze a trail: A description of the decision-making and construction of the Century Project. People’s Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Zhang J, Luo C-Y, Curtis Z, Deng S-h, Wu Y, Li Y-w (2015) Carbon dioxide emission accounting for small hydropower plants—A case study in southwest China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 47:755–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.03.027
Zhang J, Daniel A, Fang Y, Desmond A, Antwi EO (2018) Review on China’s renewable energy and future projections. Int J Smart Grid Clean Energy 7:218–224. https://doi.org/10.12720/sgce.7.3.218-224
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 41271094).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Fan, S., Sun, H. et al. Practices of environmental protection, technological innovation, economic promotion and social equity in hydropower development: a case study of cascade hydropower exploitation in China’s Dadu River basin. Clean Techn Environ Policy 23, 2827–2841 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-021-02212-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-021-02212-x